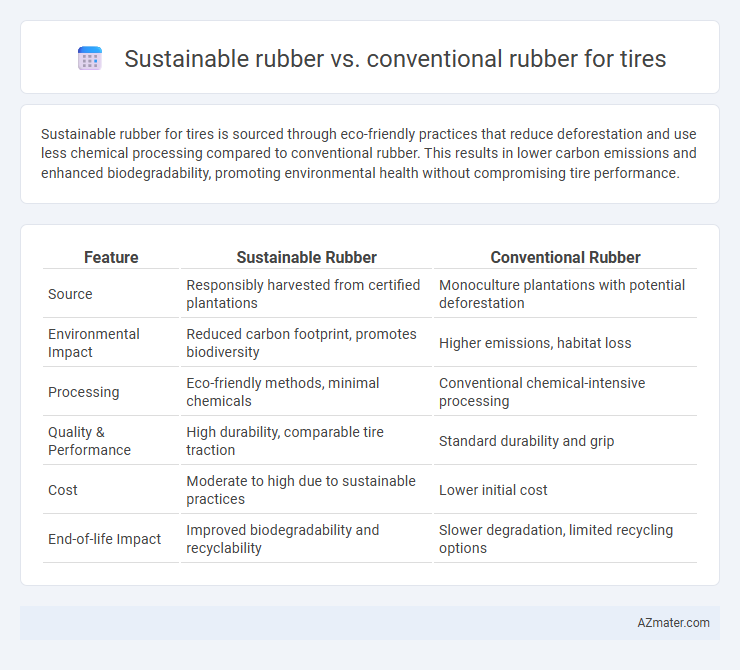
Sustainable rubber for tires is sourced through eco-friendly practices that reduce deforestation and use less chemical processing compared to conventional rubber. This results in lower carbon emissions and enhanced biodegradability, promoting environmental health without compromising tire performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sustainable Rubber | Conventional Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Responsibly harvested from certified plantations | Monoculture plantations with potential deforestation |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced carbon footprint, promotes biodiversity | Higher emissions, habitat loss |
| Processing | Eco-friendly methods, minimal chemicals | Conventional chemical-intensive processing |
| Quality & Performance | High durability, comparable tire traction | Standard durability and grip |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to sustainable practices | Lower initial cost |
| End-of-life Impact | Improved biodegradability and recyclability | Slower degradation, limited recycling options |
Introduction to Rubber in Tire Manufacturing
Rubber in tire manufacturing primarily utilizes two types: sustainable rubber derived from environmentally responsible sources and conventional rubber sourced from traditional plantations. Sustainable rubber emphasizes reduced deforestation, lower carbon emissions, and improved biodiversity, aligning with global environmental standards. Conventional rubber remains widely used due to established supply chains and consistent material properties crucial for tire performance.
Defining Conventional Rubber: Sources and Processing
Conventional rubber primarily derives from natural rubber harvested from Hevea brasiliensis trees and synthetic rubber produced from petroleum-based monomers like styrene and butadiene. The processing of conventional rubber involves latex extraction, coagulation, and vulcanization to enhance elasticity and durability for tire manufacturing. This traditional approach relies heavily on non-renewable resources and energy-intensive refining methods, raising concerns about environmental impact and resource sustainability.
What is Sustainable Rubber?
Sustainable rubber is derived from eco-friendly farming practices that minimize deforestation and promote biodiversity, using natural rubber trees managed with methods adhering to environmental and social standards. Unlike conventional rubber, which often involves large-scale monoculture plantations causing habitat loss and soil degradation, sustainable rubber prioritizes reduced chemical use, fair labor conditions, and carbon footprint reduction. This approach supports tire manufacturers seeking to lower environmental impact while maintaining performance and durability in their products.
Environmental Impact: Conventional vs Sustainable Rubber
Sustainable rubber production significantly reduces deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, and biodiversity loss compared to conventional rubber farming, which often involves clearing tropical forests and unsustainable land use practices. Life cycle assessments show that sustainable rubber cultivation lowers carbon footprints by promoting agroforestry systems and eco-friendly harvesting techniques. These environmentally conscious practices contribute to soil preservation, water conservation, and enhanced ecosystem resilience in tire manufacturing supply chains.
Economic Considerations in Rubber Sourcing
Sustainable rubber sourcing often leads to higher initial costs due to certification requirements and eco-friendly farming practices but offers long-term economic benefits through market differentiation and access to premium pricing. Conventional rubber remains cost-effective in the short term, relying on established supply chains and lower production expenses, yet may face financial risks from environmental regulations and supply volatility caused by deforestation concerns. Investing in sustainable rubber can enhance supply chain resilience and brand reputation, potentially offsetting higher upfront expenses with increased demand from environmentally conscious consumers and regulatory incentives.
Performance and Safety: Comparing Rubber Types
Sustainable rubber, derived from renewable sources and processed with eco-friendly methods, offers comparable durability and traction performance to conventional rubber in tire applications. Studies indicate that sustainable rubber maintains optimal grip on wet and dry surfaces while enhancing resistance to wear and temperature fluctuations, contributing to overall tire safety. Conventional rubber, often petroleum-based, excels in established performance metrics but raises concerns about environmental impact, making sustainable alternatives increasingly viable without compromising tire reliability.
Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
Sustainable rubber in tire production enhances supply chain transparency through certified sourcing and blockchain tracking, ensuring ethical labor practices and environmental compliance. Conventional rubber often lacks traceability, leading to challenges in verifying sustainability claims and exposing risks of deforestation and exploitation. Advanced digital tools and third-party audits in sustainable rubber supply chains offer greater accountability and improved consumer trust compared to traditional methods.
Innovations in Sustainable Rubber Technology
Innovations in sustainable rubber technology have led to the development of bio-based polymers and enhanced vulcanization processes, reducing reliance on petroleum-derived materials in tire production. Advanced genetic engineering of rubber trees improves latex yield and disease resistance, ensuring a more sustainable and consistent supply. Incorporation of recycled rubber materials and eco-friendly fillers further minimizes environmental impact while maintaining tire performance and durability.
Industry Regulations and Certification Standards
Sustainable rubber for tires adheres to stringent industry regulations such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and the Global Platform for Sustainable Natural Rubber (GPSNR) standards, ensuring environmentally responsible sourcing and reduced deforestation. Conventional rubber, often lacking these certifications, faces increasing scrutiny due to its association with deforestation, biodiversity loss, and unsustainable agricultural practices under frameworks like the European Union's Deforestation Regulation (EUDR). Tire manufacturers shifting to sustainable rubber must comply with certifications including ISO 14001 environmental management and verify traceability through blockchain technology to meet global regulatory and consumer demands.
Future Trends: Toward Greener Tire Production
Sustainable rubber, derived from responsibly managed plantations and innovative agro-forestry methods, is progressively replacing conventional rubber in tire manufacturing to reduce environmental impact and enhance carbon sequestration. Future trends indicate increased adoption of bio-based and recycled materials, alongside advances in chemical recycling technologies, to create greener tires with improved durability and reduced VOC emissions. Industry forecasts emphasize a shift towards circular economy models and transparent supply chains to meet stringent global sustainability standards and consumer demand for eco-friendly tires.
Infographic: Sustainable rubber vs Conventional rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com