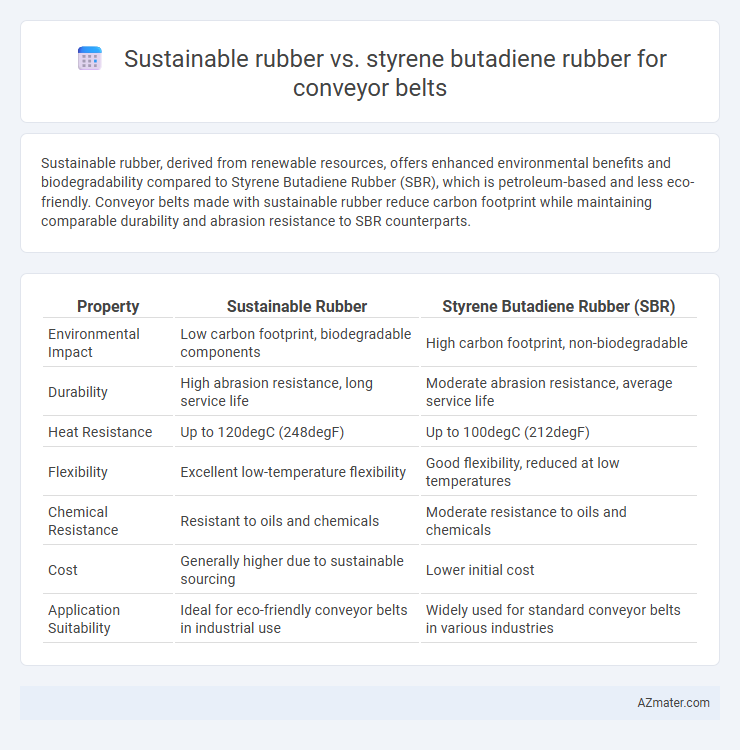
Sustainable rubber, derived from renewable resources, offers enhanced environmental benefits and biodegradability compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), which is petroleum-based and less eco-friendly. Conveyor belts made with sustainable rubber reduce carbon footprint while maintaining comparable durability and abrasion resistance to SBR counterparts.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sustainable Rubber | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable components | High carbon footprint, non-biodegradable |
| Durability | High abrasion resistance, long service life | Moderate abrasion resistance, average service life |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 120degC (248degF) | Up to 100degC (212degF) |
| Flexibility | Excellent low-temperature flexibility | Good flexibility, reduced at low temperatures |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils and chemicals | Moderate resistance to oils and chemicals |
| Cost | Generally higher due to sustainable sourcing | Lower initial cost |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for eco-friendly conveyor belts in industrial use | Widely used for standard conveyor belts in various industries |
Introduction to Conveyor Belt Materials
Conveyor belts commonly utilize materials such as sustainable rubber and styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) due to their distinct properties tailored for industrial applications. Sustainable rubber offers enhanced environmental benefits with comparable durability and elasticity, making it a viable alternative to traditional SBR, which is prized for its abrasion resistance and heat tolerance. Selection between the two materials depends on factors like operating environment, load capacity, and sustainability goals.
Overview of Sustainable Rubber
Sustainable rubber for conveyor belts is derived from renewable sources such as natural latex or bio-based synthetic alternatives, offering lower environmental impact compared to traditional Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) made from petroleum-based chemicals. It exhibits comparable mechanical properties including wear resistance, elasticity, and tensile strength while reducing carbon footprint and enhancing biodegradability. Manufacturers increasingly adopt sustainable rubber to meet regulatory requirements and promote circular economy principles within industrial belt applications.
What is Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)?
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic polymer widely used in conveyor belt manufacturing due to its excellent abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and good aging stability. Derived from the copolymerization of styrene and butadiene, SBR offers enhanced durability and elasticity under dynamic loads, making it ideal for heavy-duty material handling applications. Compared to sustainable rubber alternatives, SBR provides consistent performance in extreme conditions but raises environmental concerns due to its petrochemical origin and challenges in biodegradability.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Sustainable rubber, derived from natural latex, significantly reduces carbon emissions and biodegrades faster compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), which is petroleum-based and contributes to higher environmental pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. The production of sustainable rubber involves renewable resources, lowering fossil fuel dependency and minimizing ecological degradation, while SBR manufacturing relies on non-renewable petrochemicals with substantial energy consumption and toxic byproducts. Lifecycle assessments highlight sustainable rubber's superior environmental profile through enhanced recyclability and reduced toxic chemical leaching, making it a more eco-friendly choice for conveyor belts.
Performance and Durability Analysis
Sustainable rubber compounds for conveyor belts exhibit enhanced environmental benefits while maintaining competitive abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and flexibility compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR). Performance evaluations demonstrate that sustainable rubbers often achieve comparable elongation at break and temperature resistance, contributing to reliable operation under heavy loads and variable conditions. Durability analysis reveals sustainable rubber formulations can offer improved aging resistance and lower degradation rates, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs for conveyor belt applications.
Cost Considerations and Long-term Value
Sustainable rubber offers competitive initial costs compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) while providing enhanced durability and resistance to environmental degradation, reducing maintenance expenses over time. Styrene butadiene rubber, although often cheaper upfront, may require more frequent replacement and repair due to lower resilience against abrasion and harsh conditions typical in conveyor belt applications. Investing in sustainable rubber yields long-term value through extended belt lifespan and decreased operational downtime, proving more cost-effective in intensive industrial settings.
Maintenance and Lifespan Differences
Sustainable rubber conveyor belts exhibit enhanced resistance to abrasion and environmental degradation, resulting in lower maintenance frequency compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) belts, which are more susceptible to cracking and wear under harsh operating conditions. The lifespan of sustainable rubber belts typically exceeds that of SBR belts by up to 30%, providing longer service intervals and reduced downtime costs. Optimized formulations in sustainable rubber also improve elasticity and heat resistance, contributing to improved durability and fewer maintenance interventions.
Industrial Applications: Use Cases
Sustainable rubber, derived from natural sources such as guayule or recycled materials, exhibits enhanced biodegradability and lower environmental impact, making it ideal for eco-friendly conveyor belts in industries prioritizing sustainability. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), known for its superior abrasion resistance and temperature stability, remains the dominant choice for heavy-duty conveyor belt applications in mining, manufacturing, and construction. Industrial use cases favor sustainable rubber in food processing and green logistics sectors where reduced chemical exposure is critical, while SBR suits high-wear environments requiring prolonged belt lifespan and consistent mechanical performance.
Innovations in Sustainable Rubber Technology
Innovations in sustainable rubber technology have led to the development of eco-friendly alternatives to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) in conveyor belts, such as bio-based natural rubber blends and recycled rubber composites. These sustainable rubbers offer comparable durability, abrasion resistance, and heat tolerance while significantly reducing carbon footprint and environmental impact. Advances in green chemistry and material science enable the integration of renewable resources and enhanced recycling processes, driving the sustainability of conveyor belt manufacturing.
Future Outlook: Choosing the Right Material
Sustainable rubber formulations for conveyor belts are rapidly gaining traction due to their reduced environmental impact, biodegradability, and alignment with circular economy principles, making them a key focus in future material selection. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), known for its durability and cost-effectiveness, remains widely used but faces increasing scrutiny over its reliance on petroleum-based resources and ecological footprint. Advances in sustainable rubber technology, including bio-based composites and enhanced recyclability, position these materials as the preferred choice for industries prioritizing long-term environmental responsibility and regulatory compliance.
Infographic: Sustainable rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Conveyor belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com