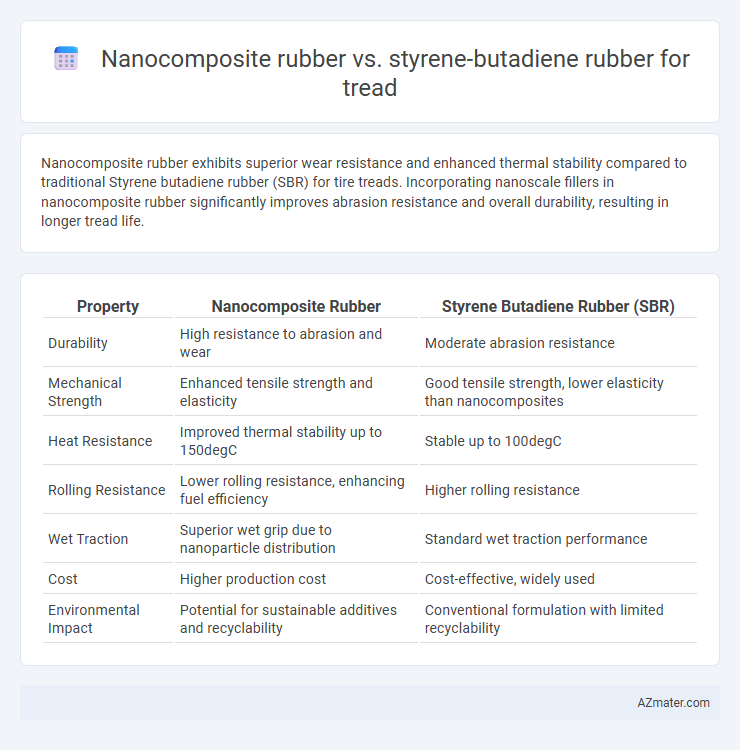
Nanocomposite rubber exhibits superior wear resistance and enhanced thermal stability compared to traditional Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) for tire treads. Incorporating nanoscale fillers in nanocomposite rubber significantly improves abrasion resistance and overall durability, resulting in longer tread life.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanocomposite Rubber | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to abrasion and wear | Moderate abrasion resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | Enhanced tensile strength and elasticity | Good tensile strength, lower elasticity than nanocomposites |
| Heat Resistance | Improved thermal stability up to 150degC | Stable up to 100degC |
| Rolling Resistance | Lower rolling resistance, enhancing fuel efficiency | Higher rolling resistance |
| Wet Traction | Superior wet grip due to nanoparticle distribution | Standard wet traction performance |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Cost-effective, widely used |
| Environmental Impact | Potential for sustainable additives and recyclability | Conventional formulation with limited recyclability |
Introduction to Tire Tread Materials
Nanocomposite rubber enhances tire tread performance by incorporating nanoscale fillers into the polymer matrix, improving wear resistance, traction, and durability compared to conventional Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR). SBR, a widely used synthetic rubber in tire treads, offers balanced properties of abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but lacks the advanced mechanical reinforcement provided by nanofillers. The integration of nanocomposites in tire treads represents a significant advancement, optimizing material properties for safer and longer-lasting tires.
Overview of Nanocomposite Rubber
Nanocomposite rubber for tread applications incorporates nanoscale fillers such as silica or carbon nanotubes, enhancing mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and thermal stability compared to traditional styrene butadiene rubber (SBR). The uniform dispersion of nanoparticles within the rubber matrix improves wear resistance and wet traction, making nanocomposite rubber a superior choice for high-performance tire treads. These advanced materials exhibit reduced rolling resistance, contributing to better fuel efficiency and longer tread life in automotive tires.
Understanding Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic polymer widely used in tire treads due to its excellent abrasion resistance, aging stability, and affordability. SBR's balanced composition of styrene and butadiene monomers provides improved wear resistance and traction compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for high-performance tire applications. In contrast, nanocomposite rubber incorporates nanoscale fillers like silica or carbon nanotubes to enhance mechanical properties, thermal stability, and durability beyond those achievable with conventional SBR formulations.
Comparative Mechanical Properties
Nanocomposite rubber exhibits superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to traditional Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), making it more durable for tire treads. The incorporation of nanoscale fillers enhances the modulus and tear resistance, resulting in improved wear performance under high-stress conditions. SBR, while offering good elasticity and cost-effectiveness, generally falls short in mechanical robustness and longevity relative to nanocomposite formulations.
Rolling Resistance and Fuel Efficiency
Nanocomposite rubber enhances tread performance by significantly reducing rolling resistance compared to styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), resulting in better fuel efficiency for vehicles. The incorporation of nano-fillers in nanocomposite rubber improves the polymer matrix, leading to lower energy loss during tire deformation. This technology supports longer driving ranges and reduced emissions by optimizing tire tread materials for efficient road contact and durability.
Wet and Dry Traction Performance
Nanocomposite rubber exhibits superior wet and dry traction performance compared to traditional Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) due to its enhanced filler dispersion and improved polymer-filler interaction. The inclusion of nanofillers in nanocomposite rubber increases the compound's tensile strength and abrasion resistance, leading to better grip on both wet and dry road surfaces. SBR typically offers good durability but falls short in providing the same level of traction performance achieved by nanocomposite-enhanced compounds.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance
Nanocomposite rubber exhibits superior abrasion and wear resistance compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) for tread applications, due to its enhanced filler dispersion and improved polymer-filler interaction. The incorporation of nanoscale fillers in nanocomposite rubber increases the hardness and reduces the rate of material loss under high-friction conditions. SBR, while widely used for its good balance of performance and cost, typically shows higher wear rates in comparison, limiting its durability on high-stress tread surfaces.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanocomposite rubber enhances tread performance with improved durability and reduced material consumption, leading to lower environmental impact compared to traditional styrene butadiene rubber (SBR). The incorporation of nanomaterials in nanocomposite rubber reduces rolling resistance and fuel consumption, contributing to better sustainability metrics. SBR, derived primarily from petrochemicals, generally exhibits higher carbon emissions and less efficient recyclability, making nanocomposite rubber a more eco-friendly alternative for sustainable tire production.
Cost Considerations and Market Availability
Nanocomposite rubber offers enhanced performance properties for tire treads but typically incurs higher production costs compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), which remains cost-effective due to established manufacturing processes and raw material availability. SBR dominates the market with widespread availability and affordability, making it the preferred choice for mass-produced tires, whereas nanocomposite rubbers are often reserved for premium or specialized applications due to limited large-scale supply chains. Cost considerations heavily favor SBR in commercial tire production, while nanocomposite rubber's higher expense is justified by improved durability and wear resistance in niche markets.
Future Trends in Tread Material Technology
Nanocomposite rubber enhances tread performance by integrating nanoscale fillers that improve abrasion resistance, traction, and durability compared to traditional Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR). Emerging trends focus on optimizing nanofiller dispersion and hybrid formulations to achieve superior wear characteristics while maintaining flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Future tread materials will increasingly leverage advanced nanocomposite technologies for enhanced safety, fuel efficiency, and environmental sustainability in tire manufacturing.
Infographic: Nanocomposite rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Tread
 azmater.com
azmater.com