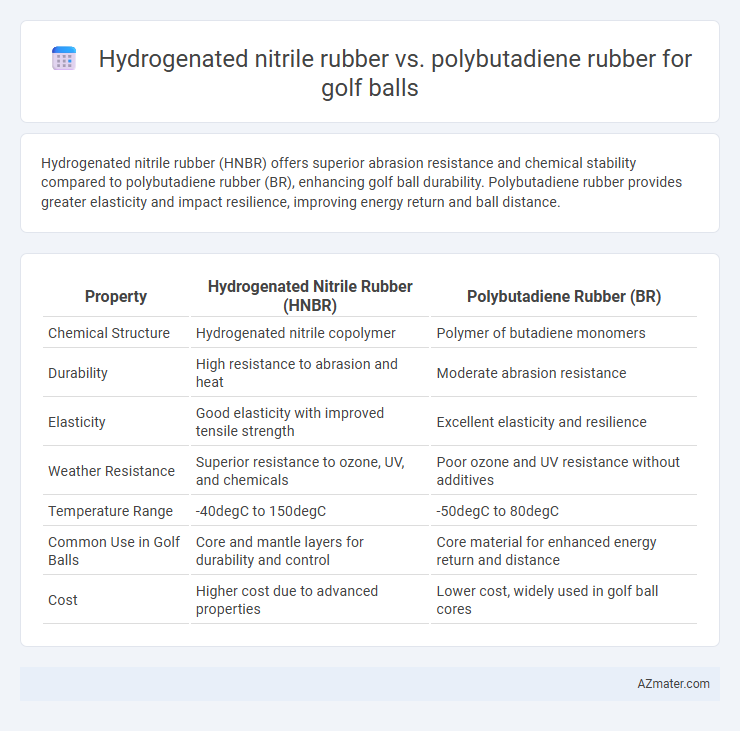
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and chemical stability compared to polybutadiene rubber (BR), enhancing golf ball durability. Polybutadiene rubber provides greater elasticity and impact resilience, improving energy return and ball distance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Polybutadiene Rubber (BR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Hydrogenated nitrile copolymer | Polymer of butadiene monomers |
| Durability | High resistance to abrasion and heat | Moderate abrasion resistance |
| Elasticity | Good elasticity with improved tensile strength | Excellent elasticity and resilience |
| Weather Resistance | Superior resistance to ozone, UV, and chemicals | Poor ozone and UV resistance without additives |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -50degC to 80degC |
| Common Use in Golf Balls | Core and mantle layers for durability and control | Core material for enhanced energy return and distance |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, widely used in golf ball cores |
Introduction to Golf Ball Materials
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and chemical stability, making it an excellent choice for golf ball cores requiring durability and consistent performance. Polybutadiene rubber (PBR), widely used for its high resilience and energy return, enhances the ball's distance by efficiently storing and releasing impact energy. The selection between HNBR and PBR significantly influences the golf ball's compression, spin rate, and overall playability, with each material tailored to different performance priorities.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and abrasion durability compared to traditional Polybutadiene Rubber, making it an ideal material for golf ball core and cover applications requiring enhanced performance. The hydrogenation process reduces unsaturation in NBR, resulting in improved resistance to oxidative degradation and maintaining elasticity under extreme conditions. Its exceptional tensile strength and resilience provide greater control over energy transfer during ball impact, optimizing distance and durability in golf balls.
Overview of Polybutadiene Rubber (PBR)
Polybutadiene rubber (PBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its high resilience, excellent abrasion resistance, and superior impact strength, making it a preferred material in golf ball cores to enhance distance and durability. Unlike hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR), PBR offers better energy return and lower heat build-up, which contributes to improved ball performance during play. Its high tensile strength and resistance to wear make PBR ideal for withstanding the repeated impact stresses experienced in golf ball applications.
Key Physical Properties: HNBR vs PBR
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior heat resistance, tensile strength, and chemical stability compared to polybutadiene rubber (PBR), making it more durable under extreme conditions. PBR offers excellent resilience and low temperature flexibility but has lower abrasion resistance and oxidative stability than HNBR. The higher tensile strength and enhanced fatigue resistance of HNBR contribute to improved longevity and performance in golf ball cores.
Durability and Resilience in Golf Balls
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior durability in golf balls due to its enhanced resistance to abrasion, heat, and chemical degradation compared to polybutadiene rubber. Polybutadiene rubber provides excellent resilience and energy return, contributing to higher ball speed and distance, but it is less resistant to wear and environmental factors. Combining HNBR's toughness with polybutadiene's elasticity can optimize golf ball performance by balancing long-lasting durability with responsive resilience.
Impact on Golf Ball Performance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) enhances golf ball durability and resilience by offering superior abrasion and heat resistance compared to polybutadiene rubber (PBR), contributing to longer-lasting performance under repeated impacts. PBR provides high initial velocity and excellent energy return, resulting in greater ball speed and distance but tends to have lower resistance to wear and deformation over time. Choosing HNBR improves consistency and control due to its stable compression properties, while PBR is preferred for maximizing driving distance with its superior compression recovery.
Weather and Chemical Resistance Comparison
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior weather resistance compared to polybutadiene rubber (BR), maintaining elasticity and structural integrity under prolonged UV exposure and ozone attack. HNBR's enhanced chemical resistance makes it more resilient against oils, solvents, and oxidative degradation, crucial for outdoor golf ball applications exposed to variable environmental conditions. In contrast, polybutadiene rubber is more susceptible to environmental stress cracking and chemical breakdown, limiting its longevity and performance in harsh weather.
Manufacturing Considerations and Cost
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and durability in golf ball manufacturing, improving layer longevity but requiring more complex processing techniques such as higher curing temperatures and specialized compounding, which increases production costs compared to polybutadiene rubber (BR). Polybutadiene rubber is favored for its excellent resilience, lower raw material cost, and simpler processing, enabling higher throughput in molding and curing stages, making it a cost-effective choice for mass production despite lower chemical and thermal resistance. The trade-off between enhanced performance and manufacturing expense drives the selection, with HNBR used in premium golf balls where durability justifies higher costs, while BR dominates standard ball production focused on cost-efficiency.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to degradation and chemical exposure, leading to longer-lasting golf balls and reduced material waste compared to polybutadiene rubber (PBR). Polybutadiene rubber, derived from petroleum-based sources, has a higher carbon footprint due to its extensive manufacturing process and limited recyclability. Sustainable golf ball production increasingly favors HNBR because its enhanced durability supports extended product life cycles, mitigating environmental impact through decreased resource consumption and improved end-of-life recyclability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Golf Balls
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, durability, and rebound resilience, making it ideal for golf balls requiring longevity and consistent performance in various weather conditions. Polybutadiene rubber (BR) provides excellent elasticity and energy return, contributing to enhanced ball speed and distance, but it may lack the overall durability of HNBR under harsh environmental stresses. Selecting the right rubber depends on balancing performance needs, with HNBR favored for durability and chemical resistance, while polybutadiene is preferred for maximizing distance and impact energy transfer.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Polybutadiene rubber for Golf ball
 azmater.com
azmater.com