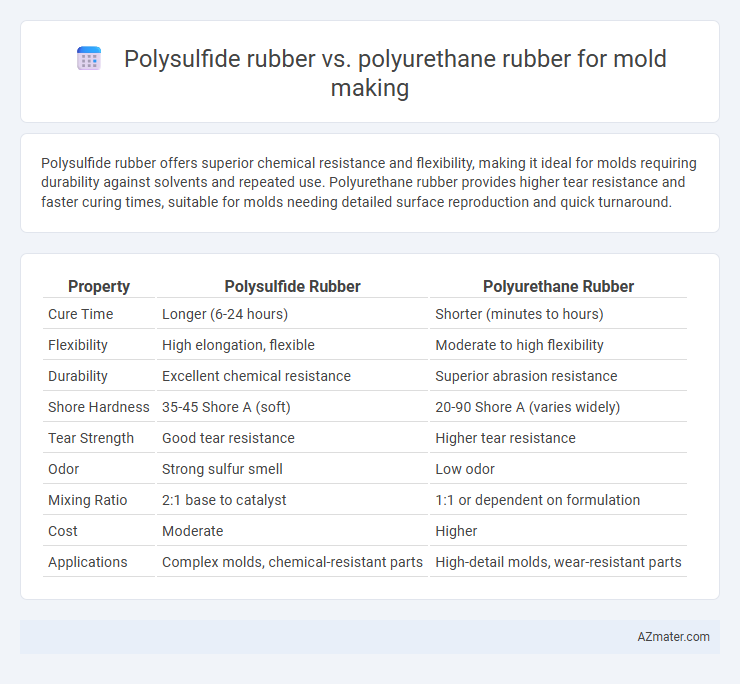
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for molds requiring durability against solvents and repeated use. Polyurethane rubber provides higher tear resistance and faster curing times, suitable for molds needing detailed surface reproduction and quick turnaround.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfide Rubber | Polyurethane Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Cure Time | Longer (6-24 hours) | Shorter (minutes to hours) |
| Flexibility | High elongation, flexible | Moderate to high flexibility |
| Durability | Excellent chemical resistance | Superior abrasion resistance |
| Shore Hardness | 35-45 Shore A (soft) | 20-90 Shore A (varies widely) |
| Tear Strength | Good tear resistance | Higher tear resistance |
| Odor | Strong sulfur smell | Low odor |
| Mixing Ratio | 2:1 base to catalyst | 1:1 or dependent on formulation |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Applications | Complex molds, chemical-resistant parts | High-detail molds, wear-resistant parts |
Introduction to Mold Making Materials
Polysulfide rubber offers excellent resistance to solvents and flexibility, making it ideal for intricate mold making with fine detail reproduction. Polyurethane rubber provides superior durability and tear resistance, suitable for molds requiring longer life and frequent use. Choosing between polysulfide and polyurethane depends on the specific application demands such as chemical exposure, mold complexity, and production volume.
Overview of Polysulfide Rubber
Polysulfide rubber is a highly flexible, sulfur-containing elastomer commonly used in mold making due to its excellent chemical resistance and low shrinkage, making it ideal for capturing fine detail. It offers superior elongation and tear resistance compared to polyurethane rubber, which enhances mold durability for casting resins, plaster, and concrete. Despite longer curing times and stronger odor, polysulfide rubber remains preferred in applications requiring precise, durable molds with outstanding dimensional stability.
Overview of Polyurethane Rubber
Polyurethane rubber offers superior tear resistance and durability compared to polysulfide rubber, making it ideal for mold making in applications requiring multiple reproductions and fine detail retention. Its excellent elongation and high tensile strength provide long-lasting molds capable of capturing intricate textures and designs. Polyurethane rubber also exhibits faster curing times and better resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and environmental degradation, enhancing mold performance in industrial and artistic production environments.
Key Differences in Chemical Composition
Polysulfide rubber contains sulfur-based chains with disulfide linkages, offering excellent chemical resistance and flexibility for mold making. Polyurethane rubber is synthesized from polyols and diisocyanates, resulting in a polymer with superior abrasion resistance and higher tensile strength. These chemical composition differences influence mold durability, flexibility, and suitability for detailed mold reproduction.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polysulfide rubber offers excellent elongation and tear resistance, making it ideal for flexible mold applications requiring high durability under stress. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance and higher tensile strength, which benefits molds exposed to repeated mechanical wear. Both materials exhibit different hardness ranges, with polysulfide typically softer and polyurethane offering greater rigidity, influencing their suitability for specific mold-making tasks.
Mold Making Process: Polysulfide vs Polyurethane
Polysulfide rubber offers excellent chemical resistance and elongation, making it ideal for molds requiring high flexibility and durability, especially in casting resins or concrete. Polyurethane rubber provides superior tear resistance and faster curing times, which enhances productivity in mold making where intricate detail and rapid turnaround are essential. Polysulfide's slower curing process demands longer demolding periods, whereas polyurethane's robust mechanical properties allow for repeated mold use with minimal deformation.
Durability and Longevity of Molds
Polysulfide rubber offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, providing molds with moderate durability suitable for short to medium production runs. Polyurethane rubber boasts superior wear resistance and higher tensile strength, resulting in molds with significantly enhanced longevity and the ability to withstand repeated use in high-volume manufacturing. Choosing polyurethane rubber ensures extended mold life and consistent replication quality in demanding industrial applications.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Polysulfide rubber offers a cost-effective solution for mold making due to its lower material price and good chemical resistance, making it ideal for small to medium production runs. Polyurethane rubber typically has higher initial costs but provides greater durability and faster curing times, which may reduce long-term expenses in large-scale or complex projects. Availability of polysulfide rubber is widespread in specialized industrial supply chains, whereas polyurethane rubber enjoys broader distribution and easier sourcing from general rubber product suppliers.
Best Applications for Each Rubber Type
Polysulfide rubber excels in mold making for casting applications requiring exceptional solvent and chemical resistance, such as automotive parts and electrical components. Polyurethane rubber is ideal for molds needing high abrasion resistance and flexibility, commonly used in prototyping and low-volume production of detailed resin or plastic parts. Selecting between polysulfide and polyurethane depends on the specific demands of durability, flexibility, and chemical exposure in the intended mold-making process.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Mold
Polysulfide rubber offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for molds requiring precision and durability in complex shapes. Polyurethane rubber provides superior tear strength and abrasion resistance, suitable for molds subjected to frequent use or heavy-duty applications. Selecting the right rubber depends on mold complexity, usage frequency, and chemical exposure to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Polysulfide rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Mold making
 azmater.com
azmater.com