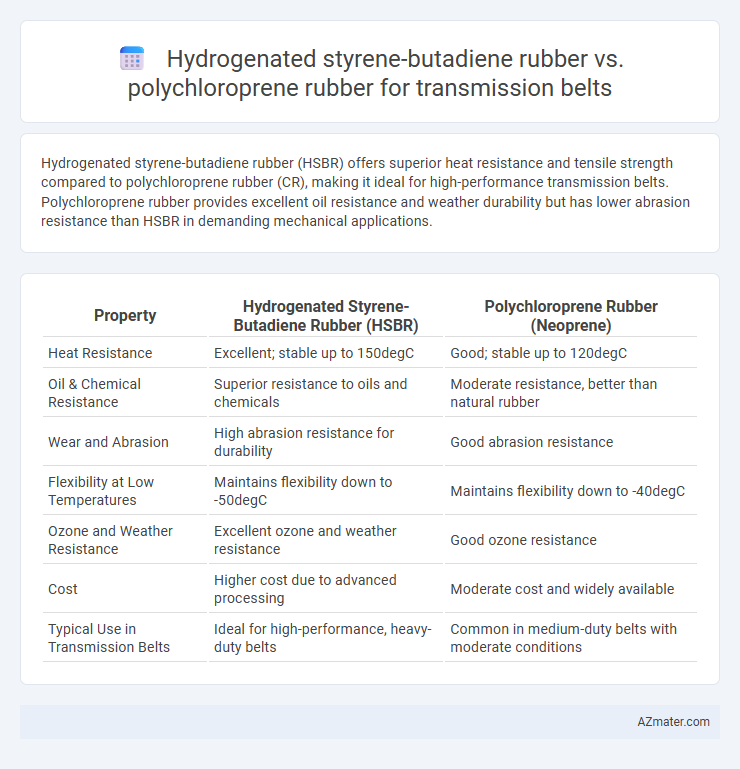
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior heat resistance and tensile strength compared to polychloroprene rubber (CR), making it ideal for high-performance transmission belts. Polychloroprene rubber provides excellent oil resistance and weather durability but has lower abrasion resistance than HSBR in demanding mechanical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) | Polychloroprene Rubber (Neoprene) |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Excellent; stable up to 150degC | Good; stable up to 120degC |
| Oil & Chemical Resistance | Superior resistance to oils and chemicals | Moderate resistance, better than natural rubber |
| Wear and Abrasion | High abrasion resistance for durability | Good abrasion resistance |
| Flexibility at Low Temperatures | Maintains flexibility down to -50degC | Maintains flexibility down to -40degC |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Excellent ozone and weather resistance | Good ozone resistance |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced processing | Moderate cost and widely available |
| Typical Use in Transmission Belts | Ideal for high-performance, heavy-duty belts | Common in medium-duty belts with moderate conditions |
Introduction to Transmission Belt Materials
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance, heat stability, and oil resistance, making it a preferred material for transmission belts in heavy-duty and high-temperature environments. Polychloroprene rubber (CR), known for its good weatherability, moderate oil resistance, and mechanical strength, is widely used in general-purpose transmission belts exposed to outdoor conditions and moderate chemical exposure. Selecting between HSBR and CR depends on specific application requirements, including temperature range, chemical exposure, and durability demands in transmission belt systems.
Overview of Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR)
Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent heat resistance, low gas permeability, and superior mechanical strength, making it highly suitable for transmission belt applications that demand durability under high stress and temperature conditions. Compared to Polychloroprene rubber (CR), HSBR offers enhanced abrasion resistance and improved aging properties, contributing to longer belt life and consistent performance in harsh environments. The hydrogenation process saturates the polymer backbone, significantly increasing chemical resistance and reducing the risk of ozone and oxidative degradation common in transmission systems.
Overview of Polychloroprene Rubber (CR)
Polychloroprene rubber (CR), known for its excellent resistance to oil, heat, and weathering, is widely used in transmission belts requiring durability under harsh conditions. Its superior mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and abrasion resistance, make it suitable for demanding industrial applications compared to hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR). CR's balanced performance in flexibility and chemical resistance ensures enhanced belt longevity and operational efficiency in automotive and manufacturing transmissions.
Mechanical Properties Comparison: HSBR vs CR
Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior heat resistance and tensile strength compared to Polychloroprene Rubber (CR), making it ideal for high-performance transmission belts requiring long service life under thermal stress. Polychloroprene rubber offers excellent oil resistance and moderate mechanical strength, suitable for applications with exposure to oils and moderate mechanical loads. HSBR outperforms CR in abrasion resistance and elasticity retention, ensuring better durability and dimensional stability in demanding transmission belt applications.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and oxidation due to its saturated polymer backbone, making it highly effective in harsh chemical environments commonly encountered in transmission belt applications. Polychloroprene rubber (Neoprene) exhibits excellent resistance to oils, solvents, and weathering, providing balanced performance in environments with moderate chemical exposure. HSBR outperforms Polychloroprene in long-term oxidative stability and aging resistance, while Polychloroprene maintains better resistance against certain oils and chlorinated solvents, influencing the choice based on specific chemical exposure profiles.
Durability and Wear Performance
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) demonstrates superior durability and wear resistance compared to polychloroprene rubber (CR) in transmission belt applications, owing to its enhanced thermal stability and chemical resistance. HSBR's hydrogenation process reduces unsaturation, leading to improved oxidative resistance and prolonged belt lifespan under high-stress conditions. Polychloroprene rubber offers good resistance to oil and weathering but generally exhibits lower wear performance and shorter service life in demanding mechanical environments.
Temperature and Heat Resistance
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior heat resistance with an operating temperature range typically between -40degC to 150degC, making it ideal for high-temperature transmission belt applications. Polychloroprene rubber (CR) offers good thermal stability typically up to 120degC but tends to degrade faster under continuous high heat exposure compared to HSBR. The enhanced saturation of HSBR's polymer backbone provides better resistance to thermal oxidation and heat aging, ensuring longer service life in demanding transmission belt environments.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior heat resistance and durability compared to polychloroprene rubber (CR), resulting in longer lifespan for transmission belts and reduced replacement frequency. While HSBR typically incurs higher initial costs, its enhanced performance translates into lower total cost of ownership by minimizing downtime and maintenance expenses. Polychloroprene rubber, though more cost-effective upfront, may lead to increased long-term operational costs due to faster wear under high-temperature environments.
Application Suitability in Transmission Belts
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and enhanced heat stability, making it suitable for high-performance transmission belts exposed to elevated temperatures and continuous friction. Polychloroprene rubber (neoprene) provides superior oil and weather resistance, ideal for transmission belts used in environments with exposure to oils, chemicals, and harsh weather conditions. Choosing between HSBR and polychloroprene depends on the specific operational demands, such as thermal resistance for HSBR or chemical resilience for polychloroprene in transmission belt applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Rubber Material
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers excellent heat resistance and oil stability, making it ideal for high-performance transmission belts exposed to elevated temperatures and aggressive lubricants. Polychloroprene rubber (CR) provides superior abrasion resistance and weatherability, suitable for belts operating in harsh environmental conditions with frequent mechanical stress. Selecting the optimal rubber material depends on the specific transmission belt application demands, balancing thermal stability and chemical resistance of HSBR against the durability and environmental resilience of CR.
Infographic: Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber vs Polychloroprene rubber for Transmission belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com