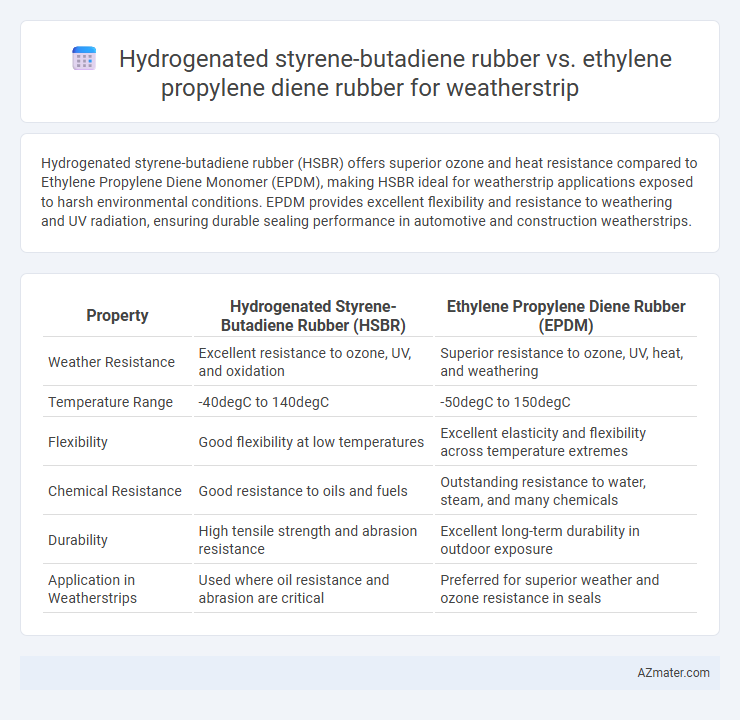
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior ozone and heat resistance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), making HSBR ideal for weatherstrip applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. EPDM provides excellent flexibility and resistance to weathering and UV radiation, ensuring durable sealing performance in automotive and construction weatherstrips.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Weather Resistance | Excellent resistance to ozone, UV, and oxidation | Superior resistance to ozone, UV, heat, and weathering |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 140degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Excellent elasticity and flexibility across temperature extremes |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and fuels | Outstanding resistance to water, steam, and many chemicals |
| Durability | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance | Excellent long-term durability in outdoor exposure |
| Application in Weatherstrips | Used where oil resistance and abrasion are critical | Preferred for superior weather and ozone resistance in seals |
Introduction to Weatherstrip Materials
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and ozone stability, making it highly effective for weatherstrip applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in UV resistance, flexibility at low temperatures, and excellent sealing properties, commonly used in automotive and construction weatherstripping. The choice between HSBR and EPDM depends on specific performance requirements such as durability, elasticity, and resistance to weathering agents.
Overview of Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR)
Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and oxygen, making it ideal for weatherstrip applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. HSBR offers superior mechanical strength and abrasion resistance compared to traditional styrene-butadiene rubber, ensuring durability and long-term performance in sealing automotive doors and windows. Its chemical stability and low compression set contribute to reliable sealing properties, outperforming Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) in demanding industrial weatherstrip applications.
Characteristics of Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) exhibits superior weather resistance, outstanding ozone and UV stability, and excellent flexibility at low temperatures, making it ideal for weatherstrip applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. EPDM's inherent resistance to heat, steam, and various polar chemicals surpasses Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR), ensuring longer service life and durability. Its excellent sealing properties and resistance to aging contribute to enhanced performance in automotive and industrial weatherstripping, maintaining elasticity and preventing leaks over time.
Comparative Weather Resistance: HSBR vs EPDM
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior ozone and oxidative resistance compared to Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), making HSBR more durable in environments with high oxygen exposure. EPDM excels in resistance to heat, UV radiation, and moisture, providing excellent long-term weathering performance for weatherstrips exposed to outdoor conditions. The choice between HSBR and EPDM depends on specific environmental factors, with HSBR preferred for oxidizing atmospheres and EPDM favored for UV and moisture-intensive applications.
Flexibility and Elasticity in Weatherstrip Applications
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior flexibility and higher resistance to heat and ozone degradation compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM), making it ideal for weatherstrip applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. EPDM provides excellent elasticity and maintains its performance in low temperatures, ensuring a tight seal and durability in weatherstrip use. The choice between HSBR and EPDM depends on the specific demands of flexibility, elasticity, and environmental resistance required for the weatherstrip application.
Aging and Ozone Resistance Performance
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) demonstrates superior aging and ozone resistance compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) in weatherstrip applications, maintaining flexibility and mechanical properties under prolonged environmental exposure. EPDM shows excellent ozone resistance due to its saturated backbone but may exhibit slightly reduced performance under extended thermal aging compared to HSBR, which benefits from hydrogenation that enhances oxidative stability. Selecting HSBR for weatherstrips ensures enhanced durability in harsh weather conditions, while EPDM remains a cost-effective option with reliable ozone resistance for moderate aging demands.
Cost Efficiency and Production Considerations
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers higher abrasion resistance and thermal stability, making it cost-efficient for weatherstrips subjected to harsh environments by reducing replacement frequency. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides superior ozone and UV resistance, often favored for outdoor applications despite a slightly higher material cost. Production considerations include HSBR's compatibility with conventional processing equipment and faster curing times, while EPDM may require specific vulcanization conditions, impacting manufacturing efficiency and overall cost.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers improved resistance to ozone and weathering but relies heavily on petrochemical feedstocks, resulting in higher carbon emissions and lower biodegradability compared to Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM). EPDM is favored for weatherstrips due to its superior environmental profile, including excellent resistance to UV, heat, and oxidation, along with enhanced recyclability and longer service life, reducing overall material waste. The sustainability advantage of EPDM stems from its greater durability and lower environmental footprint during production and disposal phases.
Typical Applications for HSBR and EPDM Weatherstrips
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) is commonly used in weatherstrips for automotive and industrial sealing applications due to its excellent abrasion resistance and chemical stability. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) weatherstrips are preferred for outdoor environments because of their superior resistance to UV rays, ozone, and extreme temperatures, making them ideal for window seals, door gaskets, and roofing membranes. HSBR suits environments requiring durability against oils and fuels, while EPDM excels in weather-exposed sealing solutions.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Rubber for Weatherstripping
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance, ozone stability, and heat aging properties, making it ideal for high-durability weatherstripping applications. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in flexibility, UV resistance, and excellent performance in extreme temperature variations, which is critical for outdoor and automotive weatherstrips. Choosing the optimal rubber depends on the specific environmental exposure and mechanical stress, with HSBR favored for durability and EPDM preferred for weather and temperature resilience.
Infographic: Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Weatherstrip
 azmater.com
azmater.com