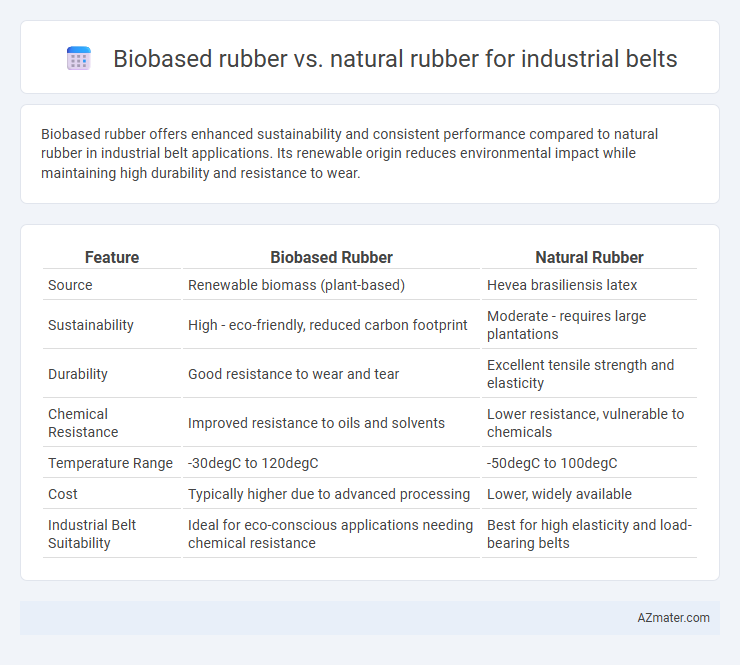
Biobased rubber offers enhanced sustainability and consistent performance compared to natural rubber in industrial belt applications. Its renewable origin reduces environmental impact while maintaining high durability and resistance to wear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biobased Rubber | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable biomass (plant-based) | Hevea brasiliensis latex |
| Sustainability | High - eco-friendly, reduced carbon footprint | Moderate - requires large plantations |
| Durability | Good resistance to wear and tear | Excellent tensile strength and elasticity |
| Chemical Resistance | Improved resistance to oils and solvents | Lower resistance, vulnerable to chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 120degC | -50degC to 100degC |
| Cost | Typically higher due to advanced processing | Lower, widely available |
| Industrial Belt Suitability | Ideal for eco-conscious applications needing chemical resistance | Best for high elasticity and load-bearing belts |
Introduction to Industrial Belt Materials
Industrial belts require materials with high durability, flexibility, and resistance to wear, making rubber a crucial component. Biobased rubber offers an eco-friendly alternative derived from renewable resources, while natural rubber, sourced from Hevea brasiliensis, provides excellent tensile strength and elasticity. Selection between biobased and natural rubber depends on factors like sustainability goals, mechanical performance, and cost-effectiveness in industrial belt manufacturing.
Defining Biobased Rubber and Natural Rubber
Biobased rubber is derived from renewable biological sources such as plant-based materials, offering sustainability advantages over traditional rubber. Natural rubber is harvested from the latex of rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis) and has long been the standard in industrial belt manufacturing due to its excellent elasticity and durability. Both materials provide essential properties for industrial belts, but biobased rubber emphasizes eco-friendly production with reduced environmental impact.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Biobased rubber offers a sustainable alternative to natural rubber for industrial belts by utilizing renewable plant-based materials, reducing dependence on rubber tree plantations that contribute to deforestation. Its production generates lower greenhouse gas emissions and decreases environmental degradation compared to traditional natural rubber harvesting. Enhanced biodegradability and reduced chemical use make biobased rubber an eco-friendly choice, promoting circular economy principles in industrial applications.
Raw Material Sourcing and Availability
Biobased rubber for industrial belts is derived from renewable plant-based sources such as guayule, dandelion, and synthetic bio-polymers, offering sustainable alternatives to traditional rubber. Natural rubber, primarily sourced from Hevea brasiliensis latex plantations, faces supply fluctuations due to climate sensitivity and geopolitical factors impacting key producing regions like Southeast Asia. Biobased rubber raw material availability is increasing with advancements in agricultural biotechnology and bio-refining processes, aiming to provide a consistent and eco-friendly supply chain for industrial belt manufacturing.
Mechanical Properties and Performance
Biobased rubber offers comparable tensile strength and abrasion resistance to natural rubber in industrial belt applications, enhancing durability and load capacity. The elasticity of biobased rubber ensures consistent performance under dynamic stress, while improved chemical resistance extends belt lifespan in harsh environments. Mechanical properties such as resilience and tear resistance make biobased rubber a sustainable alternative without compromising industrial belt efficiency.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Biobased rubber in industrial belts offers enhanced durability due to its improved resistance to abrasion, heat, and chemical exposure, often outperforming traditional natural rubber in harsh environments. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and resilience but tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to oils, ozone, and UV radiation, which can shorten its lifespan. Selecting biobased rubber for industrial belts results in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs, making it a superior choice for demanding industrial applications.
Cost Analysis: Biobased vs Natural Rubber
Biobased rubber for industrial belts often presents higher initial costs compared to natural rubber due to advanced processing technologies and raw material sourcing. Despite these upfront expenses, biobased rubber can offer long-term cost benefits through improved durability and environmental compliance, potentially reducing maintenance and replacement frequencies. Natural rubber remains cost-effective for traditional applications, but fluctuating commodity prices and sustainability concerns increasingly influence cost competitiveness in industrial belt manufacturing.
Chemical Resistance and Thermal Stability
Biobased rubber exhibits enhanced chemical resistance compared to natural rubber, making it more suitable for industrial belts exposed to harsh chemicals and oils. Its improved thermal stability allows it to withstand higher operating temperatures without significant degradation, extending the service life of industrial belts. Natural rubber, while flexible and elastic, tends to degrade faster under chemical exposure and elevated temperatures, limiting its application in demanding industrial environments.
Industry Adoption and Case Studies
Biobased rubber is gaining traction in industrial belt manufacturing due to its sustainability and comparable performance metrics to natural rubber, driving industry adoption in sectors aiming to reduce carbon footprint. Major companies in automotive and conveyor belt industries have reported successful integration of biobased rubber, highlighting improved environmental compliance without sacrificing durability or elasticity. Case studies from leading manufacturers demonstrate a 20-30% reduction in lifecycle emissions when switching from natural rubber to biobased alternatives, reinforcing its viability for large-scale industrial applications.
Future Trends in Industrial Belt Materials
Biobased rubber for industrial belts is gaining traction due to its sustainability, reduced carbon footprint, and compatibility with circular economy principles, offering a renewable alternative to traditional natural rubber. Advances in bio-polymer technology are enhancing the mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making biobased rubber increasingly viable for demanding industrial applications. Future trends point toward hybrid composite belts combining biobased and synthetic rubbers to optimize performance, durability, and environmental impact in various industrial sectors.
Infographic: Biobased rubber vs Natural rubber for Industrial belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com