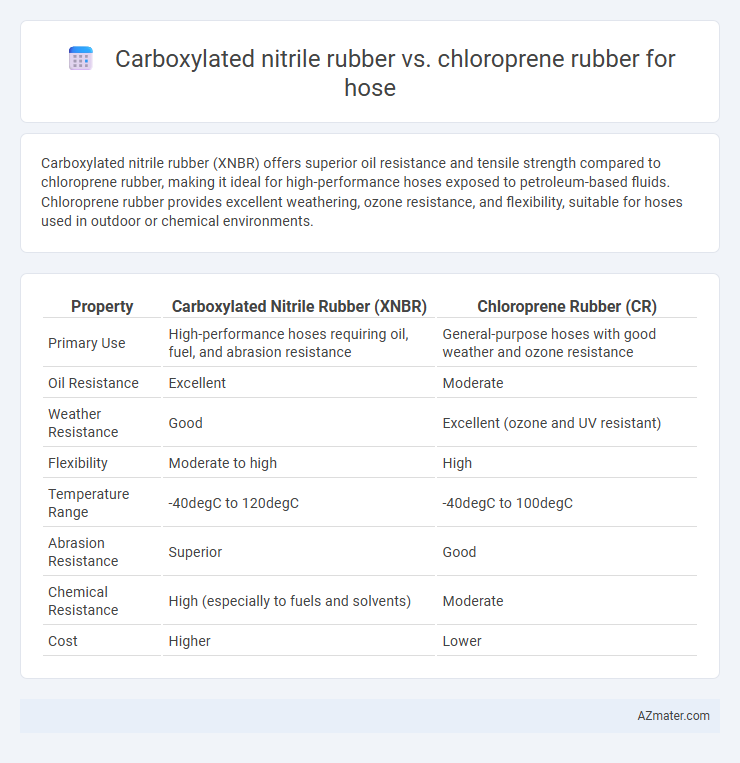
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance and tensile strength compared to chloroprene rubber, making it ideal for high-performance hoses exposed to petroleum-based fluids. Chloroprene rubber provides excellent weathering, ozone resistance, and flexibility, suitable for hoses used in outdoor or chemical environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | High-performance hoses requiring oil, fuel, and abrasion resistance | General-purpose hoses with good weather and ozone resistance |
| Oil Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Weather Resistance | Good | Excellent (ozone and UV resistant) |
| Flexibility | Moderate to high | High |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 100degC |
| Abrasion Resistance | Superior | Good |
| Chemical Resistance | High (especially to fuels and solvents) | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber and Chloroprene Rubber
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) is a high-performance elastomer known for its enhanced tensile strength, oil resistance, and improved adhesion due to carboxyl group modifications in its polymer structure. Chloroprene rubber (CR), also referred to as neoprene, offers exceptional resistance to weathering, ozone, chemicals, and moderate oil and heat exposure, making it suitable for diverse industrial hose applications. Both materials provide unique advantages in hose manufacturing, with XNBR excelling in dynamic oil resistance and CR delivering superior durability against environmental degradation.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) contains carboxyl groups (-COOH) chemically bonded to the nitrile polymer backbone, enhancing its adhesion, oil resistance, and mechanical strength compared to standard nitrile rubber. Chloroprene rubber (CR) is a polychloroprene polymer characterized by chlorine atoms along its polymer chain, providing superior weather, ozone, and flame resistance. The presence of carboxyl groups in XNBR facilitates ionic cross-linking, improving durability in hydraulic hoses, while chloroprene's chlorinated structure contributes to its flexibility and resilience in harsh environmental conditions.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior abrasion resistance, tensile strength ranging from 15 to 30 MPa, and enhanced oil and chemical resistance compared to chloroprene rubber, which typically has tensile strength between 8 and 20 MPa. Chloroprene rubber offers better weathering and ozone resistance with elongation at break around 400%, while XNBR provides higher hardness values of 60-80 Shore A and improved permeability resistance. Both materials are suitable for hose applications, but XNBR is preferred for high-performance environments requiring enhanced mechanical properties and chemical stability.
Oil and Chemical Resistance Performance
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance and excellent chemical stability, making it ideal for hoses exposed to fuel, oils, and various aggressive chemicals. Chloroprene rubber (CR) provides good resistance to ozone, weathering, and moderate oil exposure but falls short compared to XNBR in prolonged contact with petroleum-based fluids. For applications requiring enhanced performance against hydrocarbon oils and harsh chemicals, XNBR is the preferred material due to its enhanced cross-linking and polar carboxyl groups.
Temperature Resistance and Thermal Stability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior temperature resistance, typically enduring continuous use temperatures up to 125degC, with improved resistance to heat aging and ozone compared to standard nitrile rubber. Chloroprene rubber (CR) maintains thermal stability at temperatures up to 100degC, showing excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and flame, making it suitable for moderate temperature hose applications. For high-temperature hose environments requiring enhanced thermal stability, carboxylated nitrile rubber provides a more robust performance profile than chloroprene rubber.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior mechanical strength and abrasion resistance compared to chloroprene rubber (CR), making it ideal for high-pressure hose applications. XNBR exhibits enhanced tensile strength, tear resistance, and durability in harsh environments, including exposure to oils and chemicals. Chloroprene rubber provides good weathering and ozone resistance but generally falls short in mechanical robustness and long-term wear resistance relative to carboxylated nitrile rubber.
Flexibility and Elasticity in Hose Applications
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior flexibility and enhanced elasticity compared to chloroprene rubber (CR), making it ideal for dynamic hose applications requiring repeated bending and stretching. XNBR exhibits higher tensile strength and better resistance to abrasion, which improves hose durability without compromising flexibility. In contrast, chloroprene rubber provides good overall elasticity but tends to have lower tensile strength, limiting its performance in highly flexible or elastic hose environments.
Cost Considerations and Economic Factors
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and abrasion durability compared to chloroprene rubber, making it cost-effective for hoses exposed to harsh environments despite a higher initial price. Chloroprene rubber (CR) provides a more economical option with balanced resistance to weathering and flexibility, suitable for less demanding applications to reduce overall expense. Evaluating hose lifecycle costs emphasizes XNBR's long-term savings through extended service intervals versus CR's lower upfront material costs.
Typical Applications in Hose Manufacturing
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) is ideal for fuel and oil hoses due to its superior abrasion resistance, oil retention, and improved mechanical properties under harsh conditions. Chloroprene rubber (CR) is commonly used in coolant and air hoses because of its excellent weathering resistance, flame retardance, and good flexibility at low temperatures. Hose manufacturers select XNBR for applications requiring enhanced durability against oils and fuels, while CR is preferred for hoses exposed to ozone, sunlight, and moderate chemical exposure.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Specific Hose Needs
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil, fuel, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for hoses exposed to harsh chemicals and heavy mechanical wear. Chloroprene rubber (CR) excels in ozone, weather, and flame resistance, suitable for outdoor or high-temperature hose applications. Selecting the right rubber depends on the hose's operational environment and required durability, balancing chemical compatibility and environmental exposure.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Chloroprene rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com