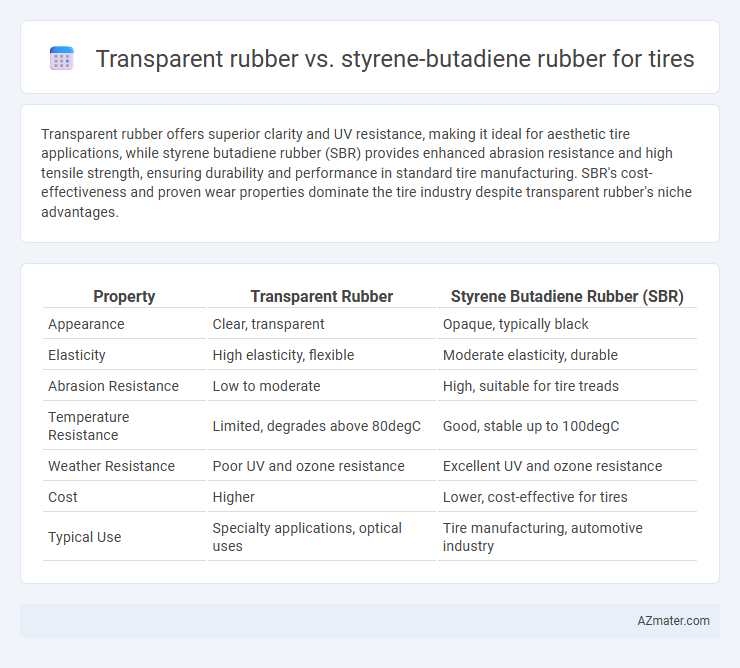
Transparent rubber offers superior clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for aesthetic tire applications, while styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides enhanced abrasion resistance and high tensile strength, ensuring durability and performance in standard tire manufacturing. SBR's cost-effectiveness and proven wear properties dominate the tire industry despite transparent rubber's niche advantages.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Transparent Rubber | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear, transparent | Opaque, typically black |
| Elasticity | High elasticity, flexible | Moderate elasticity, durable |
| Abrasion Resistance | Low to moderate | High, suitable for tire treads |
| Temperature Resistance | Limited, degrades above 80degC | Good, stable up to 100degC |
| Weather Resistance | Poor UV and ozone resistance | Excellent UV and ozone resistance |
| Cost | Higher | Lower, cost-effective for tires |
| Typical Use | Specialty applications, optical uses | Tire manufacturing, automotive industry |
Introduction to Tire Rubber Materials
Transparent rubber, often made from silicone or polyurethane, offers superior clarity and flexibility but lacks the abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness of styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), which dominates tire manufacturing due to its excellent wear resistance, good aging stability, and affordability. SBR's unique copolymer structure combines styrene's strength and butadiene's flexibility, making it ideal for withstanding the harsh conditions tires encounter. While transparent rubber excels in niche applications requiring visibility and elasticity, SBR remains the industry standard for high-performance and durable tire tread compounds.
What is Transparent Rubber?
Transparent rubber, often made from specialized formulations such as silicone or certain synthetic rubbers, offers high clarity and UV resistance, distinguishing it from the opaque Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) commonly used in tire manufacturing. Unlike SBR, which provides excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability combined with cost-effectiveness for tire treads, transparent rubber is primarily utilized in applications requiring visibility and flexibility rather than mechanical strength. The transparent rubber's unique optical properties make it suitable for niche automotive components like sensor housings or decorative elements, rather than the structural demands of tire construction.
Understanding Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic polymer widely used in tire manufacturing due to its excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability, making it essential for durable and high-performance tires. Compared to transparent rubber, SBR offers superior mechanical strength and resilience under varying temperature conditions, contributing to enhanced tire longevity and safety. Its balanced combination of styrene and butadiene monomers optimizes resistance to wear, heat, and oxidation, which are critical factors in tire tread compounds.
Physical Properties Comparison
Transparent rubber exhibits lower tensile strength and elasticity compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), which typically offers superior abrasion resistance and durability crucial for tire performance. SBR's higher resilience and better wear resistance enhance tire lifespan and traction under various road conditions. The physical hardness of Transparent rubber is generally less than that of SBR, making it less ideal for heavy-duty tire applications.
Transparency and Aesthetic Benefits
Transparent rubber offers superior clarity compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for aesthetic applications where visibility through the tire material is desired. Unlike the opaque and black appearance of SBR, transparent rubber allows for innovative tire designs with embedded graphics or lighting effects, enhancing visual appeal. This transparency also enables the integration of smart technologies, such as embedded sensors, without compromising the tire's look or performance.
Performance and Durability in Tires
Transparent rubber offers superior visual inspection capabilities but generally lacks the abrasion resistance and tensile strength of Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), which is a standard material in tire manufacturing due to its excellent wear resistance and aging stability. SBR enhances tire durability and performance by providing higher resistance to heat, oxidation, and mechanical stress, making it suitable for long-lasting, high-performance tires. While transparent rubber may be beneficial for niche applications requiring visibility, SBR remains the preferred choice for maximizing tire lifespan and overall road safety.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Transparent rubber, typically a type of silicone or clear polyurethane, offers enhanced recyclability due to its homogeneous polymer structure, reducing environmental waste compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), a synthetic polymer derived from petrochemicals. SBR production releases significant greenhouse gases and relies heavily on non-renewable resources, contributing to environmental pollution and resource depletion. Transparent rubbers often incorporate eco-friendly formulations and can be more easily reprocessed, promoting sustainability in tire manufacturing.
Cost Analysis: Transparent Rubber vs SBR
Transparent rubber typically incurs higher production costs than styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) due to specialized raw materials and complex processing techniques. SBR remains more cost-effective, benefiting from large-scale manufacturing and widespread availability of styrene and butadiene monomers. For tire applications, SBR offers better price-performance balance, making it the preferred choice in cost-sensitive markets.
Current Applications and Market Trends
Transparent rubber, primarily used in specialty tire applications and niche markets, offers unique aesthetic qualities and moderate performance but remains limited by higher costs and lower abrasion resistance compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR). Styrene butadiene rubber dominates the tire industry due to its excellent wear resistance, cost-effectiveness, and strong balance of mechanical properties, making it the preferred choice for passenger car and truck tires, accounting for over 50% of global synthetic rubber consumption. Market trends indicate increasing demand for SBR in eco-friendly and fuel-efficient tire formulations, while transparent rubber sees growth mainly in research-driven and customized tire segments.
Future Prospects for Tire Manufacturing
Transparent rubber offers potential for innovative tire designs by enabling enhanced visual inspection and integration of sensors, paving the way for smart tires with improved safety features. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) remains dominant due to its superior wear resistance, cost-effectiveness, and well-established performance in tire manufacturing. Future prospects suggest a hybrid approach where transparent rubber components complement SBR formulations to create tires that balance transparency-enabled technology with durability and performance.
Infographic: Transparent rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com