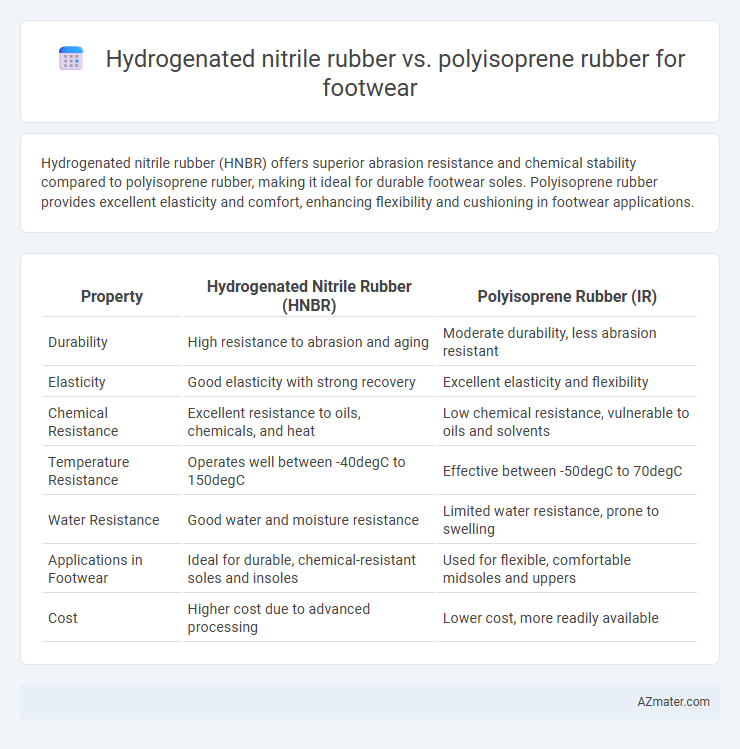
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and chemical stability compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it ideal for durable footwear soles. Polyisoprene rubber provides excellent elasticity and comfort, enhancing flexibility and cushioning in footwear applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Polyisoprene Rubber (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to abrasion and aging | Moderate durability, less abrasion resistant |
| Elasticity | Good elasticity with strong recovery | Excellent elasticity and flexibility |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and heat | Low chemical resistance, vulnerable to oils and solvents |
| Temperature Resistance | Operates well between -40degC to 150degC | Effective between -50degC to 70degC |
| Water Resistance | Good water and moisture resistance | Limited water resistance, prone to swelling |
| Applications in Footwear | Ideal for durable, chemical-resistant soles and insoles | Used for flexible, comfortable midsoles and uppers |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced processing | Lower cost, more readily available |
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its exceptional resistance to heat, oil, and chemical degradation, making it highly suitable for demanding footwear applications requiring durability and performance. Its hydrogenation process improves saturation in the polymer backbone, enhancing thermal stability and aging resistance compared to standard nitrile rubber. HNBR's elasticity and toughness ensure long-lasting comfort and protection in footwear exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Introduction to Polyisoprene Rubber (IR)
Polyisoprene rubber (IR) is a synthetic elastomer primarily composed of cis-1,4-polyisoprene, closely resembling natural rubber in elasticity, resilience, and tensile strength, making it highly suitable for footwear applications requiring flexibility and durability. Its excellent abrasion resistance and low heat buildup extend the lifespan of footwear components such as soles and insoles. Compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber, IR offers superior stretchability and comfort, essential for ergonomically designed shoes.
Key Chemical and Physical Differences
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior chemical resistance and enhanced thermal stability due to its saturated polymer backbone, making it ideal for footwear requiring durability against oils and extreme temperatures. Polyisoprene rubber, closely resembling natural rubber, offers excellent elasticity and tensile strength but lower resistance to oxidation and chemicals. The key physical differences lie in HNBR's increased hardness and abrasion resistance, while polyisoprene provides greater flexibility and comfort in footwear applications.
Durability and Wear Resistance Comparison
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior durability and wear resistance compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it a preferred choice for high-performance footwear exposed to harsh conditions. HNBR's enhanced chemical stability and resistance to abrasion extend the lifespan of soles and uppers, while polyisoprene rubber, though flexible and resilient, tends to wear faster under heavy use. This makes HNBR ideal for industrial and outdoor footwear requiring long-term durability and resistance to oils, heat, and mechanical stress.
Flexibility and Comfort in Footwear Applications
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion, making it highly durable but generally less flexible compared to polyisoprene rubber. Polyisoprene rubber, closely mimicking natural latex, provides exceptional elasticity and softness, resulting in enhanced comfort and flexibility in footwear applications. Footwear utilizing polyisoprene benefits from better cushioning and adaptability to foot movements, whereas HNBR is preferred for performance shoes requiring enhanced durability under harsh conditions.
Performance in Harsh Environmental Conditions
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemical exposure compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it highly suitable for footwear used in harsh environmental conditions. HNBR maintains exceptional tensile strength and abrasion resistance under extreme temperatures ranging from -40degC to 150degC, ensuring durability and longevity in demanding outdoor applications. Polyisoprene rubber, while flexible and resilient, lacks the enhanced chemical stability and thermal resistance of HNBR, limiting its performance in environments with aggressive chemicals or high heat.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and durability at a higher production cost compared to polyisoprene rubber, which is favored for its natural elasticity and cost-effectiveness in footwear manufacturing. Market availability of HNBR is more limited and concentrated among specialized suppliers, while polyisoprene rubber enjoys widespread global distribution due to its extensive use in various industries, including footwear. Cost analysis reveals polyisoprene as the more economical choice for mass-produced footwear, whereas HNBR is selected for niche applications requiring enhanced performance and longevity.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers enhanced durability and chemical resistance compared to polyisoprene rubber, leading to longer product lifespan and reduced waste in footwear applications. Polyisoprene rubber, being a natural elastomer derived from renewable sources, provides biodegradability advantages, lowering environmental impact during disposal. When considering sustainability, the choice depends on balancing HNBR's extended service life with polyisoprene's biodegradable nature and renewable origin.
Common Footwear Types Using HNBR vs IR
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) is widely used in performance footwear such as industrial safety shoes and athletic sneakers due to its superior oil resistance, thermal stability, and durability. Polyisoprene rubber (IR), closely resembling natural rubber, is commonly found in casual shoes and dress footwear for its excellent flexibility, elasticity, and comfort. Common footwear types utilizing HNBR include work boots and hiking shoes, while IR is favored in loafers, ballet flats, and running shoes where cushioning and flexibility are prioritized.
Choosing the Best Rubber for Footwear Production
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, durability, and heat resistance, making it ideal for footwear exposed to harsh environments or industrial use. Polyisoprene rubber, closely resembling natural rubber, provides excellent elasticity, softness, and breathability, which enhances comfort and flexibility in casual and athletic footwear. Selecting the best rubber depends on the footwear's intended use, with HNBR suited for heavy-duty applications and polyisoprene preferred for lightweight, comfort-focused designs.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Polyisoprene rubber for Footwear
 azmater.com
azmater.com