Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior flexibility, resilience, and oil resistance, making it ideal for dynamic O-ring applications requiring enhanced elasticity. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides exceptional heat, chemical, and abrasion resistance, ensuring durability in high-temperature and aggressive chemical environments.
Table of Comparison
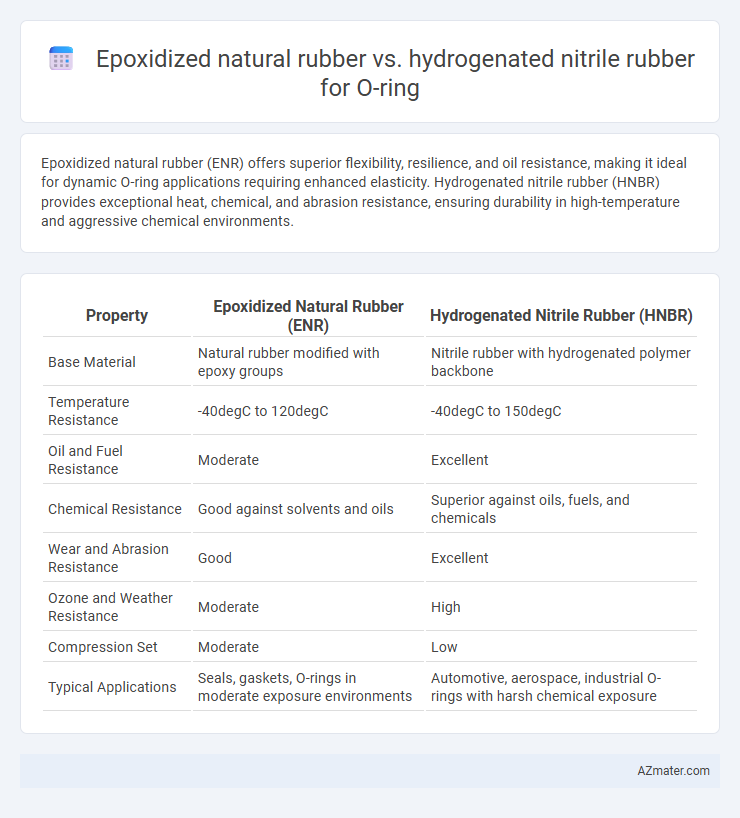
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Base Material | Natural rubber modified with epoxy groups | Nitrile rubber with hydrogenated polymer backbone |
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Oil and Fuel Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against solvents and oils | Superior against oils, fuels, and chemicals |
| Wear and Abrasion Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Compression Set | Moderate | Low |
| Typical Applications | Seals, gaskets, O-rings in moderate exposure environments | Automotive, aerospace, industrial O-rings with harsh chemical exposure |
Introduction to O-Ring Materials
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced oil resistance and improved mechanical properties compared to traditional natural rubber, making it suitable for O-rings used in dynamic sealing applications with moderate chemical exposure. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior heat, ozone, and chemical resistance, particularly in high-temperature environments and aggressive fluids, commonly required for O-rings in automotive and industrial sectors. Selecting between ENR and HNBR depends on specific operational conditions such as temperature range, chemical compatibility, and mechanical performance required for optimal O-ring sealing efficiency.
Overview of Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR)
Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) is a modified form of natural rubber with enhanced oil, ozone, and chemical resistance due to the introduction of epoxide groups in its molecular structure. ENR offers superior elasticity, heat resistance up to 120degC, and improved aging resistance compared to conventional natural rubber, making it suitable for O-ring applications in automotive and industrial seals. Its inherent hydrophilicity and compatibility with polar substances differentiate it from Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR), which excels in high-temperature and chemical resistance but lacks the flexibility of ENR.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) exhibits exceptional chemical resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for demanding O-ring applications in automotive and industrial environments. HNBR retains flexibility at low temperatures and offers superior resistance to oil, fuel, and ozone compared to Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR). Its enhanced durability and resistance to wear and aging extend the service life of O-rings in harsh conditions.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) features epoxy groups introduced into the polyisoprene backbone, enhancing its polarity and improving oil resistance and gas permeability compared to natural rubber. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) possesses a fully hydrogenated nitrile butadiene structure, providing superior heat, ozone, and chemical resistance as well as excellent mechanical strength and compression set properties. ENR offers moderate thermal stability and flexibility, while HNBR excels in high-temperature environments and aggressive chemical exposure, making HNBR more suitable for demanding O-ring applications requiring durability under extreme conditions.
Mechanical Performance Analysis
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior elasticity and enhanced tensile strength compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR), making it well-suited for dynamic O-ring applications requiring flexibility. HNBR exhibits exceptional abrasion resistance, higher hardness, and better compression set properties, providing durability in high-temperature and chemically aggressive environments. Mechanical performance analysis shows ENR balances flexibility with moderate durability, while HNBR excels in maintaining sealing integrity under stress and exposure to oils and chemicals.
Temperature and Environmental Resistance
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers improved ozone and weather resistance compared to conventional natural rubber, maintaining flexibility at temperatures between -40degC and 120degC, making it suitable for moderate thermal applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) excels in high-temperature performance, withstanding continuous exposure up to 150degC and intermittent peaks around 165degC, while also delivering superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and ozone. For O-rings exposed to harsh environmental conditions and elevated temperatures, HNBR provides enhanced durability and longer service life than ENR.
Chemical Compatibility with Fluids and Gases
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) demonstrates excellent chemical compatibility with polar fluids such as alcohols, ketones, and certain oils, making it suitable for O-rings exposed to these media. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to hydrocarbons, fuels, and ozone, providing enhanced durability in aggressive chemical environments involving aliphatic and aromatic fluids. The choice between ENR and HNBR for O-rings often depends on specific fluid types and operating conditions, with ENR favored for polar solvents and HNBR preferred for petroleum-based fluids and high-temperature applications.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) generally offers lower material costs compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) due to its natural origin and simpler processing methods, making it a cost-effective choice for O-ring applications with moderate performance requirements. ENR's availability is often more stable in tropical regions where natural rubber is abundant, whereas HNBR, synthesized through complex hydrogenation of nitrile rubber, may face higher procurement costs and supply variability linked to petrochemical markets. Choosing between ENR and HNBR involves balancing ENR's cost and regional availability advantages against HNBR's superior chemical resistance and extended service life in demanding environments.
Industry Applications and Suitability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers excellent oil and chemical resistance, making it suitable for automotive and industrial O-ring applications where flexibility and durability in harsh environments are required. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior heat, ozone, and abrasion resistance, ideal for high-performance sealing in aerospace, automotive fuel systems, and hydraulic equipment. While ENR is preferred for medium-temperature applications with moderate chemical exposure, HNBR excels in high-temperature environments demanding superior mechanical stability and chemical resistance.
Choosing the Right Material for Your O-Ring Needs
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers excellent flexibility, abrasion resistance, and moderate chemical resistance, making it ideal for dynamic sealing applications in automotive and industrial machinery. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior heat resistance, oil resistance, and mechanical strength, suitable for high-temperature environments and aggressive chemical exposure. Selecting the right O-ring material depends on application-specific factors such as temperature range, fluid compatibility, and mechanical stress requirements.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile rubber for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com