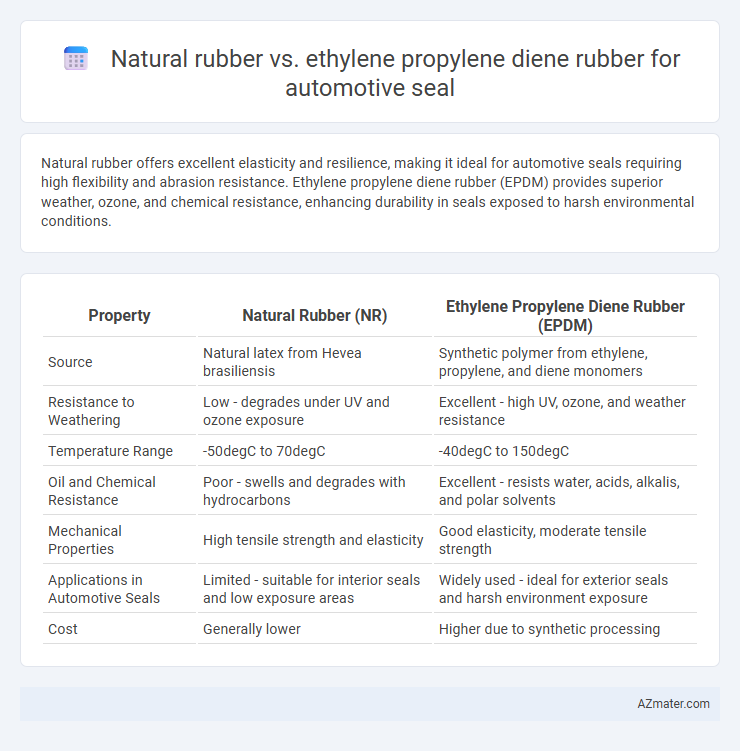
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and resilience, making it ideal for automotive seals requiring high flexibility and abrasion resistance. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides superior weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, enhancing durability in seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Natural Rubber (NR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural latex from Hevea brasiliensis | Synthetic polymer from ethylene, propylene, and diene monomers |
| Resistance to Weathering | Low - degrades under UV and ozone exposure | Excellent - high UV, ozone, and weather resistance |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 70degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Oil and Chemical Resistance | Poor - swells and degrades with hydrocarbons | Excellent - resists water, acids, alkalis, and polar solvents |
| Mechanical Properties | High tensile strength and elasticity | Good elasticity, moderate tensile strength |
| Applications in Automotive Seals | Limited - suitable for interior seals and low exposure areas | Widely used - ideal for exterior seals and harsh environment exposure |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to synthetic processing |
Introduction: Importance of Seal Materials in Automotive Applications
Seal materials in automotive applications must exhibit superior resistance to temperature extremes, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress to prevent fluid leaks and ensure vehicle safety. Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and low-temperature flexibility but is vulnerable to oil and ozone degradation, limiting its effectiveness in modern engines. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides exceptional resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it a preferred choice for automotive seals subjected to harsh environmental conditions.
Overview of Natural Rubber and EPDM Rubber
Natural rubber offers excellent tensile strength, elasticity, and resilience, making it suitable for automotive seals that require high flexibility and resistance to abrasion. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber is valued for its superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and a wide range of temperatures, which enhances the durability and lifespan of automotive seals in harsh environments. Both materials are essential in automotive applications, with natural rubber preferred for mechanical performance and EPDM favored for environmental resistance.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Natural rubber (NR) is primarily composed of cis-1,4-polyisoprene, a hydrocarbon polymer with a high degree of unsaturation in its molecular backbone, which imparts excellent elasticity and tensile strength. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber consists of ethylene, propylene, and a diene comonomer, resulting in a saturated polymer backbone with isolated double bonds that enhance resistance to ozone, weathering, and heat. The chemical structure of EPDM provides superior chemical stability and aging resistance compared to NR, which is more prone to oxidative degradation due to its unsaturated double bonds.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Natural rubber exhibits superior tensile strength and elasticity, making it ideal for automotive seals requiring high flexibility and resistance to dynamic stresses. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering but generally has lower tensile strength compared to natural rubber. EPDM's mechanical properties provide enhanced durability in harsh environmental conditions, while natural rubber excels in applications demanding greater mechanical resilience and flexibility.
Resistance to Weathering and Ozone
Natural rubber demonstrates excellent flexibility and mechanical properties but suffers from poor resistance to weathering and ozone, leading to cracking and degradation in automotive seals exposed to harsh environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers superior resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering, maintaining elasticity and durability in outdoor and high-temperature conditions typical for automotive seals. EPDM's molecular structure provides enhanced protection against oxidative aging, making it the preferred choice for long-lasting automotive sealing applications.
Performance in High and Low Temperature Environments
Natural rubber demonstrates excellent elasticity and flexibility at low temperatures, maintaining effective sealing performance down to approximately -50degC, while its performance deteriorates above 70degC due to oxidation and heat aging. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) exhibits superior thermal stability, operating efficiently in a broad temperature range from -50degC to 150degC, resisting heat, ozone, and weathering degradation. EPDM's enhanced resistance to high-temperature aging and its strong sealing capabilities under extreme thermal cycling make it preferred for automotive seals exposed to varying environmental conditions.
Compatibility with Automotive Fluids
Natural rubber (NR) exhibits excellent compatibility with a wide range of automotive fluids, including gasoline, motor oils, and hydraulic fluids, making it suitable for sealing applications exposed to these substances. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber shows superior resistance to polar fluids such as antifreeze, brake fluids, and water-based solutions, but it can swell or degrade when exposed to petroleum-based oils and fuels. Selecting the appropriate elastomer depends on the specific automotive fluid exposure, with NR preferred for hydrocarbon fluids and EPDM favored for glycol-based and aqueous environments.
Durability and Service Life in Automotive Seals
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and resilience, making it suitable for automotive seals exposed to dynamic motion and moderate temperatures, but it degrades faster under ozone and oil exposure, limiting its durability. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides superior resistance to heat, ozone, weathering, and automotive fluids, significantly enhancing the service life of seals in harsh environments. EPDM's excellent aging properties and chemical stability make it the preferred choice for automotive sealing applications requiring long-term durability and reliability.
Cost Implications and Production Considerations
Natural rubber offers lower raw material costs compared to ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it a cost-effective choice for automotive seals in high-volume production. EPDM, however, demands higher processing temperatures and more specialized mixing equipment, which can increase production expenses but yields superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and heat. Choosing between natural rubber and EPDM depends on balancing initial material costs against long-term durability requirements and manufacturing capabilities in automotive sealing applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Automotive Seals
Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility, high tensile strength, and superior resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to dynamic stress and low temperatures. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in resistance to heat, ozone, weathering, and chemical degradation, providing longer-lasting seals in under-hood and exterior applications. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific operating conditions: natural rubber suits dynamic, low-temperature environments, while EPDM is preferable for high-temperature and chemical exposure scenarios.
Infographic: Natural rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Automotive seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com