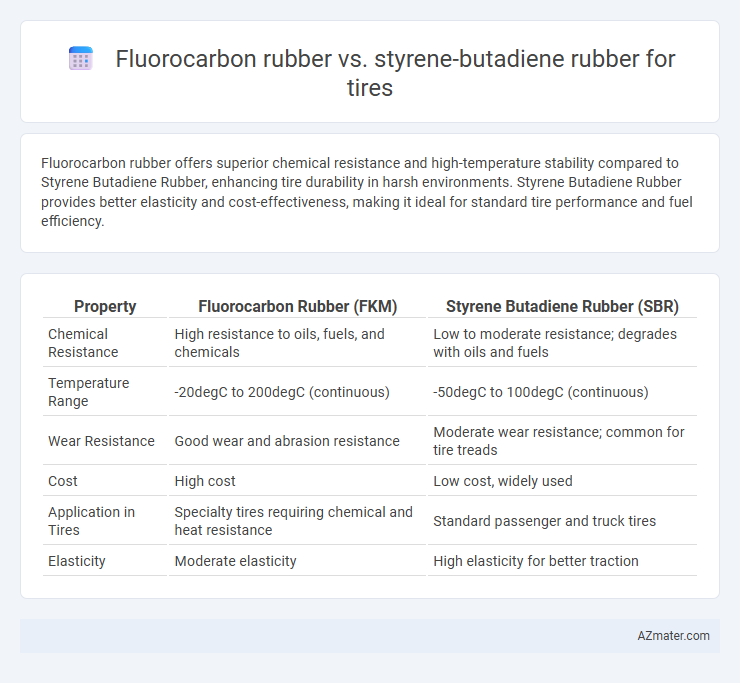
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber, enhancing tire durability in harsh environments. Styrene Butadiene Rubber provides better elasticity and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for standard tire performance and fuel efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Low to moderate resistance; degrades with oils and fuels |
| Temperature Range | -20degC to 200degC (continuous) | -50degC to 100degC (continuous) |
| Wear Resistance | Good wear and abrasion resistance | Moderate wear resistance; common for tire treads |
| Cost | High cost | Low cost, widely used |
| Application in Tires | Specialty tires requiring chemical and heat resistance | Standard passenger and truck tires |
| Elasticity | Moderate elasticity | High elasticity for better traction |
Introduction to Fluorocarbon and Styrene Butadiene Rubbers
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits exceptional chemical resistance, heat stability, and durability, making it ideal for high-performance tire applications exposed to harsh environments and extreme temperatures. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), one of the most commonly used synthetic rubbers in tire manufacturing, offers excellent abrasion resistance, aging stability, and cost efficiency for general-purpose tires. The distinct molecular structures and properties of FKM and SBR influence tire performance, with FKM providing superior resilience under aggressive chemical and thermal conditions compared to the versatile and economically favorable SBR.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) consists of copolymers containing vinylidene fluoride and hexafluoropropylene, providing high chemical resistance and thermal stability due to strong carbon-fluorine bonds. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) comprises styrene and butadiene monomers with a flexible chain structure that offers good abrasion resistance but lower chemical and heat resistance compared to FKM. The distinct chemical composition of FKM results in superior durability and resistance to oils, fuels, and extreme temperatures, making it ideal for harsh tire environments, whereas SBR focuses on cost-effectiveness and mechanical performance in standard tire applications.
Key Physical Properties: FKM vs SBR
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 250degC, and excellent ozone and weather resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), which typically withstands temperatures only up to 100degC and exhibits moderate abrasion resistance. FKM's tensile strength ranges from 10 to 25 MPa with elongation at break around 150-300%, whereas SBR shows tensile strength between 15 to 25 MPa but lower resistance to oils and fuels. The high durability and low gas permeability of FKM make it ideal for high-performance tire applications, while SBR remains cost-effective with good mechanical properties for standard tire use.
Temperature Resistance and Performance in Tires
Fluorocarbon rubber exhibits superior temperature resistance compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), maintaining excellent mechanical properties at temperatures exceeding 200degC, whereas SBR typically degrades beyond 100degC. This enhanced thermal stability translates to improved tire performance under extreme heat conditions, such as high-speed driving and heavy loads, by reducing tread wear and deformation. Consequently, tires incorporating Fluorocarbon rubber achieve longer service life and higher durability in demanding environments compared to conventional SBR-based tires.
Chemical and Oil Resistance in Tire Applications
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits superior chemical and oil resistance compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) in tire applications, maintaining performance under exposure to hydrocarbons, fuels, and aggressive chemicals. FKM's molecular structure provides excellent resistance to swelling, degradation, and hardening when in contact with oils and solvents, enhancing tire durability and lifespan. In contrast, SBR, while commonly used for its abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, has limited chemical resistance and is prone to degradation when exposed to oils and aggressive chemicals, reducing its suitability for specialized tire components requiring enhanced chemical stability.
Durability and Longevity of FKM vs SBR Tires
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits superior durability and longevity compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) in tire applications due to its excellent resistance to heat, chemicals, and ozone, which significantly reduces degradation during prolonged use. FKM tires maintain structural integrity at high temperatures and withstand exposure to oils and fuels, resulting in extended tire life and enhanced performance in harsh environments. In contrast, SBR rubber, while cost-effective and offering good abrasion resistance, tends to exhibit faster wear and reduced lifespan under extreme operating conditions.
Cost Analysis: Fluorocarbon vs Styrene Butadiene Rubber
Fluorocarbon rubber generally incurs higher production costs compared to styrene butadiene rubber due to its complex synthesis and superior chemical resistance properties. Styrene butadiene rubber offers a cost-effective solution with adequate abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it widely used in tire manufacturing. While fluorocarbon rubber enhances durability and heat resistance, its elevated price often restricts use to specialized tire applications where performance justifies the expense.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Fluorocarbon rubber exhibits exceptional chemical resistance and longevity, resulting in less frequent tire replacement and reduced environmental waste compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), which is more biodegradable but wears out faster, increasing landfill contribution. The energy-intensive production and limited recyclability of fluorocarbon rubber raise concerns about its carbon footprint, while SBR utilizes more sustainable sourcing and recycling methods, promoting circular economy principles in tire manufacturing. Evaluating tire sustainability involves balancing fluorocarbon rubber's durability benefits against SBR's lower environmental degradation and enhanced end-of-life material recovery.
Typical Tire Applications for Each Rubber Type
Fluorocarbon rubber is typically utilized in high-performance tire applications where superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and ozone resistance are critical, such as in racing tires and aircraft tires. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) is widely used in passenger car tires and truck tires due to its excellent abrasion resistance, good aging stability, and cost-effectiveness. Each rubber type optimizes specific tire performance characteristics, with fluorocarbon rubber enhancing durability in extreme environments, while SBR offers balanced traction and wear in everyday driving conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Tire Manufacturing
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and aging performance, making it ideal for high-performance and specialty tires exposed to extreme conditions. Styrene butadiene rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance, cost-effectiveness, and good wet traction, commonly used in standard passenger and truck tires. Selecting the right rubber depends on balancing performance requirements, environmental exposure, and budget constraints in tire manufacturing.
Infographic: Fluorocarbon rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com