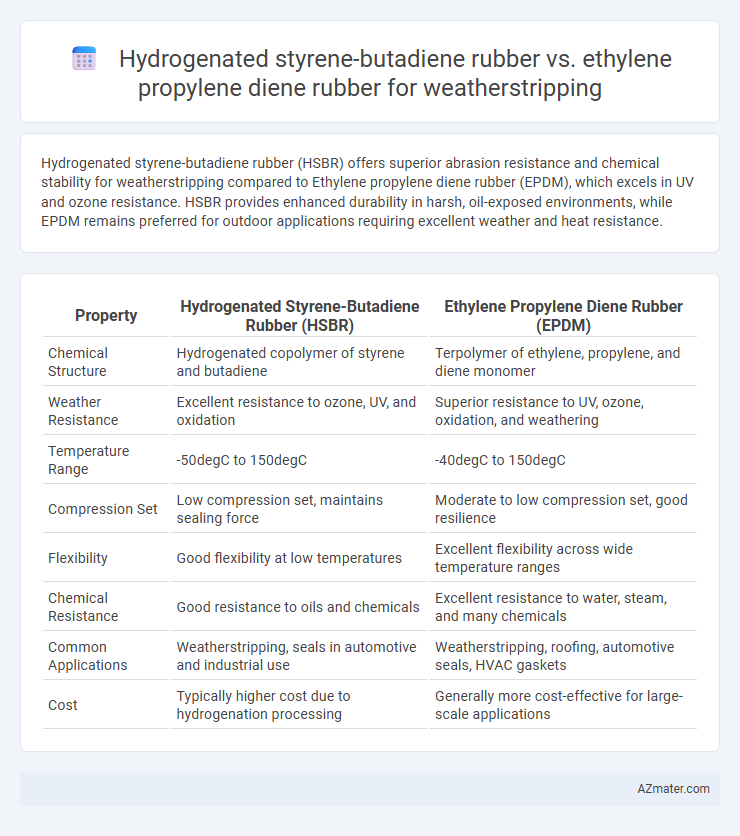
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and chemical stability for weatherstripping compared to Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM), which excels in UV and ozone resistance. HSBR provides enhanced durability in harsh, oil-exposed environments, while EPDM remains preferred for outdoor applications requiring excellent weather and heat resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Hydrogenated copolymer of styrene and butadiene | Terpolymer of ethylene, propylene, and diene monomer |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent resistance to ozone, UV, and oxidation | Superior resistance to UV, ozone, oxidation, and weathering |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 150degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Compression Set | Low compression set, maintains sealing force | Moderate to low compression set, good resilience |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Excellent flexibility across wide temperature ranges |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and chemicals | Excellent resistance to water, steam, and many chemicals |
| Common Applications | Weatherstripping, seals in automotive and industrial use | Weatherstripping, roofing, automotive seals, HVAC gaskets |
| Cost | Typically higher cost due to hydrogenation processing | Generally more cost-effective for large-scale applications |
Introduction to Weatherstripping Materials
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and ozone stability, making it ideal for weatherstripping applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in excellent resistance to heat, UV rays, and oxidation, providing long-lasting sealing performance in outdoor weatherstripping. Both materials ensure effective sealing, with HSBR favored for durability and EPDM chosen for flexibility and resistance to weather elements.
Overview of Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR)
Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and chemical degradation compared to conventional styrene-butadiene rubber, making it highly durable for weatherstripping applications. Its improved hydrogenation process enhances tensile strength and elongation, providing excellent elasticity and resilience under varying temperature conditions. HSBR's molecular structure allows for enhanced rubber aging properties, ensuring long-lasting weather sealing and protection against environmental factors.
Properties and Benefits of HSBR in Weatherstripping
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior weather resistance and ozone stability compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM), making it highly effective in weatherstripping applications where durability under harsh climatic conditions is critical. HSBR exhibits excellent tensile strength and abrasion resistance, ensuring long-lasting performance in sealing gaps against water, dust, and air infiltration. Its ability to maintain elasticity and resist aging under UV exposure enhances the lifespan and reliability of weatherstripping components in automotive and industrial environments.
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM): A Comprehensive Guide
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) outperforms Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) in weatherstripping applications due to its exceptional resistance to heat, ozone, and UV exposure. EPDM's superior elasticity and long-term durability ensure reliable sealing against water, dust, and air infiltration in automotive and construction environments. Its ability to maintain flexibility across a wide temperature range (-40degC to 120degC) makes EPDM the preferred choice for robust weatherstripping solutions.
Key Performance Comparisons: HSBR vs EPDM
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength compared to ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), making HSBR more durable in high-stress weatherstripping applications. EPDM excels in UV resistance, ozone stability, and flexibility across a wider temperature range (-40degC to 120degC), which enhances weather and aging performance for outdoor exposure. While HSBR provides better oil and chemical resistance, EPDM remains the preferred choice for weatherstripping due to its exceptional weatherability and elastic recovery properties.
Weather Resistance and Durability
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits superior weather resistance due to its enhanced saturation, making it highly resistant to ozone, UV radiation, and oxidation, which are critical factors for effective weatherstripping. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber is also renowned for excellent weather resistance, particularly against UV exposure, ozone, and extreme temperatures, delivering robust durability in outdoor applications. Compared to EPDM, HSBR generally offers better mechanical strength and abrasion resistance, while EPDM provides longer service life in harsh weather conditions, making each material suitable for specific weatherstripping needs based on environmental exposure and mechanical demands.
Flexibility and Compression Set Characteristics
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior flexibility and excellent resistance to compression set, making it highly effective for weatherstripping applications requiring durable sealing under dynamic movement. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) also provides good flexibility but typically exhibits a higher compression set compared to HSBR, leading to potential loss of seal integrity over time. HSBR's enhanced chemical stability and lower permanent deformation make it a preferred choice for long-term weather resistance and consistent gasket performance.
Cost-Effectiveness and Manufacturing Considerations
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and heat stability for weatherstripping applications, often leading to longer service life but at a higher raw material cost compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber. EPDM is favored for its excellent weather, ozone, and UV resistance, combined with lower production costs and easier processing, making it more cost-effective for large-scale manufacturing. Manufacturing considerations highlight EPDM's compatibility with various vulcanization systems and simpler compounding, reducing cycle times and overall production expenses relative to HSBR.
Common Applications in Weatherstripping
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) is widely used in weatherstripping applications requiring excellent abrasion resistance and low-temperature flexibility, such as automotive door seals and window gaskets. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in outdoor weatherstripping due to its superior resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures, making it ideal for roofing seals, HVAC system gaskets, and exterior door seals. Both materials provide effective sealing solutions, but EPDM is preferred for prolonged exposure to harsh environmental conditions.
Choosing the Right Rubber Material for Weatherstripping Needs
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and enhanced chemical stability, making it ideal for weatherstripping applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions and oils. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in ozone, UV, and weather resistance, providing superior durability in outdoor weatherstripping applications with extreme temperature fluctuations. Selecting the right rubber material depends on the specific exposure factors, with HSBR preferred for chemical resilience and EPDM favored for long-term outdoor weather protection.
Infographic: Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Weatherstripping
 azmater.com
azmater.com