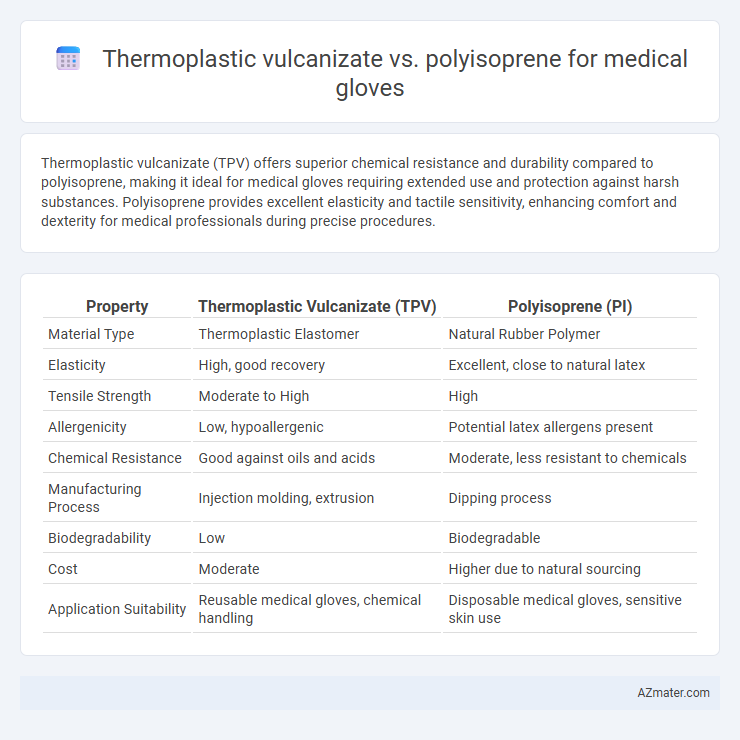
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to polyisoprene, making it ideal for medical gloves requiring extended use and protection against harsh substances. Polyisoprene provides excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity, enhancing comfort and dexterity for medical professionals during precise procedures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV) | Polyisoprene (PI) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Elastomer | Natural Rubber Polymer |
| Elasticity | High, good recovery | Excellent, close to natural latex |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate to High | High |
| Allergenicity | Low, hypoallergenic | Potential latex allergens present |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against oils and acids | Moderate, less resistant to chemicals |
| Manufacturing Process | Injection molding, extrusion | Dipping process |
| Biodegradability | Low | Biodegradable |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to natural sourcing |
| Application Suitability | Reusable medical gloves, chemical handling | Disposable medical gloves, sensitive skin use |
Introduction to Medical Glove Materials
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) and polyisoprene are prominent materials used in medical glove manufacturing due to their unique properties. TPV offers superior elasticity, chemical resistance, and durability, making it suitable for long-lasting and reusable gloves. Polyisoprene closely mimics natural rubber latex's softness and tactile sensitivity while being hypoallergenic, thus preferred for disposable gloves in sensitive environments.
Overview of Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV)
Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV) is a dynamic elastomeric material combining the flexibility of rubber with the processability of thermoplastics, making it ideal for medical gloves requiring durability and comfort. TPV offers excellent chemical resistance, superior tensile strength, and enhanced elasticity compared to traditional materials like Polyisoprene, which is a natural rubber with high elasticity but lower chemical resistance. The unique blend of vulcanized rubber particles within a thermoplastic matrix in TPV provides consistent performance, increased puncture resistance, and improved user safety in medical environments.
Overview of Polyisoprene
Polyisoprene is a synthetic elastomer closely resembling natural rubber in elasticity, comfort, and tactile sensitivity, making it ideal for medical gloves requiring high flexibility and hypoallergenic properties. Its biocompatibility and resistance to tear and puncture provide reliable protection against contaminants while reducing allergic reactions common with latex. Polyisoprene gloves are preferred in surgical and examination contexts where dexterity and sensitivity are critical for precision tasks.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) consist of a blend of crosslinked rubber particles dispersed within a thermoplastic matrix, typically polypropylene, providing a balance of elasticity and processability. Polyisoprene is a natural or synthetic elastomer composed of repeating units of isoprene monomers, characterized by its cis-1,4-polyisoprene structure, which offers excellent elasticity and tensile strength. The crosslinked network in TPVs enhances chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to the linear polyisoprene chains, making TPVs suitable for medical gloves requiring durable performance and flexibility.
Flexibility and Elasticity Comparison
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) medical gloves offer superior flexibility due to their blend of rubber and thermoplastic properties, enabling repeated stretching without permanent deformation. Polyisoprene gloves provide exceptional elasticity with a natural rubber-like feel, allowing high tensile strength and excellent recovery after stretching. When comparing both, TPV excels in long-term flexibility and durability, while polyisoprene delivers unmatched elasticity and tactile sensitivity critical for precise medical applications.
Barrier Performance and Protection
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) medical gloves offer superior barrier performance due to their excellent chemical resistance and durability against punctures and tears, making them ideal for high-risk medical environments. Polyisoprene gloves provide outstanding elasticity and tactile sensitivity but have comparatively lower resistance to certain chemicals and punctures, potentially reducing protection in hazardous situations. The choice between TPV and polyisoprene hinges on balancing the need for enhanced chemical barrier protection with tactile comfort and flexibility in medical applications.
Allergenicity and Skin Compatibility
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) gloves exhibit lower allergenicity compared to polyisoprene gloves due to the absence of natural latex proteins, making TPV an ideal choice for individuals with latex allergies. Polyisoprene gloves, while mimicking the elasticity and softness of natural latex, may still trigger allergic reactions in sensitive users because of residual proteins. Both materials offer good skin compatibility, but TPV's synthetic composition reduces the risk of dermatitis and sensitization, enhancing its suitability for prolonged medical use.
Manufacturing Process and Efficiency
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) gloves benefit from a streamlined manufacturing process combining thermoplastic and elastomer properties, allowing for faster molding cycles and reduced curing times compared to polyisoprene gloves, which require traditional latex dipping and vulcanization. TPVs offer consistent material flow and high reproducibility, improving production efficiency and reducing waste. In contrast, polyisoprene gloves, while providing superior elasticity and tactile sensitivity, involve longer batch processing and increased quality control steps due to natural rubber variability.
Cost Effectiveness and Sustainability
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) medical gloves offer superior cost-effectiveness due to their recyclability and lower raw material expenses compared to natural Polyisoprene gloves, which rely on more expensive and less sustainable rubber harvesting. TPV gloves provide enhanced sustainability by enabling easier recycling and reduced environmental impact, while Polyisoprene gloves, despite excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity, have challenges related to biodegradability and resource-intensive production. Choosing TPV over Polyisoprene supports economic efficiency and aligns with environmentally conscious healthcare procurement goals.
Application Suitability in Medical Glove Industry
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior chemical resistance and durability, making it ideal for medical gloves requiring frequent exposure to disinfectants and sterilization processes. Polyisoprene provides exceptional elasticity and tactile sensitivity, closely mimicking natural latex, which benefits procedures demanding precise dexterity and comfort. For medical glove applications, TPV suits tasks involving heavy-duty protection, while polyisoprene excels in scenarios prioritizing flexibility and reduced allergy risks.
Infographic: Thermoplastic vulcanizate vs Polyisoprene for Medical glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com