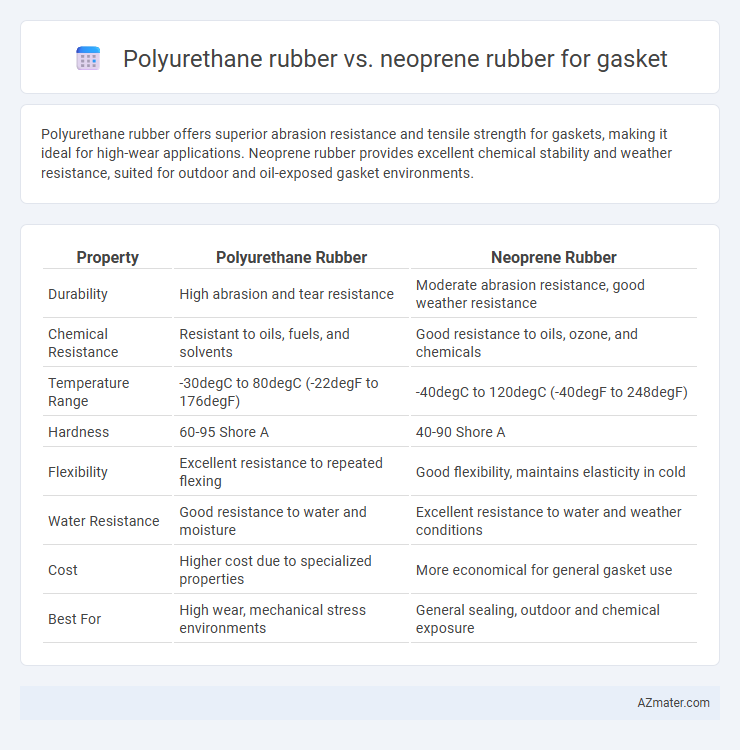
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength for gaskets, making it ideal for high-wear applications. Neoprene rubber provides excellent chemical stability and weather resistance, suited for outdoor and oil-exposed gasket environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane Rubber | Neoprene Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High abrasion and tear resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance, good weather resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils, fuels, and solvents | Good resistance to oils, ozone, and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 80degC (-22degF to 176degF) | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) |
| Hardness | 60-95 Shore A | 40-90 Shore A |
| Flexibility | Excellent resistance to repeated flexing | Good flexibility, maintains elasticity in cold |
| Water Resistance | Good resistance to water and moisture | Excellent resistance to water and weather conditions |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized properties | More economical for general gasket use |
| Best For | High wear, mechanical stress environments | General sealing, outdoor and chemical exposure |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Neoprene Rubber Gaskets
Polyurethane rubber gaskets offer exceptional abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent elasticity, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and flexibility. Neoprene rubber gaskets provide superior chemical resistance, weather resistance, and good thermal stability, suitable for sealing in harsh environments and exposure to oils, solvents, and ozone. Both materials are widely used in industrial sealing solutions, with polyurethane preferred for mechanical wear and neoprene favored for chemical and environmental resilience.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Polyurethane rubber consists of linear or cross-linked polymers formed from the reaction between diisocyanates and polyols, resulting in high abrasion resistance and flexibility ideal for gaskets exposed to mechanical wear. Neoprene rubber is a synthetic chloroprene polymer with a saturated hydrocarbon backbone and chlorine atoms that provide excellent chemical stability, oil resistance, and weatherability necessary for gaskets in harsh chemical environments. The structural differences in polyurethane's segmented block copolymer chains versus neoprene's polychloroprene backbone dictate their respective performance in sealing applications where chemical exposure and mechanical durability vary.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyurethane rubber offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to neoprene rubber, making it ideal for gaskets subjected to high mechanical stress and wear. Neoprene rubber excels in compression set resistance and flexibility, providing better sealing performance under fluctuating temperatures and dynamic loading. Selecting between polyurethane and neoprene depends on specific gasket requirements such as load-bearing capacity and environmental durability.
Temperature Resistance Capabilities
Polyurethane rubber offers excellent abrasion resistance but typically withstands temperatures only up to 80degC (176degF), limiting its use in high-temperature gasket applications. Neoprene rubber provides better temperature resistance, functioning effectively from -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF), making it ideal for gaskets exposed to fluctuating or higher temperatures. The enhanced thermal stability of neoprene ensures reliable sealing performance in automotive, industrial, and HVAC gasket environments.
Chemical and Oil Resistance
Polyurethane rubber offers excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, hydraulic fluids, and aliphatic hydrocarbons, making it ideal for gaskets in environments with exposure to harsh chemicals and mechanical wear. Neoprene rubber exhibits good chemical stability and moderate resistance to oils, ozone, and weathering but is less resistant to aromatic and ketone solvents compared to polyurethane. For gasket applications requiring superior chemical and oil resistance, especially in dynamic sealing environments, polyurethane typically outperforms neoprene with enhanced durability and longer service life.
Durability and Longevity
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making it highly durable for gaskets exposed to mechanical wear and harsh environments. Neoprene rubber excels in chemical stability and weather resistance, providing long-lasting performance in applications involving oils, solvents, and varying temperatures. Choosing between polyurethane and neoprene gaskets depends on the specific durability requirements and environmental conditions of the sealing application.
Flexibility and Compression Set
Polyurethane rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for gaskets requiring high durability and elasticity under dynamic stress. Neoprene rubber exhibits good flexibility and moderate compression set, providing effective sealing performance in moderate temperature ranges and exposure to oils or chemicals. When comparing compression set resistance, polyurethane typically outperforms neoprene, maintaining gasket integrity and shape after prolonged compression cycles.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for high-performance gaskets, but its higher initial cost may impact upfront investment. Neoprene rubber provides balanced chemical resistance and moderate durability at a lower price, often leading to cost savings in applications with less demanding environmental factors. Evaluating lifecycle costs, including maintenance and replacement frequency, is crucial to determining the most cost-effective choice between polyurethane and neoprene gaskets.
Typical Applications in Industries
Polyurethane rubber gaskets excel in industries requiring high abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, such as automotive, construction, and heavy machinery, where durability and flexibility are critical. Neoprene rubber gaskets are widely used in chemical processing, marine, and refrigeration industries due to their excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, ozone, and weathering. Both materials serve crucial roles in sealing applications, with polyurethane preferred for mechanical wear and neoprene favored for chemical and environmental stability.
How to Select the Right Rubber Gasket Material
When selecting the right rubber gasket material, consider polyurethane for its superior abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and ability to withstand harsh mechanical stress, making it ideal for dynamic sealing applications. Neoprene offers excellent chemical stability, weather resistance, and moderate oil resistance, well-suited for outdoor or exposure to petrochemicals. Evaluating the specific operating environment, including chemical exposure, temperature range, and mechanical requirements, ensures optimal gasket performance and longevity.
Infographic: Polyurethane rubber vs Neoprene rubber for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com