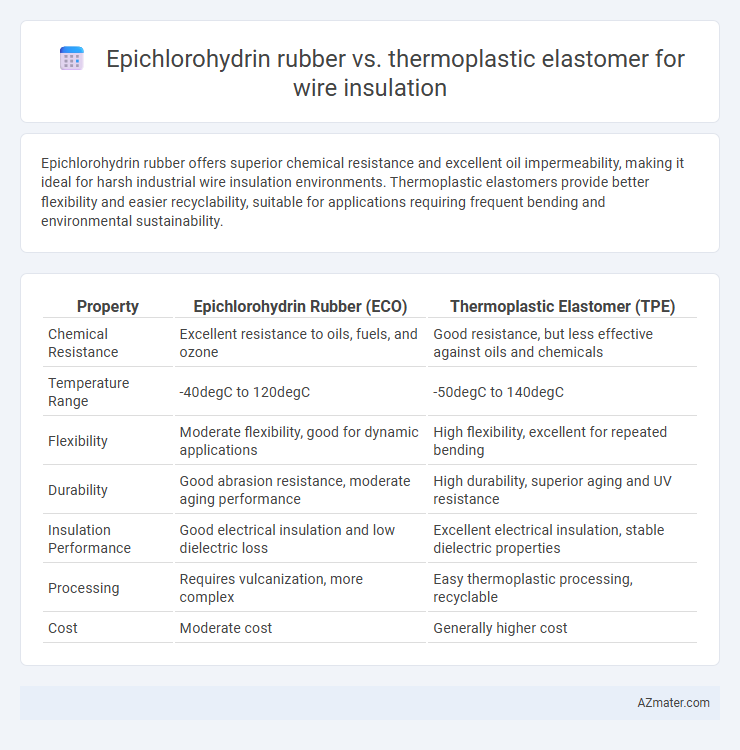
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior chemical resistance and excellent oil impermeability, making it ideal for harsh industrial wire insulation environments. Thermoplastic elastomers provide better flexibility and easier recyclability, suitable for applications requiring frequent bending and environmental sustainability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone | Good resistance, but less effective against oils and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -50degC to 140degC |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, good for dynamic applications | High flexibility, excellent for repeated bending |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance, moderate aging performance | High durability, superior aging and UV resistance |
| Insulation Performance | Good electrical insulation and low dielectric loss | Excellent electrical insulation, stable dielectric properties |
| Processing | Requires vulcanization, more complex | Easy thermoplastic processing, recyclable |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Generally higher cost |
Introduction to Wire Insulation Materials
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent resistance to heat, oil, and ozone, making it a preferred choice for demanding electrical wire insulation applications. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) provide flexibility, ease of processing, and recyclability, which are advantageous in manufacturing insulated wires with complex designs. Both materials contribute distinct mechanical and electrical properties critical for optimizing wire insulation performance in various industrial environments.
Overview of Epichlorohydrin Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to oil, fuel, ozone, and weathering, making it suitable for wire insulation in harsh environments. It offers superior electrical insulation properties, good flexibility at low temperatures, and strong chemical resistance compared to many other elastomers. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) provide ease of processing and recyclability but typically lack the chemical and temperature resistance attributes inherent to epichlorohydrin rubber used in high-performance wire insulation applications.
Overview of Thermoplastic Elastomers
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) for wire insulation combine the flexibility and elasticity of rubber with the processability of plastics, offering superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to epichlorohydrin rubber. TPEs provide excellent mechanical strength, durability, and ease of recycling, making them ideal for high-performance electrical applications where insulation integrity and environmental considerations are critical. Their adaptability in formulation allows tailored properties such as UV resistance, flame retardancy, and improved aging characteristics, outperforming traditional elastomeric materials in demanding wire insulation environments.
Key Mechanical Properties Comparison
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior resistance to oil, ozone, and weathering, with tensile strength ranging from 15 to 25 MPa and elongation at break of approximately 300-450%, making it ideal for durable wire insulation in harsh environments. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) offer flexibility and easier processing, with tensile strength typically between 10 to 20 MPa and elongation around 500-700%, which provides enhanced elasticity and reusability. The choice hinges on balancing mechanical robustness and processing advantages, with Epichlorohydrin preferred for chemical resistance and TPEs for flexibility in wire insulation applications.
Thermal Resistance and Stability
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits excellent thermal resistance, maintaining stability at temperatures up to 150degC, which makes it suitable for wire insulation in high-heat environments. Thermoplastic elastomers typically withstand lower temperature ranges around 120degC but offer superior flexibility and ease of processing. The superior thermal stability of epichlorohydrin rubber ensures long-term insulation performance where consistent heat resistance is critical.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Durability
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance against oils, fuels, and ozone, making it ideal for wire insulation in harsh chemical environments, while thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) offer moderate chemical resistance but excel in flexibility and recyclability. Epichlorohydrin's excellent environmental durability includes resistance to weathering, UV radiation, and low-temperature flexibility, ensuring long-term performance in demanding outdoor applications. Thermoplastic elastomers, though less resistant to aggressive chemicals, provide enhanced environmental sustainability through easy processing and reduced environmental impact during disposal.
Electrical Performance in Wire Insulation
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior electrical insulation properties, including high dielectric strength and excellent resistance to electrical tracking and ozone degradation, making it ideal for wire insulation in harsh environments. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) provide reliable electrical insulation with good flexibility and ease of processing but may exhibit lower dielectric strength and electrical tracking resistance compared to epichlorohydrin rubber. Epichlorohydrin's enhanced electrical performance ensures longer service life and safety in high-voltage and exposed wire applications.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, making it suitable for wire insulation where oil and heat resistance are critical, but it requires curing processes such as vulcanization, which can complicate manufacturing cycles. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) enable faster processing with simpler extrusion methods and recyclability, reducing production costs and allowing for continuous manufacturing without the need for curing. Choosing between these materials depends on production speed, environmental resistance, and post-processing flexibility requirements in wire insulation applications.
Cost and Sustainability Factors
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, but it tends to be more expensive and less environmentally friendly due to its chlorine content and energy-intensive production process. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) provide a cost-effective alternative with easier recyclability and lower environmental impact, supporting circular economy goals. In wire insulation applications, TPEs typically yield lower lifecycle costs and improved sustainability profiles compared to epichlorohydrin rubber.
Applications and Industry Recommendations
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals, making it ideal for automotive and industrial wire insulation exposed to harsh environments. Thermoplastic elastomers provide superior flexibility and ease of processing, preferred in consumer electronics and telecommunications where lightweight, recyclable materials are essential. Industry recommendations favor epichlorohydrin for heavy-duty oilfield and machinery cables, while thermoplastic elastomers dominate applications requiring rapid manufacturing and environmental sustainability.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Thermoplastic elastomer for Wire insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com