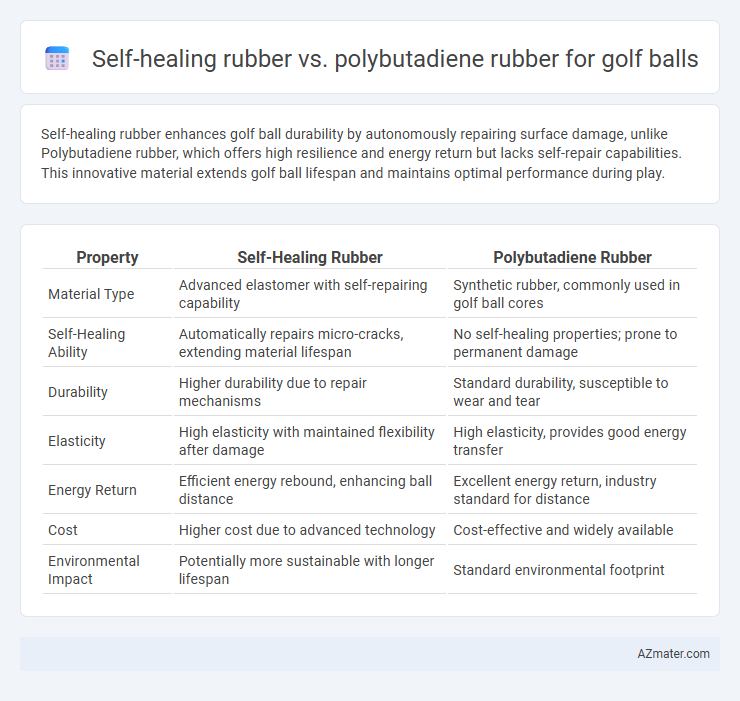
Self-healing rubber enhances golf ball durability by autonomously repairing surface damage, unlike Polybutadiene rubber, which offers high resilience and energy return but lacks self-repair capabilities. This innovative material extends golf ball lifespan and maintains optimal performance during play.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Self-Healing Rubber | Polybutadiene Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Advanced elastomer with self-repairing capability | Synthetic rubber, commonly used in golf ball cores |
| Self-Healing Ability | Automatically repairs micro-cracks, extending material lifespan | No self-healing properties; prone to permanent damage |
| Durability | Higher durability due to repair mechanisms | Standard durability, susceptible to wear and tear |
| Elasticity | High elasticity with maintained flexibility after damage | High elasticity, provides good energy transfer |
| Energy Return | Efficient energy rebound, enhancing ball distance | Excellent energy return, industry standard for distance |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced technology | Cost-effective and widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially more sustainable with longer lifespan | Standard environmental footprint |
Introduction to Golf Ball Materials
Self-healing rubber offers enhanced durability and longevity for golf balls by automatically repairing micro-cracks, contrasting with traditional polybutadiene rubber known for its high resilience and energy return. Polybutadiene rubber, the standard core material, delivers optimal distance through superior compression and rebound properties, while self-healing rubber aims to extend the lifespan of the ball under repetitive impact conditions. Innovations in self-healing additives integrated into golf ball cores could revolutionize performance maintenance, reducing frequent replacements common with conventional polybutadiene-based designs.
Overview of Self-Healing Rubber
Self-healing rubber offers advanced molecular networks that restore integrity after damage, enhancing durability and lifespan in golf balls compared to traditional polybutadiene rubber. Unlike polybutadiene, which relies on its excellent rebound resilience but suffers permanent damage upon cracking, self-healing rubber incorporates reversible bonds or microcapsules that autonomously repair micro-tears. This innovation improves performance consistency and reduces the frequency of golf ball replacement, making it a promising material for premium golf ball construction.
Properties of Polybutadiene Rubber
Polybutadiene rubber exhibits exceptional resilience and abrasion resistance, making it the preferred material for golf ball cores to enhance durability and energy transfer during impact. Its low heat buildup and excellent elasticity contribute to superior distance and ball control, outperforming many self-healing rubber variants. The high molecular weight and cis-1,4 content in polybutadiene also provide enhanced tensile strength and rebound resilience critical for optimal golf ball performance.
Durability Comparison
Self-healing rubber in golf balls offers enhanced durability by automatically repairing microcracks and surface damage, extending the ball's lifespan compared to traditional polybutadiene rubber. Polybutadiene rubber, though durable due to its high resilience and impact resistance, lacks the self-repairing capability, making it more prone to degradation over repeated use. The integration of self-healing polymers significantly improves the durability of golf balls, maintaining performance and structural integrity under extensive play conditions.
Impact on Golf Ball Performance
Self-healing rubber enhances golf ball performance by improving durability and maintaining consistent compression after repeated impacts, leading to longer-lasting distance and feel. Polybutadiene rubber is widely used in golf ball cores for its high resilience and energy return, providing optimal initial velocity and distance. However, self-healing rubber offers superior damage resistance, reducing performance degradation from impact-induced micro-cracks that typically occur in polybutadiene cores.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Self-healing rubber in golf balls offers potential long-term durability benefits but comes with higher raw material and processing costs compared to traditional polybutadiene rubber, which is favored for its cost-effectiveness and established manufacturing protocols. Polybutadiene rubber is widely used due to its excellent resilience and compatibility with existing molding and curing techniques, significantly lowering production expenses. Manufacturers must weigh the premium investment in self-healing rubber technology against the proven economic efficiency and scalability of polybutadiene for mass production.
Environmental Sustainability
Self-healing rubber enhances the environmental sustainability of golf balls by extending their lifespan and reducing waste compared to traditional Polybutadiene rubber, which often degrades and requires more frequent replacement. The self-healing capabilities minimize the need for manufacturing new balls, lowering raw material consumption and carbon emissions associated with production. Polybutadiene rubber, while durable, lacks intrinsic repair properties, resulting in higher ecological footprints throughout the golf ball lifecycle.
Market Trends and Adoption
The self-healing rubber market for golf balls is gaining traction as manufacturers seek innovative materials that enhance durability and performance, with industry reports projecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 8% through 2028. Polybutadiene rubber remains dominant due to its superior resilience and cost-effectiveness, capturing a significant share of the golf ball core material market. Emerging adoption of self-healing rubber technology is driven by consumer demand for longer-lasting golf balls, signaling a gradual shift in market preferences toward advanced polymer composites.
Pros and Cons: Self-Healing vs Polybutadiene Rubber
Self-healing rubber in golf balls offers enhanced durability by automatically repairing micro-cracks, extending the ball's lifespan and maintaining performance consistency during play. Polybutadiene rubber provides superior resilience and high energy return, resulting in greater distance and control, but it is prone to damage accumulation and wear over time. While self-healing rubber improves longevity and reduces replacement frequency, polybutadiene remains preferred for competitive play due to its proven performance benefits despite lower durability.
Future Innovations in Golf Ball Technology
Self-healing rubber offers significant advancements in golf ball durability and performance by enabling micro-crack repair, extending ball lifespan, and maintaining consistent playability over time. Polybutadiene rubber, known for its high resilience and energy return, remains a staple in golf ball cores but lacks the self-repairing properties that future innovations demand. Integrating self-healing polymers with polybutadiene matrices represents a promising direction for next-generation golf balls, combining enhanced energy efficiency with improved durability for superior player experience.
Infographic: Self-healing rubber vs Polybutadiene rubber for Golf ball
 azmater.com
azmater.com