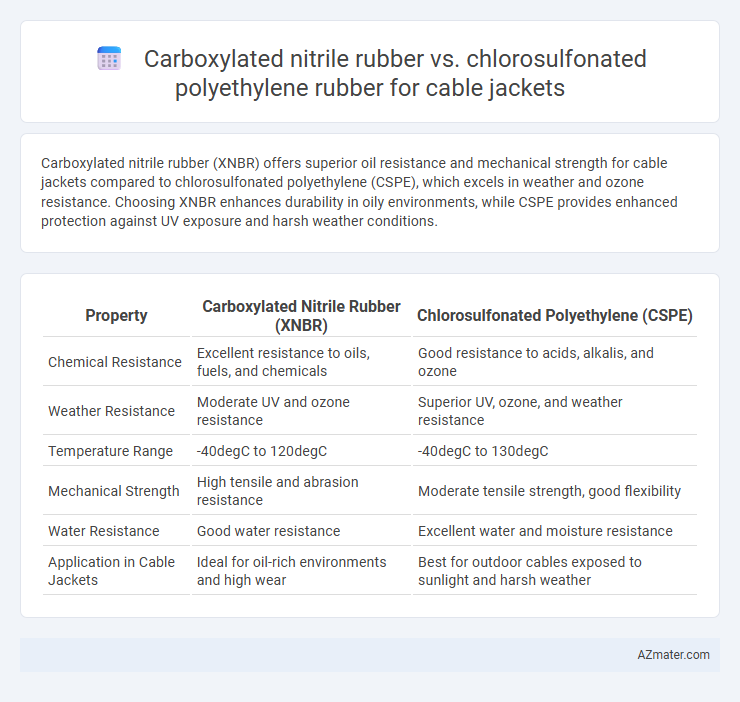
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance and mechanical strength for cable jackets compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE), which excels in weather and ozone resistance. Choosing XNBR enhances durability in oily environments, while CSPE provides enhanced protection against UV exposure and harsh weather conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Good resistance to acids, alkalis, and ozone |
| Weather Resistance | Moderate UV and ozone resistance | Superior UV, ozone, and weather resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 130degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile and abrasion resistance | Moderate tensile strength, good flexibility |
| Water Resistance | Good water resistance | Excellent water and moisture resistance |
| Application in Cable Jackets | Ideal for oil-rich environments and high wear | Best for outdoor cables exposed to sunlight and harsh weather |
Overview of Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber and Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) is a high-performance elastomer known for its excellent oil resistance, abrasion resistance, and enhanced tensile strength, making it suitable for demanding cable jacket applications. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber offers superior weatherability, chemical resistance, and flame retardancy, which are critical properties for cable jackets exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Both XNBR and CSM provide durable protection, but XNBR excels in mechanical wear environments while CSM is preferred for outdoor and chemical-exposure scenarios.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) features nitrile groups with carboxyl (-COOH) modifications along its polymer chain, enhancing polarity and oil resistance due to the acrylonitrile and carboxyl functional groups. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber consists of polyethylene backbone with chlorosulfonyl (-SO2Cl) and chlorine substitutions, providing superior weathering, chemical resistance, and flame retardancy. The chemical structure of XNBR leads to excellent mechanical strength and oil resistance, while CSPE's chlorosulfonyl groups contribute to outstanding UV stability and flexibility, making each suitable for different cable jacket performance requirements.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE), making it ideal for high-performance cable jackets requiring durability. CSPE excels in chemical resistance and excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and UV exposure, ensuring long-term outdoor cable protection. XNBR demonstrates better oil and fuel resistance, while CSPE provides enhanced flexibility at low temperatures and inherent flame retardancy.
Thermal Resistance and Temperature Performance
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior thermal resistance with continuous operating temperatures typically up to 120degC, making it ideal for cable jackets exposed to moderate heat conditions. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber provides enhanced temperature performance, maintaining structural integrity and flexibility at higher temperatures up to 130degC and excellent resistance to ozone and UV degradation. Both materials exhibit excellent abrasion resistance, but CSPE's higher thermal tolerance makes it more suitable for cables used in harsher thermal environments.
Oil, Chemical, and Solvent Resistance
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil and chemical resistance due to its enhanced polarity and cross-linking density, making it highly effective in protecting cable jackets in harsh environments. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber demonstrates excellent resistance to a broad range of solvents and ultraviolet radiation but shows comparatively lower performance against petroleum-based oils and aggressive chemicals. Choosing XNBR for cable jackets ensures improved durability and lifespan in oil-rich or chemically aggressive settings, while CSPE provides better performance in outdoor and solvent-exposed applications.
Weathering, Ozone, and UV Resistance
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior ozone and weathering resistance compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE), making it ideal for cable jackets exposed to harsh environmental conditions. CSPE rubber offers excellent UV resistance and maintains flexibility over a wide temperature range, enhancing cable durability under prolonged sunlight exposure. Both materials provide robust protection, but XNBR's enhanced chemical stability delivers better performance in ozone-rich atmospheres, while CSPE excels in long-term UV aging resistance.
Mechanical Strength and Abrasion Resistance
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) demonstrates superior mechanical strength with high tensile and tear resistance, making it ideal for cable jackets exposed to mechanical stress. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber offers excellent abrasion resistance and chemical durability, providing robust protection against wear and environmental factors. Choosing between XNBR and CSPE depends on whether priority is given to mechanical toughness or enhanced abrasion resistance in cable jacket applications.
Flexibility and Handling in Cable Applications
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior flexibility and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for cable jackets requiring enhanced flexibility and durability in dynamic environments. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) provides robust chemical resistance and weatherability but tends to be stiffer, impacting handling ease in cable installation. For cable applications prioritizing flexibility and ease of handling, XNBR is generally preferred due to its balanced elasticity and resistance properties.
Cost Implications and Availability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) generally offers a cost advantage over chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE) rubber due to its lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making it a budget-friendly choice for cable jackets. In terms of availability, XNBR is widely accessible globally, supported by established production infrastructure, whereas CSPE supply can be limited and more region-specific due to specialized synthesis requirements. The combination of lower costs and broader availability positions XNBR as a practical option for large-scale cable jacket applications requiring effective oil and abrasion resistance.
Best Use Cases: Choosing the Right Material for Cable Jackets
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance and abrasion durability, making it ideal for cable jackets in automotive and industrial environments exposed to oils and mechanical wear. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM), renowned for its excellent weathering, UV, and chemical resistance, suits cable jackets in outdoor applications requiring long-term exposure to harsh environmental conditions. Selecting between XNBR and CSM depends on specific use cases, prioritizing oil and abrasion resistance for indoor or machinery-heavy settings versus superior weather and chemical resilience for demanding outdoor installations.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber for Cable jacket
 azmater.com
azmater.com