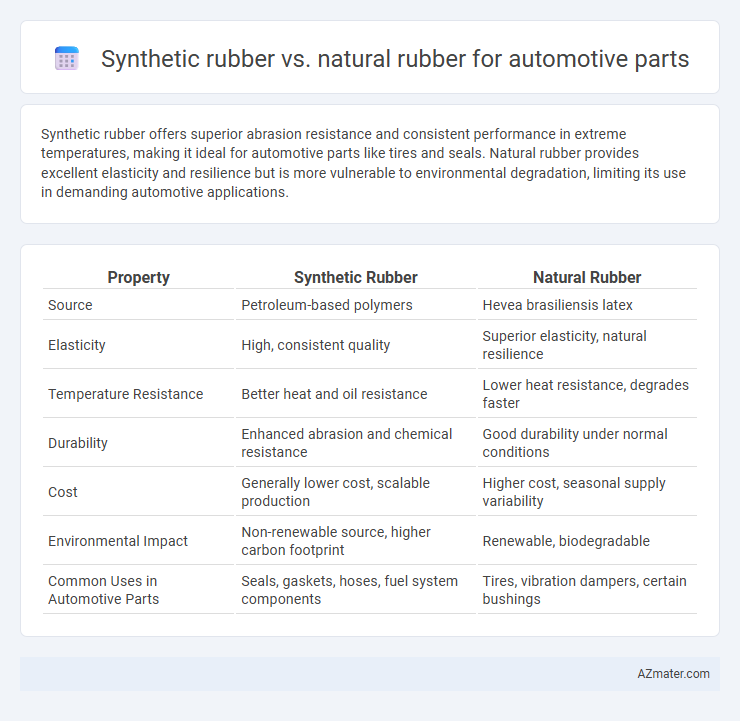
Synthetic rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and consistent performance in extreme temperatures, making it ideal for automotive parts like tires and seals. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and resilience but is more vulnerable to environmental degradation, limiting its use in demanding automotive applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Synthetic Rubber | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Petroleum-based polymers | Hevea brasiliensis latex |
| Elasticity | High, consistent quality | Superior elasticity, natural resilience |
| Temperature Resistance | Better heat and oil resistance | Lower heat resistance, degrades faster |
| Durability | Enhanced abrasion and chemical resistance | Good durability under normal conditions |
| Cost | Generally lower cost, scalable production | Higher cost, seasonal supply variability |
| Environmental Impact | Non-renewable source, higher carbon footprint | Renewable, biodegradable |
| Common Uses in Automotive Parts | Seals, gaskets, hoses, fuel system components | Tires, vibration dampers, certain bushings |
Introduction to Rubber Types in Automotive Applications
Synthetic rubber, derived from petrochemicals, offers enhanced durability, heat resistance, and consistent quality, making it ideal for automotive parts exposed to extreme conditions such as tires, seals, and hoses. Natural rubber, sourced from the latex of rubber trees, provides superior elasticity, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance, which benefits applications like vibration isolators and flexible mounts in vehicles. Automotive manufacturers select rubber types based on performance requirements, cost-effectiveness, and environmental considerations, balancing the strengths of synthetic and natural variants for optimal part functionality.
Overview of Synthetic Rubber
Synthetic rubber, primarily derived from petrochemical feedstocks like styrene and butadiene, offers enhanced durability and resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion compared to natural rubber. It is widely used in automotive parts such as tires, seals, and belts due to its consistent quality and ability to withstand harsh operating conditions. Key types include styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), nitrile rubber (NBR), and neoprene, each providing specialized properties tailored to specific automotive applications.
Overview of Natural Rubber
Natural rubber, derived from the latex of Hevea brasiliensis trees, offers superior elasticity and resilience crucial for automotive parts such as tires, seals, and hoses. Its high tensile strength and excellent resistance to wear and tear provide durable performance under diverse temperature and stress conditions. Natural rubber's biodegradability and inherent flexibility make it a preferred choice for applications requiring enhanced grip and shock absorption.
Key Differences Between Synthetic and Natural Rubber
Synthetic rubber used in automotive parts offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for engine mounts, seals, and gaskets. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and resilience, which benefits tires and vibration-dampening components but lacks durability under extreme temperatures. The chemical composition of synthetic rubber, typically derived from petroleum byproducts, allows for tailored properties, whereas natural rubber, sourced from latex of rubber trees, retains biodegradability and higher fatigue resistance.
Performance Characteristics in Automotive Parts
Synthetic rubber offers superior resistance to heat, abrasion, and chemicals compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for automotive parts exposed to harsh environments such as engine mounts and seals. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and resilience, which are crucial for parts like tires and vibration dampers that require flexibility and shock absorption. Performance characteristics such as durability, temperature tolerance, and resistance to oil and ozone significantly influence the selection between synthetic and natural rubber in automotive manufacturing.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Synthetic rubber, such as styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), offers superior resistance to abrasion, oils, and temperature variations, leading to enhanced durability in automotive parts like tires and seals. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and tensile strength but tends to degrade faster under exposure to heat, ozone, and chemicals, limiting its longevity. The longevity of synthetic rubber in automotive applications typically surpasses natural rubber by maintaining performance under harsh environmental and mechanical stresses.
Cost Considerations: Synthetic vs Natural Rubber
Synthetic rubber typically presents a lower cost for automotive parts due to its consistent manufacturing process and availability from petrochemical sources, which reduces price volatility compared to natural rubber. Natural rubber costs are influenced by agricultural factors such as weather conditions and labor expenses, often resulting in higher and less predictable prices. The cost efficiency of synthetic rubber makes it a preferred choice for large-scale automotive production where budget control is critical.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Synthetic rubber, primarily derived from petrochemicals, poses significant environmental challenges due to its reliance on non-renewable fossil fuels and high greenhouse gas emissions during production. Natural rubber, harvested from rubber trees, offers greater sustainability through its renewable source and carbon sequestration benefits, although concerns about deforestation and biodiversity loss remain. Automotive manufacturers increasingly favor natural rubber or bio-based synthetic alternatives to reduce ecological footprints and promote circular economy principles.
Common Automotive Parts Using Each Rubber Type
Synthetic rubber, such as styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and nitrile rubber (NBR), is commonly used in automotive parts like tires, hoses, seals, and belts due to its superior resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion. Natural rubber is predominantly found in parts requiring high elasticity and resilience, including suspension bushings, vibration dampers, and weatherstripping. The choice between synthetic and natural rubber depends on specific performance requirements, environmental exposure, and durability needs for automotive applications.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Automotive Applications
Selecting the right rubber for automotive parts requires understanding the distinct properties of synthetic and natural rubber. Synthetic rubber, such as styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and nitrile rubber (NBR), offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion, making it ideal for engine mounts, seals, and hoses exposed to harsh conditions. Natural rubber excels in elasticity and tensile strength, providing optimal performance for tires, vibration dampers, and dynamic components where flexibility and resilience are critical.
Infographic: Synthetic rubber vs Natural rubber for Automotive part
 azmater.com
azmater.com