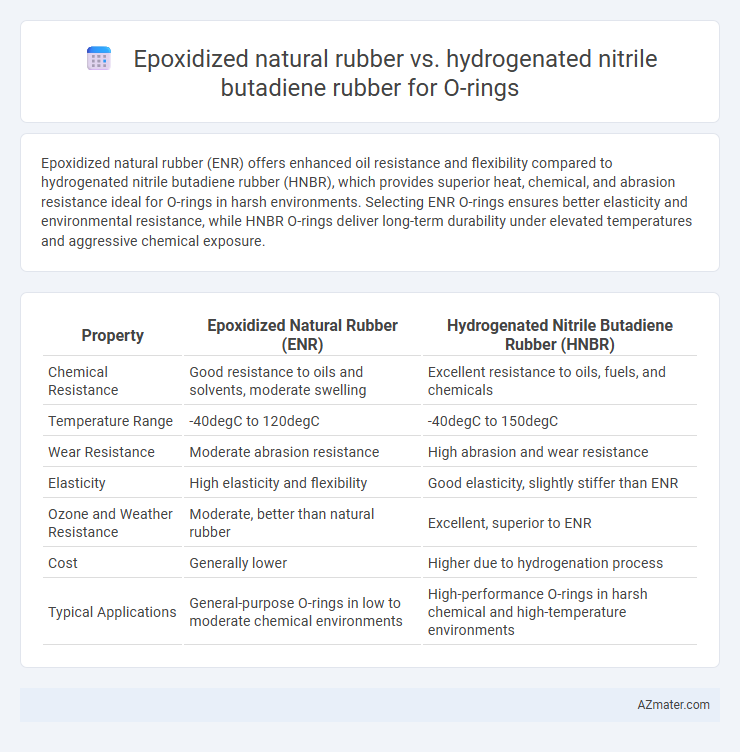
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced oil resistance and flexibility compared to hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR), which provides superior heat, chemical, and abrasion resistance ideal for O-rings in harsh environments. Selecting ENR O-rings ensures better elasticity and environmental resistance, while HNBR O-rings deliver long-term durability under elevated temperatures and aggressive chemical exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and solvents, moderate swelling | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance | High abrasion and wear resistance |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and flexibility | Good elasticity, slightly stiffer than ENR |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Moderate, better than natural rubber | Excellent, superior to ENR |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to hydrogenation process |
| Typical Applications | General-purpose O-rings in low to moderate chemical environments | High-performance O-rings in harsh chemical and high-temperature environments |
Introduction to Elastomers in O-Ring Applications
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced oil resistance and flexibility in O-ring applications due to its modified molecular structure, making it suitable for moderate-temperature environments. Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior chemical, heat, and abrasion resistance, which is ideal for high-performance sealing in automotive and industrial O-rings. Both elastomers provide distinct advantages, with ENR favored for its environmental resistance and HNBR preferred for demanding operational conditions.
Overview of Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR)
Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) is a modified form of natural rubber with enhanced oil resistance and improved mechanical properties, making it suitable for O-rings exposed to hydrocarbons and chemicals. ENR exhibits superior elasticity, abrasion resistance, and resilience compared to traditional natural rubber, while maintaining good heat resistance up to around 120degC. Its unique epoxide groups improve polar interactions, increasing compatibility with polar fluids and providing better sealing performance than Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR) in certain applications.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical strength compared to Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR), making it highly suitable for demanding O-ring applications in automotive and industrial environments. HNBR's resistance to oils, fuels, and high temperatures up to 150degC ensures reliable sealing performance under harsh conditions. This elastomer also provides excellent abrasion and compression set resistance, extending O-ring service life in dynamic sealing applications.
Key Material Properties Comparison: ENR vs HNBR
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced oil resistance, improved tensile strength, and superior flexibility compared to traditional natural rubber, making it suitable for high-performance O-rings exposed to hydrocarbons. Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) excels in heat and chemical resistance, maintaining stability in temperatures up to 150-160degC and resisting oils, fuels, and ozone more effectively than ENR. ENR provides better elasticity and lower compression set, while HNBR delivers superior resistance to thermal degradation and abrasion, influencing material selection based on specific operational environments.
Chemical Resistance: ENR and HNBR Performance
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits excellent chemical resistance to polar solvents, oils, and fuels due to its epoxide groups enhancing polarity and interaction with chemicals, making it suitable for various industrial O-ring applications. Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) displays superior chemical resistance against petroleum-based oils, fuels, and heat due to its hydrogenated backbone, which offers enhanced thermal stability and resistance to oxidation and ozone. For O-ring performance, HNBR outperforms ENR in harsh environments involving high temperatures and aggressive hydrocarbons, while ENR excels in resistance to polar chemicals and improved mechanical properties under mild chemical exposure.
Temperature Stability in O-Ring Service
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior temperature stability in O-ring applications, maintaining elasticity and resilience up to approximately 120degC, which makes it ideal for moderate heat environments. In contrast, hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) provides enhanced thermal resistance, effectively operating between -40degC and 150degC with excellent resistance to heat aging and chemical exposure. When selecting O-rings for temperature-critical services, HNBR's higher thermal endurance ensures long-term stability, while ENR balances moderate temperature performance with improved oil and ozone resistance.
Mechanical and Physical Properties Analysis
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers excellent elasticity, abrasion resistance, and enhanced oil resistance due to its epoxy groups, making it suitable for dynamic O-ring applications requiring flexibility and moderate chemical resistance. Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior tensile strength, heat resistance up to 150degC, and excellent chemical resistance against oils, fuels, and solvents, ensuring long-term durability in harsh environments. While ENR provides better elasticity and resilience, HNBR outperforms in mechanical strength and thermal stability, making HNBR the preferred choice for high-performance O-rings exposed to extreme mechanical and chemical conditions.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers moderate cost efficiency and is widely available due to its derivation from natural latex, making it a competitive choice for O-ring applications in standard environments. Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR), though more expensive, provides superior chemical resistance and durability, justifying its higher cost in demanding conditions where longevity and performance are critical. Availability of ENR is generally more consistent globally, whereas HNBR supply can be limited and price-volatile due to its specialized production and reliance on synthetic raw materials.
Typical Industrial Applications of ENR and HNBR O-Rings
Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) O-rings excel in applications requiring enhanced oil resistance and mechanical strength, commonly used in automotive fuel systems, industrial machinery seals, and chemical processing equipment. Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR) O-rings offer superior resistance to heat, ozone, and aggressive chemicals, making them ideal for high-temperature environments such as aerospace hydraulics, oilfield equipment, and automotive air conditioning systems. Both materials provide excellent sealing performance, with ENR favored for flexibility and cost-effectiveness, while HNBR is preferred for durability and long-term reliability under extreme conditions.
Choosing the Right Material: ENR vs HNBR for O-Rings
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers excellent elasticity and resistance to oils and chemicals, making it suitable for general-purpose O-rings exposed to moderate temperatures and mechanical stress. Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior heat resistance, enhanced durability, and exceptional chemical stability, ideal for O-rings in high-temperature and harsh chemical environments. Selecting the right material depends on application-specific requirements such as operating temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical demands, with ENR favored for flexibility and cost-effectiveness, while HNBR is preferred for performance-critical sealing solutions.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com