Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior wear resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for rollers in harsh industrial environments. Polyurethane rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, preferred for rollers requiring high durability and flexibility under heavy loads.
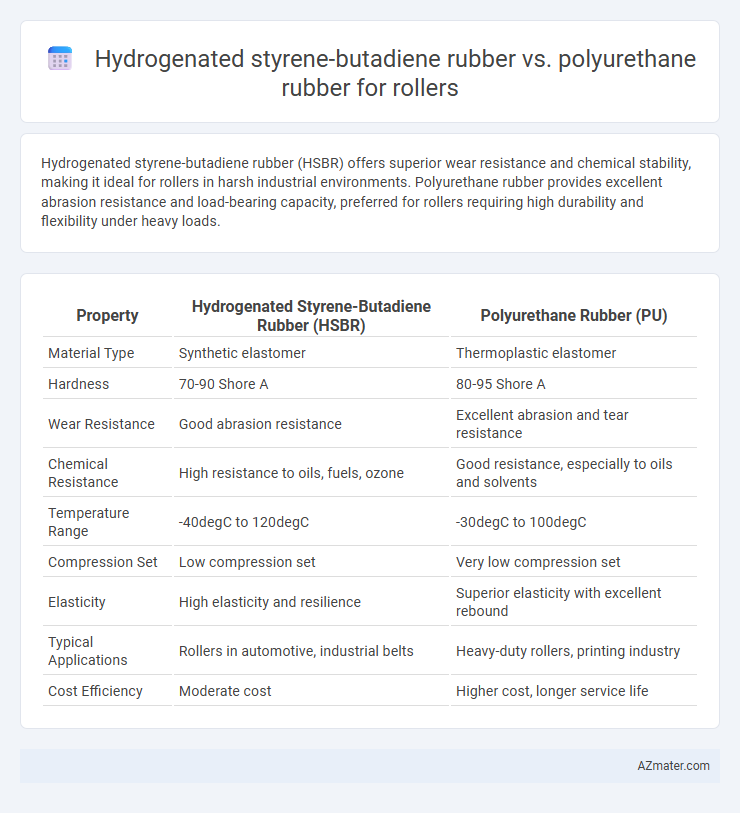
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic elastomer | Thermoplastic elastomer |
| Hardness | 70-90 Shore A | 80-95 Shore A |
| Wear Resistance | Good abrasion resistance | Excellent abrasion and tear resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to oils, fuels, ozone | Good resistance, especially to oils and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -30degC to 100degC |
| Compression Set | Low compression set | Very low compression set |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and resilience | Superior elasticity with excellent rebound |
| Typical Applications | Rollers in automotive, industrial belts | Heavy-duty rollers, printing industry |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate cost | Higher cost, longer service life |
Introduction to Roller Materials
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers exceptional resistance to heat, abrasion, and oil, making it ideal for rollers in demanding industrial applications requiring durability and chemical stability. Polyurethane rubber provides superior elasticity, high load-bearing capacity, and excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for rollers subjected to heavy mechanical stress and impact. Selecting between HSBR and polyurethane rollers depends on specific operational needs such as temperature exposure, load conditions, and desired lifespan.
Overview of Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR)
Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior heat resistance, ozone, and chemical stability compared to traditional SBR, making it ideal for high-performance roller applications in industrial settings. Its hydrogenation process reduces unsaturation in the polymer backbone, enhancing durability and extending service life under harsh operating conditions. HSBR's excellent elasticity and wear resistance provide consistent roller performance, especially in demanding environments requiring resistance to oxidation and oil exposure.
Overview of Polyurethane Rubber
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and resilience compared to hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber, making it ideal for rollers subjected to heavy wear and tear. Its excellent load-bearing capacity and chemical resistance ensure prolonged service life in demanding industrial applications. The material's flexibility and ability to maintain performance under varying temperatures enhance roller efficiency and durability.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and thermal stability compared to polyurethane rubber, making it ideal for high-wear roller applications in harsh environments. Polyurethane rubber exhibits higher tensile strength and better elasticity, providing enhanced load-bearing capacity and impact resistance in rollers subjected to dynamic stresses. The choice between HSBR and polyurethane depends on the specific mechanical demands, with HSBR excelling in durability and heat resistance, while polyurethane delivers improved flexibility and mechanical resilience.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers moderate abrasion resistance with improved chemical stability compared to non-hydrogenated variants, making it suitable for rollers subjected to moderate wear conditions. Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior abrasion and wear resistance due to its high tensile strength and elasticity, often outperforming HSBR in applications demanding prolonged durability and resistance to surface degradation. For roller applications requiring high abrasion resistance and extended service life, polyurethane rubber is typically the preferred material over hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior chemical resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone compared to polyurethane rubber, making it ideal for rollers exposed to harsh industrial chemicals. Polyurethane rubber offers excellent abrasion resistance and mechanical strength but is more susceptible to degradation by hydrocarbons and certain solvents. Environmental resistance is higher in HSBR under oxidative and thermal stress, whereas polyurethane performs better in applications requiring flexibility and resistance to physical wear.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) typically offers a lower initial cost compared to polyurethane rubber, making it a cost-effective choice for roller applications with moderate wear requirements. Polyurethane rubber, while more expensive upfront, provides superior abrasion resistance and longevity, reducing total lifecycle expenses through less frequent replacements and maintenance. Economic considerations should balance HSBR's affordability against polyurethane's enhanced durability, which can lead to lower long-term operational costs in demanding environments.
Applications in Industrial Rollers
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance, heat stability, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for industrial rollers in environments with high friction and moderate chemical exposure. Polyurethane rubber provides superior load-bearing capacity, elasticity, and resistance to oils and solvents, excelling in heavy-duty roller applications requiring enhanced durability and precision. Industrial rollers utilizing HSBR are often deployed in printing, packaging, and paper industries, while polyurethane rubber rollers are preferred in steel processing, heavy machinery, and conveyor systems.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers a longer lifespan for rollers due to its enhanced abrasion resistance and superior chemical stability compared to polyurethane rubber, which tends to wear faster under intense mechanical stress. Polyurethane rubber requires more frequent maintenance because it is more susceptible to hydrolysis and surface degradation, especially in harsh environments involving oils and solvents. The improved durability of HSBR minimizes downtime and replacement costs, making it a cost-effective choice for applications demanding high longevity and low upkeep.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Rollers
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for applications requiring durability in harsh environments. Polyurethane rubber delivers excellent load-bearing capacity and elasticity, providing enhanced resilience under heavy mechanical stress. Selecting the right roller material depends on operational demands: HSBR suits chemical exposure and longevity, while polyurethane excels in impact resistance and flexibility.
Infographic: Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Roller
 azmater.com
azmater.com