Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability for hoses, making it ideal for general-purpose applications. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) provides superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, making it the preferred choice for hoses in automotive and industrial fluid handling.
Table of Comparison
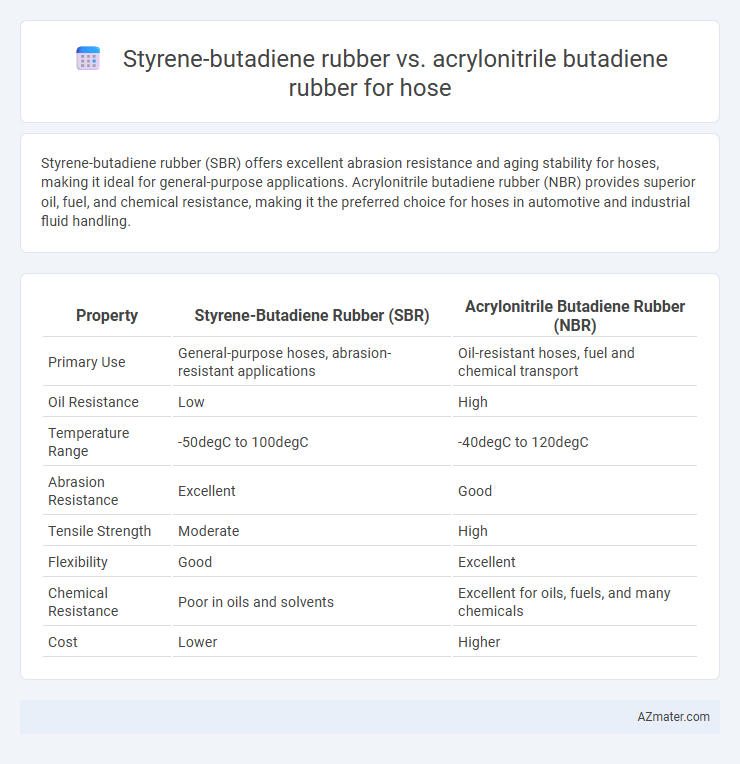
| Property | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | General-purpose hoses, abrasion-resistant applications | Oil-resistant hoses, fuel and chemical transport |
| Oil Resistance | Low | High |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 100degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Abrasion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate | High |
| Flexibility | Good | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Poor in oils and solvents | Excellent for oils, fuels, and many chemicals |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR)
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic copolymer known for its excellent abrasion resistance, aging stability, and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for hose applications requiring durability and flexibility. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) offers superior oil and chemical resistance due to its high acrylonitrile content, making it ideal for hoses exposed to fuels, oils, and harsh chemicals. Both polymers serve distinct purposes in hose manufacturing, with SBR favored for general industrial uses and NBR preferred in environments demanding enhanced resistance to petrochemicals.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) consists of a copolymer of styrene and butadiene with a typical styrene content of 23-28%, providing improved abrasion resistance and aging stability for hose applications. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) features a copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, with acrylonitrile content ranging from 18% to 50%, enhancing oil, fuel, and chemical resistance in hoses. The polar nitrile groups in NBR increase resistance to hydrocarbons, while SBR's non-polar structure offers better mechanical strength and flexibility.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and moderate aging stability, making it suitable for general-purpose hose applications requiring durability under mechanical stress. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) provides superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance with higher tensile strength, ideal for hoses exposed to harsh chemical environments and extreme temperatures. SBR typically exhibits better flexibility and cost-effectiveness, whereas NBR excels in environment-specific performance parameters such as compression set and resistance to swelling.
Resistance to Oil and Chemicals
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate resistance to oils and chemicals, making it suitable for general-purpose hoses exposed to mild petroleum products and solvents. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), on the other hand, exhibits superior resistance to oils, fuels, and various chemicals due to its high acrylonitrile content, which significantly enhances its impermeability and durability in aggressive environments. For hoses requiring prolonged exposure to hydrocarbons and chemical agents, NBR outperforms SBR in maintaining structural integrity and preventing swelling or degradation.
Temperature Performance in Hose Applications
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) exhibits moderate temperature resistance, typically withstanding continuous use between -50degC and 70degC, making it suitable for general-purpose hose applications with limited thermal demands. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) offers superior temperature performance, tolerating a wider range from -40degC up to 100degC, which enhances its suitability for hoses exposed to higher temperatures and oil resistance. NBR's enhanced thermal stability combined with excellent chemical resistance makes it preferable for industrial hoses requiring durability under elevated temperatures and oil contact conditions.
Durability and Abrasion Resistance
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance, making it suitable for hoses exposed to high wear and tear in industrial applications. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) outperforms SBR in oil and chemical resistance while maintaining good durability, ideal for hoses used in fuel or hydraulic systems. When prioritizing abrasion resistance, SBR excels, but for enhanced durability in chemically aggressive environments, NBR provides superior performance.
Flexibility and Elasticity Differences
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate flexibility and elasticity, making it suitable for hoses requiring good abrasion resistance but less dynamic movement. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) exhibits superior elasticity and flexibility, especially in oil-resistant hose applications, due to its higher nitrile content that enhances resilience under strain and deformation. The elasticity of NBR hoses allows for better recovery and durability in fluctuating pressure environments compared to the stiffer and less elastic SBR counterparts.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers cost-effectiveness due to its lower raw material expenses and widespread production, making it a preferred choice for general-purpose hoses. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) provides superior oil and chemical resistance but at a higher price point, limiting its use primarily to specialized industrial hose applications. Market availability favors SBR because of its broad demand and extensive supply chain, while NBR is less common and often requires sourcing from specialized suppliers.
Typical Hose Applications for SBR and NBR
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is commonly used in general-purpose industrial hoses, such as air and water hoses, due to its good abrasion resistance and moderate chemical stability. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) excels in applications requiring superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for fuel hoses, hydraulic lines, and oil transfer hoses. The selection between SBR and NBR depends largely on the fluid compatibility and environmental exposure of the hose application.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Hose Needs
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for general-purpose hoses subjected to rough handling and wear. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) excels in oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, providing superior durability in industrial and automotive hose applications involving hydrocarbons. Selecting the right rubber depends on the hose's exposure environment, with SBR preferred for mechanical durability and NBR for chemical resilience.
Infographic: Styrene-butadiene rubber vs Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com