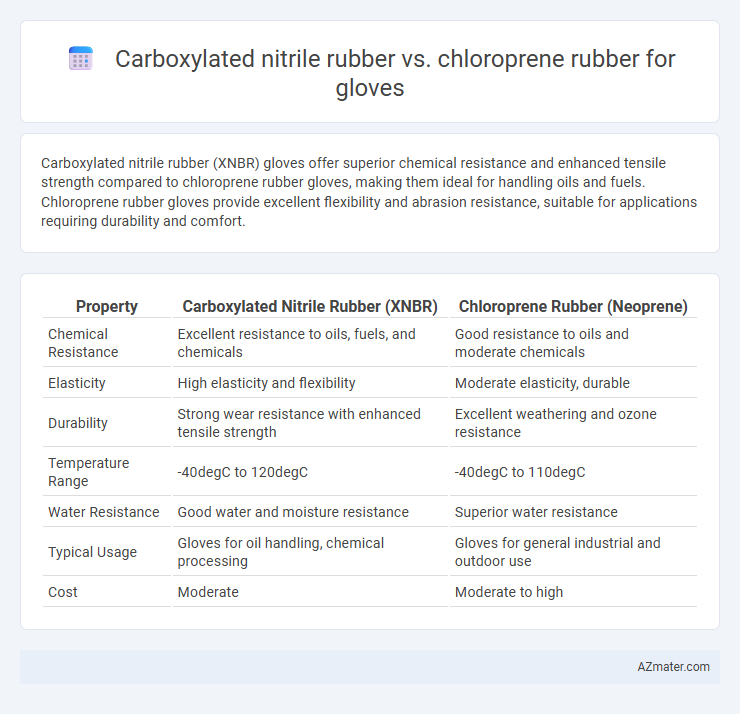
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) gloves offer superior chemical resistance and enhanced tensile strength compared to chloroprene rubber gloves, making them ideal for handling oils and fuels. Chloroprene rubber gloves provide excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance, suitable for applications requiring durability and comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Chloroprene Rubber (Neoprene) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Good resistance to oils and moderate chemicals |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and flexibility | Moderate elasticity, durable |
| Durability | Strong wear resistance with enhanced tensile strength | Excellent weathering and ozone resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 110degC |
| Water Resistance | Good water and moisture resistance | Superior water resistance |
| Typical Usage | Gloves for oil handling, chemical processing | Gloves for general industrial and outdoor use |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate to high |
Introduction to Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber and Chloroprene Rubber
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for enhanced oil resistance, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for protective gloves in industrial applications. Chloroprene rubber (CR), commonly known as neoprene, provides excellent chemical, weather, and ozone resistance, widely used in gloves requiring durability and flexibility. Both materials offer distinct advantages for glove manufacturing, with XNBR excelling in mechanical properties and CR in environmental resistance.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) contains acrylonitrile and butadiene copolymers with carboxyl groups that enhance crosslinking density, resulting in improved chemical resistance and tensile strength compared to standard nitrile rubber. Chloroprene rubber (CR) is composed of polychloroprene chains with chlorine atoms providing inherent flame resistance and elasticity. The polar carboxyl groups in XNBR promote stronger intermolecular bonding, optimizing barrier properties for gloves, whereas CR's molecular structure offers balanced flexibility and durability against oils and chemicals.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) gloves exhibit higher tensile strength and superior abrasion resistance compared to chloroprene rubber gloves, making them suitable for demanding industrial applications. XNBR offers better oil and chemical resistance, while chloroprene provides enhanced flexibility and moderate chemical stability. Both materials deliver excellent elasticity, but XNBR's improved tear resistance ensures longer glove lifespan in harsh environments.
Chemical Resistance and Protection Levels
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) gloves offer superior chemical resistance against oils, fuels, and solvents compared to chloroprene rubber gloves, making them ideal for industrial applications involving hydrocarbons. Chloroprene rubber gloves provide excellent protection against a broader range of chemicals, including acids, bases, and alcohols, while maintaining good durability and flexibility. For higher protection levels in aggressive chemical environments, XNBR gloves are preferred, whereas chloroprene gloves balance chemical resistance with enhanced comfort for extended wear.
Comfort, Fit, and Tactile Sensitivity
Carboxylated nitrile rubber gloves offer superior tactile sensitivity and enhanced flexibility, providing a comfortable fit for prolonged wear due to their excellent elasticity and soft texture. Chloroprene rubber gloves deliver a snug, anatomically contoured fit with excellent resistance to chemicals and temperature, ensuring consistent comfort during extended use. Both materials provide reliable protection, but carboxylated nitrile edges out in terms of superior dexterity and tactile precision, essential for delicate tasks.
Durability and Tear Resistance
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior durability and tear resistance compared to chloroprene rubber, making it ideal for gloves used in high-wear environments. XNBR's enhanced cross-linking and polarity contribute to its excellent resistance against abrasion, cuts, and mechanical stress. Chloroprene rubber offers moderate durability but falls short in tear resistance when exposed to harsh conditions or repeated flexing.
Allergic Reactions and Skin Sensitivities
Carboxylated nitrile rubber gloves exhibit lower allergenic potential compared to chloroprene rubber gloves, making them more suitable for individuals with latex sensitivities or allergic reactions. Chloroprene rubber, while resistant to many chemicals, can trigger contact dermatitis in sensitive users due to residual proteins and accelerators. Selecting carboxylated nitrile gloves helps minimize skin irritation and allergic responses in healthcare and industrial applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber gloves offer superior chemical resistance and durability at a moderate cost, making them a cost-effective choice for industrial and medical applications. Chloroprene rubber gloves provide excellent flexibility and resilience but usually come at a higher price point due to their synthetic composition. Market availability favors chloroprene gloves in specialty sectors, while carboxylated nitrile gloves enjoy broader distribution across commercial and healthcare supply chains.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) gloves exhibit better resistance to oils and chemicals with enhanced tensile strength, while chloroprene rubber (CR) gloves provide excellent flexibility and weather resistance. From an environmental perspective, XNBR production typically involves fewer toxic byproducts compared to CR, which relies on chlorinated compounds that can generate hazardous waste. Sustainable glove manufacturing favors XNBR for its lower ecological footprint and potential for improved recyclability, although CR remains valued for durability in harsh conditions.
Choosing the Right Glove Material for Specific Applications
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for gloves used in oil handling and heavy-duty industrial tasks. Chloroprene rubber (CR) provides excellent flexibility, moderate chemical resistance, and good weathering properties, suitable for gloves in general-purpose applications and environments requiring dexterity and durability. Selecting the right glove material depends on the specific chemical exposure, mechanical stress, and comfort requirements of the application to ensure optimal protection and performance.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Chloroprene rubber for Glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com