Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior tensile strength, enhanced elasticity, and improved UV and ozone resistance compared to traditional EPDM rubber used in weatherstrips. This results in longer-lasting, more durable weatherstripping with better performance in extreme temperatures and environmental conditions.
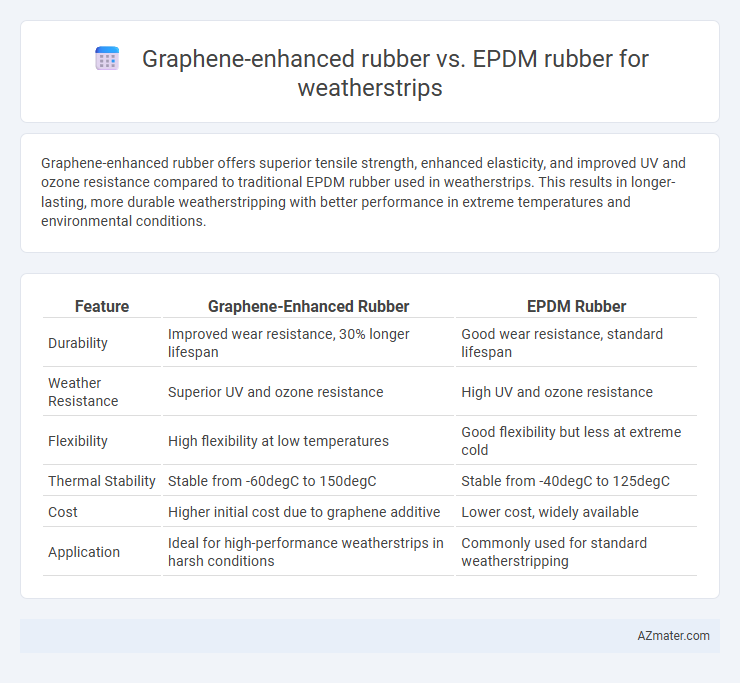
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graphene-Enhanced Rubber | EPDM Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Improved wear resistance, 30% longer lifespan | Good wear resistance, standard lifespan |
| Weather Resistance | Superior UV and ozone resistance | High UV and ozone resistance |
| Flexibility | High flexibility at low temperatures | Good flexibility but less at extreme cold |
| Thermal Stability | Stable from -60degC to 150degC | Stable from -40degC to 125degC |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to graphene additive | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application | Ideal for high-performance weatherstrips in harsh conditions | Commonly used for standard weatherstripping |
Introduction to Weatherstrip Materials
Weatherstrip materials play a crucial role in sealing gaps to prevent water, air, and noise infiltration, with EPDM rubber being a standard choice due to its excellent weather resistance and flexibility. Graphene-enhanced rubber introduces superior mechanical strength, enhanced thermal conductivity, and increased durability compared to conventional EPDM, improving weatherstrip performance under extreme conditions. This advanced composite material offers promising advancements in extending the lifespan and efficiency of weatherstrips used in automotive and construction industries.
What is Graphene-Enhanced Rubber?
Graphene-enhanced rubber incorporates graphene nanoparticles into traditional rubber matrices, significantly boosting mechanical strength, elasticity, and durability for weatherstrip applications. This advanced composite exhibits superior resistance to abrasion, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures compared to standard EPDM rubber. Enhanced weatherstripping performance with graphene-enriched rubber ensures longer-lasting seals and improved protection against environmental elements.
Overview of EPDM Rubber
EPDM rubber, or Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer, is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent weather resistance, ozone stability, and flexibility, making it a preferred choice for weatherstrips in automotive and construction industries. Its molecular structure enables superior resistance to UV rays, extreme temperatures, and moisture, ensuring long-lasting performance in sealing applications. Compared to graphene-enhanced rubber, EPDM offers proven durability but lacks the enhanced mechanical strength and electrical conductivity provided by graphene additives.
Comparative Mechanical Properties
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits superior tensile strength and elongation at break compared to EPDM rubber, resulting in enhanced durability and resistance to deformation in weatherstripping applications. Its improved tear resistance and abrasion resistance contribute to a longer lifespan under harsh environmental conditions, outperforming standard EPDM. The incorporation of graphene also enhances the material's flexibility and compression set recovery, maintaining seal integrity against temperature fluctuations and mechanical stress.
Weather Resistance Comparison
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits superior weather resistance compared to EPDM rubber due to its enhanced impermeability and ability to withstand UV radiation, ozone, and extreme temperatures. The integration of graphene significantly improves the material's mechanical strength and reduces degradation from prolonged environmental exposure, ensuring longer-lasting weatherstrips. In contrast, standard EPDM rubber can suffer from accelerated aging and cracking when exposed to harsh weather conditions without graphene reinforcement.
Longevity and Durability
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits superior longevity and durability compared to traditional EPDM rubber for weatherstripping applications, due to graphene's exceptional tensile strength and resistance to environmental degradation. Its enhanced molecular structure improves abrasion resistance and maintains flexibility under extreme temperatures and UV exposure, resulting in prolonged service life. This advanced material significantly reduces maintenance frequency and replacement costs, making it ideal for high-performance weatherstripping solutions.
Energy Efficiency and Sealing Performance
Graphene-enhanced rubber significantly improves energy efficiency and sealing performance in weatherstrips due to its exceptional thermal conductivity and durability, which reduces heat transfer and prevents air leakage. EPDM rubber offers reliable weather resistance and elasticity but falls short in thermal insulation capabilities compared to graphene composites. The incorporation of graphene enhances weatherstrip longevity and maintains airtight seals under extreme temperature fluctuations, leading to superior energy savings.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior durability and flexibility compared to EPDM rubber, potentially reducing long-term maintenance costs despite its higher initial price. Manufacturing processes for graphene-enhanced rubber require specialized equipment and controlled conditions, increasing production complexity relative to the well-established, cost-effective methods used for EPDM rubber. The trade-off between advanced performance properties and elevated manufacturing costs influences material selection for weatherstrips in automotive and construction applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits superior durability and flexibility compared to conventional EPDM rubber, resulting in increased product lifespan and reduced material waste. The incorporation of graphene reduces energy consumption during manufacturing by enhancing thermal conductivity and processing efficiency. EPDM rubber, while widely recyclable and resistant to UV and ozone degradation, lacks the advanced environmental benefits brought by graphene's reinforcement, making graphene-enhanced rubber a more sustainable choice for weatherstripping applications.
Market Trends and Future Prospects
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits superior mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and weather resistance compared to traditional EPDM rubber, driving increased adoption in weatherstrip applications. Market trends indicate growing interest in graphene composites due to their enhanced durability and eco-friendly properties, appealing to automotive and construction industries focused on long-lasting seals. Future prospects suggest continued innovation and cost reductions in graphene production, positioning graphene-enhanced rubber as a leading material for high-performance weatherstrips.
Infographic: Graphene-enhanced rubber vs EPDM rubber for Weatherstrip
 azmater.com
azmater.com