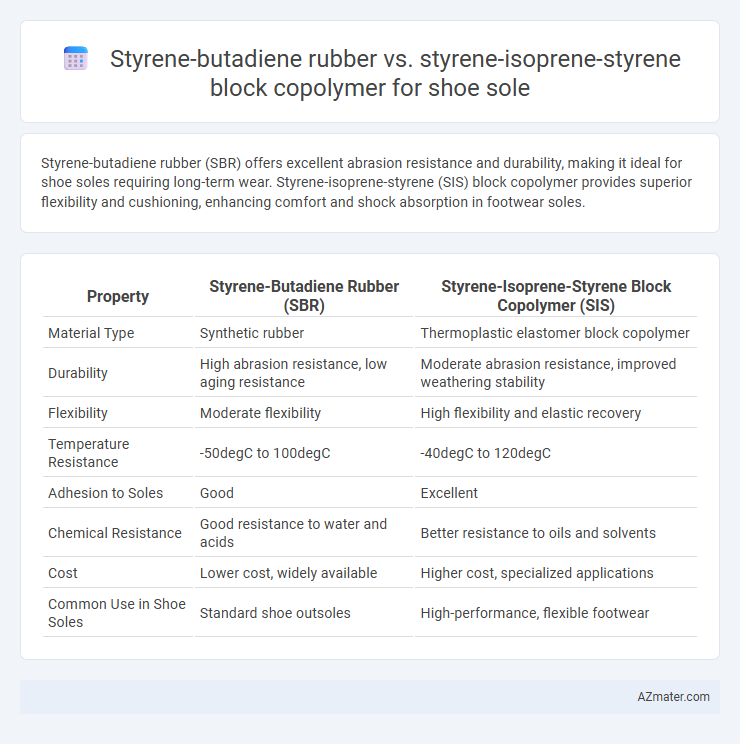
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and durability, making it ideal for shoe soles requiring long-term wear. Styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) block copolymer provides superior flexibility and cushioning, enhancing comfort and shock absorption in footwear soles.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Styrene-Isoprene-Styrene Block Copolymer (SIS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic rubber | Thermoplastic elastomer block copolymer |
| Durability | High abrasion resistance, low aging resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance, improved weathering stability |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility and elastic recovery |
| Temperature Resistance | -50degC to 100degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Adhesion to Soles | Good | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to water and acids | Better resistance to oils and solvents |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, specialized applications |
| Common Use in Shoe Soles | Standard shoe outsoles | High-performance, flexible footwear |
Introduction to Styrene-Butadiene Rubber and Styrene-Isoprene-Styrene
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic copolymer made from styrene and butadiene, known for its excellent abrasion resistance and high durability, making it a popular material for shoe soles requiring strong wear resistance. Styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) block copolymer consists of polystyrene end blocks and a polyisoprene midblock, offering superior elasticity and flexibility compared to SBR, which enhances comfort and flexibility in footwear applications. Both materials contribute distinct mechanical properties, with SBR providing toughness and SIS delivering improved resilience and softness in shoe sole performance.
Key Differences in Chemical Structure
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a copolymer consisting of styrene and butadiene monomers arranged in a random or alternating sequence, providing elasticity and abrasion resistance ideal for shoe soles. Styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) block copolymer features distinct polystyrene end blocks and a mid-block of polyisoprene, resulting in a thermoplastic elastomer with superior flexibility and tensile strength. The key difference lies in SBR's random copolymer structure versus SIS's block architecture, influencing their mechanical properties and performance in footwear applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) exhibits excellent abrasion resistance and good aging stability, making it suitable for durable shoe soles with enhanced wear life. Styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) block copolymer offers superior elasticity and flexibility due to its thermoplastic elastomer structure, resulting in improved cushioning and comfort in footwear applications. While SBR provides higher toughness and resistance to deformation under stress, SIS excels in maintaining shape recovery and resilience, beneficial for high-performance or athletic shoe soles.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent durability and wear resistance due to its high abrasion resistance and strong grip, making it ideal for shoe soles subjected to heavy use. Styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) block copolymer provides enhanced flexibility and cushioning but generally exhibits lower abrasion resistance compared to SBR, affecting long-term durability. For applications demanding maximum wear resistance and toughness, SBR remains the preferred material, while SIS is better suited for comfort-focused footwear with moderate durability requirements.
Flexibility and Comfort for Shoe Soles
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance but tends to be less flexible compared to styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) block copolymers, which provide superior elasticity and softness, enhancing the shoe sole's comfort and flexibility. SIS block copolymer's unique tri-block structure allows better energy return and cushioning, making it ideal for footwear that demands long-term comfort and flexibility. The higher flexibility of SIS contributes to reduced foot fatigue and improved adaptability to various walking surfaces.
Grip and Slip Resistance Performance
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and good slip resistance, making it suitable for durable shoe soles in various conditions. Styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) block copolymer provides enhanced elasticity and superior grip due to its flexible isoprene mid-block, improving traction on wet and smooth surfaces. For optimal grip and slip resistance performance, SIS-based soles deliver greater flexibility and surface contact, while SBR ensures robust wear resistance under heavy use.
Processing and Manufacturability
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent processability for shoe sole manufacturing due to its compatibility with conventional rubber compounding and molding techniques, enabling efficient vulcanization and consistent product quality. Styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) block copolymer exhibits superior elasticity and softness but requires precise temperature control during extrusion and molding, posing challenges for large-scale manufacturability. SBR's established processing parameters and cost-effectiveness make it more suitable for high-volume shoe sole production compared to the more specialized processing demands of SIS block copolymers.
Cost Effectiveness for Footwear Applications
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior cost effectiveness for shoe soles due to its lower raw material price and efficient processing compared to Styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) block copolymer, making it ideal for mass-market footwear production. SBR provides excellent abrasion resistance and wear durability at a fraction of the cost of SIS, which, though offering enhanced elasticity and flexibility, incurs higher expenses limiting its use to premium or specialty shoes. For large-scale manufacturing prioritizing affordability without compromising essential durability, SBR remains the preferred elastomer in footwear applications.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is widely used in shoe soles due to its durability but is derived primarily from non-renewable petrochemical sources, contributing to environmental concerns such as carbon emissions and limited biodegradability. Styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) block copolymer offers potential sustainability benefits through improved elasticity and recyclability, although it remains dependent on fossil fuels and often requires complex synthesis processes that increase its environmental footprint. Advances in bio-based alternatives and recycling methods for both SBR and SIS are critical to enhancing the environmental sustainability of shoe sole materials in the footwear industry.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Material for Shoe Soles
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for durable and budget-friendly shoe soles. Styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) block copolymer provides superior flexibility and resilience, enhancing comfort and shock absorption in high-performance footwear. Selecting the best material depends on balancing durability needs with comfort requirements, where SBR suits heavy-duty applications and SIS favors lightweight, flexible designs.
Infographic: Styrene-butadiene rubber vs Styrene-isoprene-styrene block copolymer for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com