Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat, oil, and abrasion resistance compared to Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO), making HNBR ideal for high-temperature automotive seals. Epichlorohydrin rubber excels in fuel resistance and flexibility at low temperatures but has lower thermal stability than HNBR in demanding engine environments.
Table of Comparison
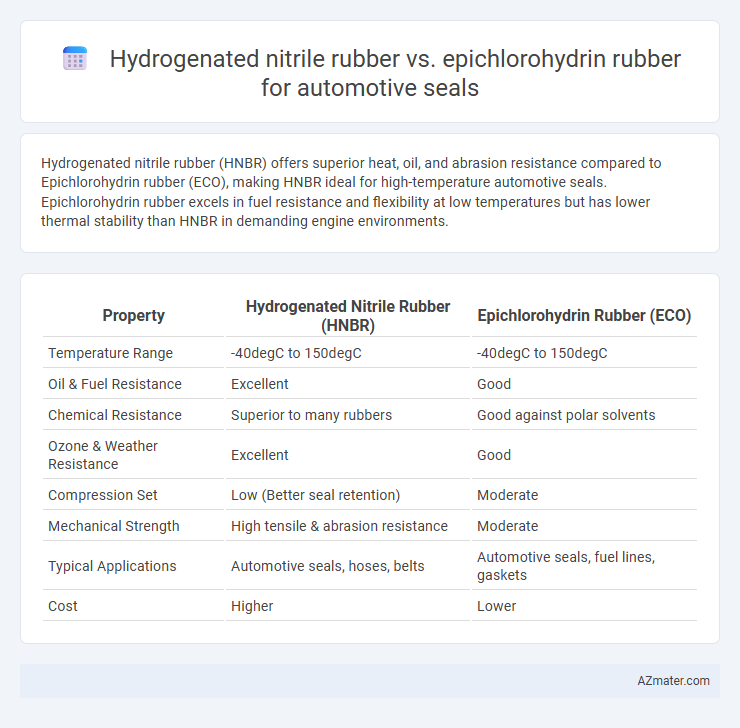
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Oil & Fuel Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Chemical Resistance | Superior to many rubbers | Good against polar solvents |
| Ozone & Weather Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Compression Set | Low (Better seal retention) | Moderate |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile & abrasion resistance | Moderate |
| Typical Applications | Automotive seals, hoses, belts | Automotive seals, fuel lines, gaskets |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Automotive Seal Materials
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers exceptional heat resistance, oil and fuel stability, making it suitable for automotive seals exposed to aggressive fluids and high temperatures. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) provides excellent ozone resistance, flexibility in low temperatures, and good fuel resistance, ideal for sealing applications requiring durability in harsh environmental conditions. The choice between HNBR and ECO depends primarily on the specific chemical exposure, temperature range, and mechanical demands of the automotive sealing application.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals, making it an ideal material for automotive seals exposed to harsh under-the-hood conditions. Its enhanced abrasion resistance and mechanical strength outperform epichlorohydrin rubber, ensuring longer seal life and reliability in fuel system components and engine gaskets. HNBR's broad temperature tolerance ranges from -40degC to 150degC, supporting stable performance in diverse automotive environments.
Overview of Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO)
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers excellent resistance to oil, ozone, and weathering, making it highly suitable for automotive seals exposed to harsh engine environments. Compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR), ECO provides superior low-temperature flexibility and enhanced fuel and lubricant resistance, which is critical for maintaining sealing performance under varied thermal conditions. Its balanced chemical stability and durable mechanical properties ensure reliable sealing in fuel system components and coolant hoses within modern vehicles.
Physical Properties Comparison: HNBR vs ECO
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and thermal stability compared to epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO), making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to high temperatures and aggressive fluids. ECO exhibits excellent low-temperature flexibility and resistance to polar solvents and oils but has lower mechanical strength and wear resistance than HNBR. The choice between HNBR and ECO depends on the specific sealing requirements, with HNBR favored for durability and high-performance applications, while ECO suits environments requiring enhanced chemical resistance and flexibility.
Chemical Resistance: HNBR versus ECO
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) demonstrates superior chemical resistance compared to epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) in automotive seal applications, especially against oils, fuels, and high-temperature fluids. HNBR withstands harsh environments with excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and aging, making it ideal for long-term sealing performance in engine and transmission systems. ECO offers good resistance to ketones, esters, and alcohols but falls short in durability against high-temperature oils and oxidative degradation, limiting its use in more demanding automotive chemical conditions.
Temperature Performance in Automotive Seals
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior temperature resistance, maintaining elasticity and sealing integrity in automotive seals between -40degC and 150degC, making it ideal for high-heat engine environments. Epichlorohydrin rubber (CO) functions effectively within a narrower temperature range of approximately -40degC to 120degC but excels in resistance to oils and fuels. The enhanced thermal stability of HNBR provides longer service life and reliability in dynamic automotive sealing applications exposed to extreme temperature fluctuations.
Wear and Aging Characteristics
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior wear resistance and excellent aging properties, maintaining flexibility and sealing performance under high temperatures and exposure to oils commonly found in automotive environments. Epichlorohydrin rubber (CO) also offers good resistance to oil and fuel but tends to have lower wear resistance and faster degradation under prolonged thermal and oxidative stress. The enhanced molecular saturation of HNBR results in better durability and longer service life for automotive seals compared to epichlorohydrin rubber.
Cost and Processability in Manufacturing
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability for automotive seals but generally incurs higher material costs compared to epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO). ECO provides excellent oil and fuel resistance with a more cost-effective pricing structure, making it favorable for large-scale manufacturing runs. Processability-wise, HNBR requires higher curing temperatures and longer vulcanization cycles, while epichlorohydrin rubber is easier to mold and cure at lower temperatures, enhancing production efficiency.
Typical Automotive Applications for HNBR and ECO
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) is widely used in automotive seals for engine components, such as crankshaft and camshaft seals, due to its exceptional resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion, making it ideal for under-the-hood applications. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) is preferred in automotive air conditioning seals and fuel system components because of its superior resistance to refrigerants, oxygenated fuels, and good low-temperature flexibility. Both materials offer specialized performance tailored to their chemical and thermal resistance needs, with HNBR excelling in durability under high temperatures and ECO providing reliable sealing in refrigerant and fuel environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Automotive Sealing
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and abrasion durability, making it ideal for high-performance automotive seals exposed to extreme temperatures and aggressive fluids. Epichlorohydrin rubber (CO) provides excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and moderate chemical exposure, often preferred for seals in fuel systems and air conditioning components. Selecting between HNBR and Epichlorohydrin depends on the specific operational environment, with HNBR favored for high-temperature, high-stress applications and Epichlorohydrin suited for moderate conditions requiring good oil and ozone resistance.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Epichlorohydrin rubber for Automotive seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com