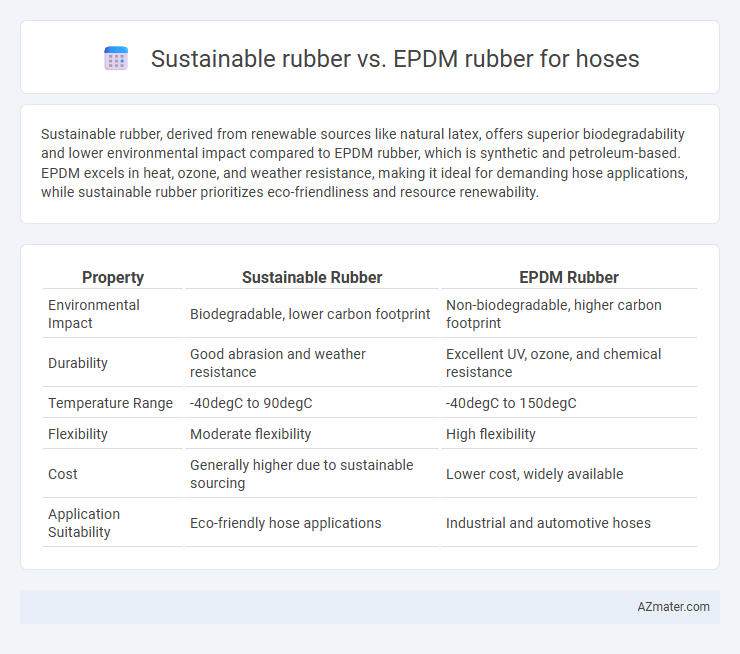
Sustainable rubber, derived from renewable sources like natural latex, offers superior biodegradability and lower environmental impact compared to EPDM rubber, which is synthetic and petroleum-based. EPDM excels in heat, ozone, and weather resistance, making it ideal for demanding hose applications, while sustainable rubber prioritizes eco-friendliness and resource renewability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sustainable Rubber | EPDM Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Durability | Good abrasion and weather resistance | Excellent UV, ozone, and chemical resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 90degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility |
| Cost | Generally higher due to sustainable sourcing | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application Suitability | Eco-friendly hose applications | Industrial and automotive hoses |
Introduction to Sustainable Rubber and EPDM Rubber
Sustainable rubber, derived from renewable sources or recycled materials, offers an eco-friendly alternative to traditional synthetic rubbers, reducing environmental impact and promoting resource conservation in hose manufacturing. EPDM rubber, a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, is widely used in hoses requiring durability and flexibility under harsh conditions. Comparing sustainable rubber and EPDM rubber involves evaluating factors like environmental footprint, mechanical performance, and long-term durability in industrial and automotive hose applications.
Material Composition and Sources
Sustainable rubber for hoses primarily consists of natural latex sourced from Hevea brasiliensis trees, emphasizing renewable, biodegradable components with lower environmental impact. EPDM rubber, a synthetic elastomer derived from ethylene, propylene, and a diene monomer, relies on petrochemical feedstocks and offers enhanced resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemicals. The contrast between bio-based sustainable rubber and petrochemical-derived EPDM highlights differences in raw material origin, environmental footprint, and performance attributes relevant to hose applications.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Sustainable rubber, derived from renewable natural latex sources, significantly reduces carbon footprint and biodegrades more efficiently compared to synthetic EPDM rubber, which relies on petrochemical processes with higher greenhouse gas emissions. Environmental Impact Assessment highlights that sustainable rubber's cultivation supports biodiversity and soil health, whereas EPDM production involves energy-intensive manufacturing and generates non-biodegradable waste. Lifecycle analysis confirms sustainable rubber hoses exhibit lower environmental toxicity, promoting eco-friendly alternatives in industrial applications.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Sustainable rubber for hoses is produced using eco-friendly methods such as renewable natural latex harvesting and reduced chemical treatments, minimizing environmental impact and energy consumption. EPDM rubber manufacturing involves synthetic polymerization processes using ethylene, propylene, and diene monomers, which typically require petrochemical raw materials and generate higher carbon emissions. The shift to sustainable rubber emphasizes closed-loop recycling, biodegradable additives, and lower VOC emissions compared to the conventional high-temperature vulcanization and sulfur curing techniques used in EPDM hose production.
Durability and Performance in Hoses
Sustainable rubber, derived from renewable sources like natural latex or bio-based polymers, offers enhanced environmental benefits while maintaining strong durability and flexibility essential for hose applications. EPDM rubber, a synthetic elastomer known for excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, provides superior performance in demanding industrial environments requiring long-lasting, non-reactive hose solutions. Comparing durability, sustainable rubber hoses show competitive abrasion resistance and flexibility, but EPDM excels in chemical and UV resistance, making it the preferred choice for harsh outdoor or industrial settings.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Sustainable rubber offers a competitive cost advantage over EPDM rubber for hoses due to lower raw material expenses and reduced environmental compliance fees, which can significantly impact long-term savings. While EPDM rubber provides excellent durability and resistance properties, its higher production costs and energy consumption result in greater overall expenses. Choosing sustainable rubber supports economic efficiency through reduced lifecycle costs and potential incentives related to eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
Sustainable rubber hoses are increasingly manufactured to meet stringent environmental standards such as REACH and RoHS, ensuring low VOC emissions and reduced ecological impact, which aligns with global regulatory compliance. EPDM rubber hoses commonly comply with industry norms like FDA CFR 21 for food safety and ASTM standards for durability but may lack the eco-certifications associated with sustainable alternatives. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and EcoLabel are more frequently obtained by sustainable rubber producers, enhancing market acceptance in eco-conscious sectors.
Real-World Application Case Studies
Sustainable rubber hoses, derived from renewable natural latex, offer superior biodegradability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional EPDM rubber, which excels in chemical and temperature resistance for industrial applications. Real-world case studies from agriculture highlight sustainable rubber hoses improving soil health by minimizing microplastic runoff, while EPDM hoses remain preferred in chemical plants for their durability against harsh substances. Manufacturing sectors increasingly adopt sustainable rubber to meet green compliance, whereas EPDM maintains dominance in automotive and HVAC systems due to its long lifecycle performance.
Future Trends in Hose Material Innovation
Sustainable rubber, derived from renewable resources or recycled materials, is increasingly favored for hose manufacturing due to its reduced environmental impact and compliance with evolving regulations on carbon emissions. EPDM rubber remains a benchmark for durability, heat resistance, and chemical stability, driving ongoing enhancements through nanocomposites and bio-based additives to boost performance and sustainability. Future trends in hose material innovation emphasize hybrid blends combining sustainable rubber and advanced EPDM formulations to achieve superior mechanical properties alongside eco-friendly credentials.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Hose Needs
Sustainable rubber offers eco-friendly properties such as biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint, making it ideal for environmentally conscious hose applications. EPDM rubber excels in durability, chemical resistance, and high temperature tolerance, suitable for industrial hoses exposed to harsh conditions. Selecting the right rubber depends on balancing environmental impact with performance requirements like flexibility, weather resistance, and chemical compatibility.
Infographic: Sustainable rubber vs EPDM rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com