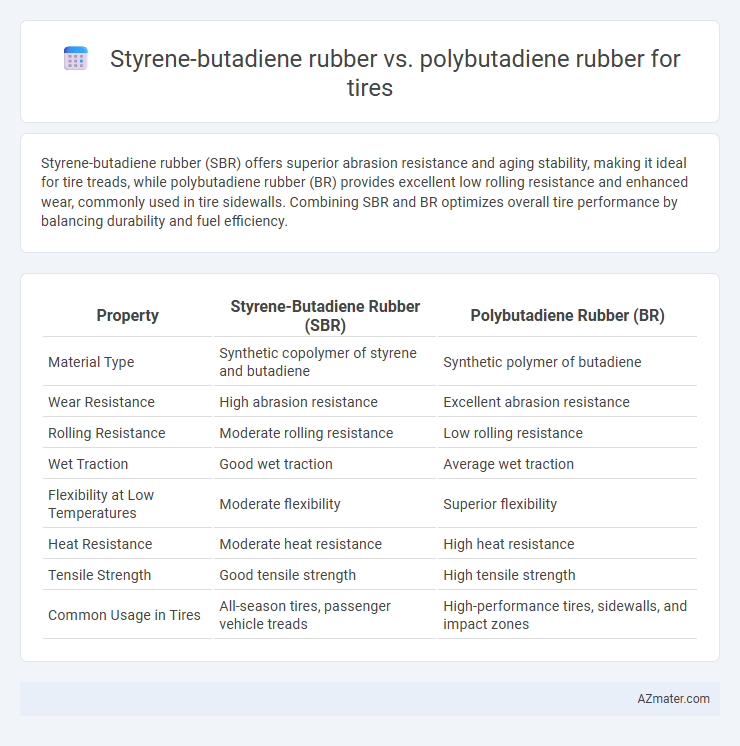
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and aging stability, making it ideal for tire treads, while polybutadiene rubber (BR) provides excellent low rolling resistance and enhanced wear, commonly used in tire sidewalls. Combining SBR and BR optimizes overall tire performance by balancing durability and fuel efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Polybutadiene Rubber (BR) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic copolymer of styrene and butadiene | Synthetic polymer of butadiene |
| Wear Resistance | High abrasion resistance | Excellent abrasion resistance |
| Rolling Resistance | Moderate rolling resistance | Low rolling resistance |
| Wet Traction | Good wet traction | Average wet traction |
| Flexibility at Low Temperatures | Moderate flexibility | Superior flexibility |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance | High heat resistance |
| Tensile Strength | Good tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Common Usage in Tires | All-season tires, passenger vehicle treads | High-performance tires, sidewalls, and impact zones |
Introduction to Styrene-Butadiene and Polybutadiene Rubber
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic copolymer consisting of styrene and butadiene, widely used in tire manufacturing due to its excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability. Polybutadiene rubber (BR), a homopolymer of butadiene, offers superior elasticity, low rolling resistance, and enhanced wear performance, making it ideal for high-performance tire treads. Combining SBR and BR in tire compounds optimizes durability, traction, and fuel efficiency for diverse driving conditions.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) consists of copolymerized styrene and butadiene units, providing a balanced combination of abrasion resistance and aging stability, while polybutadiene rubber (BR) is a homopolymer of butadiene characterized by higher cis-1,4 content, resulting in superior elasticity and low-temperature flexibility. The random distribution of styrene in SBR's polymer chain enhances its hardness and tensile strength, whereas the predominantly cis-1,4 structure in BR contributes to increased resilience and wear resistance in tire treads. These chemical and structural differences directly influence tire performance, with SBR favored for sidewalls and general tread compounds, and BR chosen for high-performance tread components requiring improved wear and dynamic properties.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is typically produced via emulsion polymerization, resulting in a copolymer with controlled styrene content that enhances abrasion resistance and aging stability in tire treads. Polybutadiene rubber (BR) is commonly synthesized through solution polymerization, yielding a high cis-1,4 content polymer known for excellent resilience and low rolling resistance in tire sidewalls. The emulsion process for SBR allows for easier molecular weight control and incorporation of antioxidants, whereas the solution process for BR provides superior microstructure control essential for dynamic performance in tires.
Performance Characteristics in Tire Applications
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance and good aging stability, making it ideal for tire treads that require durability and traction, while polybutadiene rubber (BR) provides superior elasticity and low rolling resistance, improving fuel efficiency and ride comfort. SBR's balanced wear resistance and grip are widely utilized in passenger car tires, whereas BR's high resilience and crack resistance are favored in high-performance and off-road tires. The combination of SBR and BR in tire compounds optimizes overall performance by leveraging SBR's toughness and BR's elasticity for improved tire longevity and dynamic response.
Wear Resistance and Longevity
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior wear resistance compared to polybutadiene rubber (BR) due to its higher abrasion resistance, making it ideal for tire treads subject to heavy road contact. Polybutadiene rubber excels in enhancing tire longevity by providing excellent crack resistance and low heat buildup, which reduces degradation over time. Combining SBR with BR in tire formulations optimizes both wear resistance and lifespan, resulting in durable, high-performance tires.
Rolling Resistance and Fuel Efficiency
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers improved abrasion resistance and better aging stability, contributing to moderate rolling resistance in tires, which enhances fuel efficiency compared to traditional compounds. Polybutadiene rubber (BR) provides superior elasticity and lower hysteresis losses, resulting in significantly reduced rolling resistance that directly translates to higher fuel savings and longer tread life. Tires combining SBR and BR leverage the balance between durability and low rolling resistance, optimizing overall fuel efficiency for passenger and commercial vehicles.
Wet and Dry Traction Capabilities
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) provides superior wet traction due to its higher polarity and enhanced abrasion resistance, making it ideal for tire treads exposed to wet conditions. Polybutadiene rubber (BR) excels in dry traction and wear resistance, offering improved durability and rolling resistance under dry road conditions. Combining SBR and BR in tire compounds optimizes both wet and dry performance, balancing traction and tread life for versatile driving environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and polybutadiene rubber (BR) differ in environmental impact and sustainability, with SBR derived primarily from petroleum-based styrene and butadiene, contributing to higher carbon emissions during production. Polybutadiene rubber, often partially bio-based, offers improved wear resistance and lower rolling resistance, enhancing tire fuel efficiency and reducing greenhouse gas emissions over the tire's lifespan. The recycling potential of both materials varies, with innovations in devulcanization processes improving the circular economy aspects of BR, positioning it as a more sustainable option in tire manufacturing.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) dominates tire manufacturing due to its lower production cost and higher market availability compared to polybutadiene rubber (BR), which is more expensive and less widely produced. SBR offers a balanced combination of abrasion resistance and aging stability, making it cost-effective for passenger car tires, while BR is preferred for high-performance or off-road tires due to superior wear resistance despite higher prices. Market data indicates SBR accounts for over 50% of global tire rubber consumption, reflecting its cost efficiency and widespread supply chain presence.
Choosing the Right Rubber: Application-Specific Recommendations
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability, making it ideal for tire treads that require durability on rough surfaces. Polybutadiene rubber (BR) provides superior resilience and low rolling resistance, enhancing tire performance in high-speed and fuel-efficient applications. Selecting the right rubber hinges on balancing wear resistance with elasticity to meet specific tire performance criteria such as traction, longevity, and fuel economy.
Infographic: Styrene-butadiene rubber vs Polybutadiene rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com