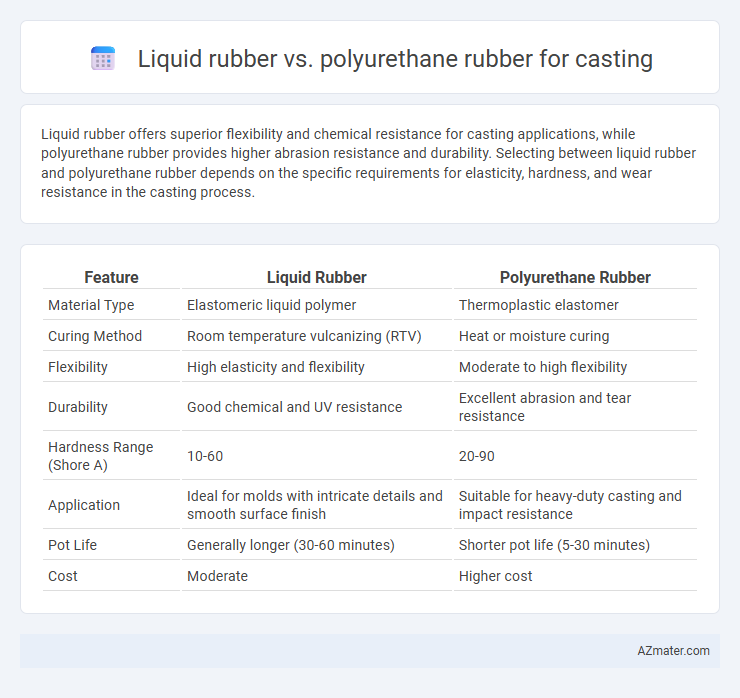
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and chemical resistance for casting applications, while polyurethane rubber provides higher abrasion resistance and durability. Selecting between liquid rubber and polyurethane rubber depends on the specific requirements for elasticity, hardness, and wear resistance in the casting process.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Liquid Rubber | Polyurethane Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Elastomeric liquid polymer | Thermoplastic elastomer |
| Curing Method | Room temperature vulcanizing (RTV) | Heat or moisture curing |
| Flexibility | High elasticity and flexibility | Moderate to high flexibility |
| Durability | Good chemical and UV resistance | Excellent abrasion and tear resistance |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 10-60 | 20-90 |
| Application | Ideal for molds with intricate details and smooth surface finish | Suitable for heavy-duty casting and impact resistance |
| Pot Life | Generally longer (30-60 minutes) | Shorter pot life (5-30 minutes) |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher cost |
Introduction to Rubber Casting Materials
Liquid rubber and polyurethane rubber are two prevalent materials used in rubber casting, each offering distinct properties suitable for various applications. Liquid rubber, typically silicone-based, provides excellent flexibility, high tear resistance, and superior temperature stability, making it ideal for intricate molds requiring detailed replication. Polyurethane rubber exhibits greater hardness variability, enhanced abrasion resistance, and faster cure times, often preferred for casting durable parts and prototypes with strong mechanical performance.
What is Liquid Rubber?
Liquid rubber is a versatile, synthetic material known for its elasticity and durability, commonly used in casting applications to create flexible molds and coatings. It offers excellent chemical resistance and weatherproofing properties, making it ideal for both industrial and artistic purposes. Compared to polyurethane rubber, liquid rubber generally provides superior flexibility and tear resistance, ensuring high-quality, long-lasting castings.
Overview of Polyurethane Rubber
Polyurethane rubber is a versatile elastomer widely used in casting due to its excellent abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and flexibility. It offers superior durability and chemical resistance compared to liquid rubber, making it ideal for manufacturing durable molds and industrial parts. Its ability to cure rapidly and produce detailed, smooth surfaces enhances efficiency and quality in casting applications.
Key Differences in Chemical Composition
Liquid rubber primarily consists of silicone-based polymers with a high degree of flexibility and resistance to extreme temperatures, making it ideal for detailed casting and flexible molds. Polyurethane rubber is formed from reactive polyol and isocyanate compounds, resulting in a material with superior toughness, abrasion resistance, and rapid cure times suitable for durable prototypes and functional parts. The chemical composition differences dictate their mechanical properties, curing processes, and specific casting applications, with liquid silicone offering more elasticity and polyurethane providing enhanced strength and resilience.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and tear resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring extended wear under dynamic stress, while polyurethane rubber excels in hardness and abrasion resistance, providing enhanced durability for heavy-duty casting projects. Polyurethane typically demonstrates longer lifespan in harsh chemical and UV exposure environments due to its excellent resistance to degradation, whereas liquid rubber maintains elasticity and impact absorption over time but may show faster wear under constant abrasive conditions. Selecting between these materials depends on specific casting demands, with polyurethane preferred for robust, mechanical durability and liquid rubber favored for flexibility and shock-absorbing properties.
Flexibility and Elasticity Factors
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility with elongation rates typically between 300% to 600%, making it ideal for molds requiring high stretchability. Polyurethane rubber provides excellent elasticity with elongation values ranging from 200% to 500%, coupled with higher tear resistance and durability. For applications demanding maximum flexibility and repeated deformation, liquid rubber excels, while polyurethane rubber balances elasticity with robustness for more resilient castings.
Ease of Use and Curing Processes
Liquid rubber for casting offers a straightforward mixing process with a one-part formula, making it easier to use for beginners and small projects. Polyurethane rubber typically requires precise two-part mixing ratios and controlled environmental conditions, which can complicate the curing process. Liquid rubber generally cures more slowly at room temperature, while polyurethane rubber cures rapidly but often demands post-curing or heat activation for optimal properties.
Cost Analysis: Liquid Rubber vs Polyurethane Rubber
Liquid rubber generally offers a lower initial material cost compared to polyurethane rubber, making it a cost-effective choice for small to medium-sized casting projects. Polyurethane rubber, although more expensive upfront, provides superior durability and resistance to wear, which can reduce replacement and maintenance expenses over time. When evaluating total cost of ownership, polyurethane rubber can be more economical for high-volume production runs due to its longer lifespan and better performance characteristics.
Ideal Applications for Each Material
Liquid rubber excels in applications requiring superior flexibility, waterproofing, and ease of use in molds for delicate or detailed casting projects such as prototypes, art pieces, and specialized molds. Polyurethane rubber is ideal for durable, abrasion-resistant castings like automotive parts, industrial components, and flexible molds that endure repeated use and harsh conditions. Selecting the appropriate material depends on the balance between flexibility, durability, and the specific environmental stresses of the casting application.
Pros and Cons Summary
Liquid rubber offers excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and ease of use for casting complex shapes, making it ideal for prototypes and molds requiring intricate details. Polyurethane rubber provides higher durability, abrasion resistance, and tensile strength, suitable for functional parts exposed to wear and mechanical stress. However, liquid rubber may have limited mechanical strength and longer curing times, while polyurethane can be more expensive and sensitive to moisture during processing.
Infographic: Liquid rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Casting
 azmater.com
azmater.com