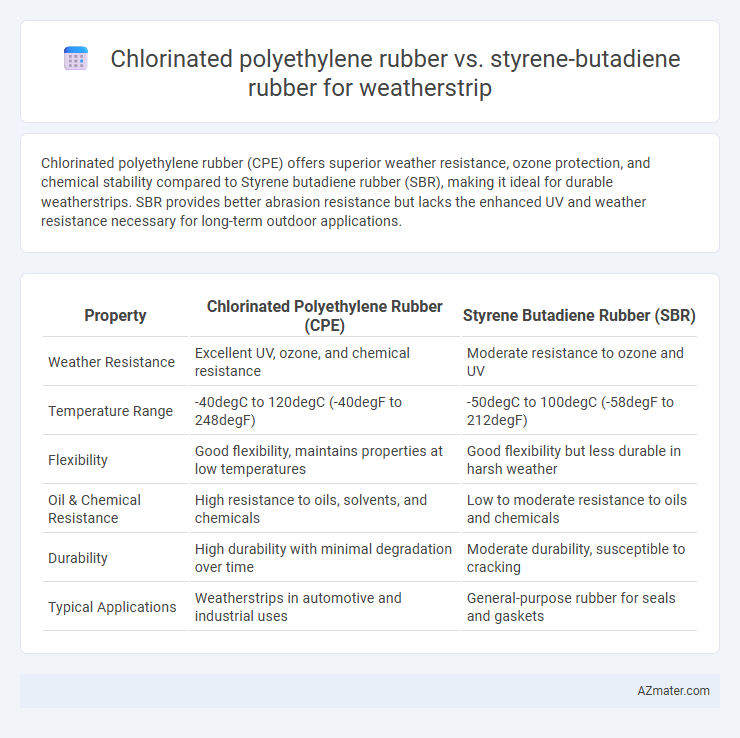
Chlorinated polyethylene rubber (CPE) offers superior weather resistance, ozone protection, and chemical stability compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for durable weatherstrips. SBR provides better abrasion resistance but lacks the enhanced UV and weather resistance necessary for long-term outdoor applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorinated Polyethylene Rubber (CPE) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Weather Resistance | Excellent UV, ozone, and chemical resistance | Moderate resistance to ozone and UV |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) | -50degC to 100degC (-58degF to 212degF) |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility, maintains properties at low temperatures | Good flexibility but less durable in harsh weather |
| Oil & Chemical Resistance | High resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals | Low to moderate resistance to oils and chemicals |
| Durability | High durability with minimal degradation over time | Moderate durability, susceptible to cracking |
| Typical Applications | Weatherstrips in automotive and industrial uses | General-purpose rubber for seals and gaskets |
Introduction to Weatherstrip Materials
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) rubber offers superior weather resistance, chemical stability, and flexibility, making it ideal for weatherstripping applications exposed to harsh outdoor environments. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but has lower resistance to ozone, UV, and temperature extremes compared to CPE. The choice between CPE and SBR for weatherstrip materials depends on specific performance requirements like durability, weather exposure, and environmental conditions.
Overview of Chlorinated Polyethylene Rubber (CPE)
Chlorinated Polyethylene Rubber (CPE) is a highly durable synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, chemicals, and UV radiation, making it ideal for weatherstrip applications. Its superior flexibility and toughness at low temperatures, combined with good oil and acid resistance, outperform many conventional rubbers in outdoor environmental sealing. CPE's chlorine content enhances flame retardancy and improves its overall lifespan in harsh conditions compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR).
Overview of Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic rubber widely used in weatherstrip applications due to its excellent abrasion resistance and good aging stability compared to natural rubber. It offers moderate resistance to heat, oxidation, and ozone, making it suitable for automotive and industrial weatherseals exposed to varying environmental conditions. SBR's cost-effectiveness and versatile mechanical properties provide a practical alternative to chlorinated polyethylene rubber, especially where flexibility and durability are essential.
Comparative Weather Resistance: CPE vs SBR
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) rubber demonstrates superior weather resistance compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), exhibiting enhanced resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and oxidative degradation. CPE maintains flexibility and physical properties under prolonged exposure to harsh environmental conditions, making it ideal for weatherstripping applications subjected to extreme weather. In contrast, SBR tends to harden and crack over time when exposed to sunlight and ozone, reducing its durability and lifespan in outdoor sealing contexts.
Flexibility and Elasticity Under Temperature Variations
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) rubber exhibits superior flexibility and elasticity under a wide temperature range, maintaining performance in extreme cold and heat, making it ideal for weatherstrip applications exposed to varying climates. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate elasticity but tends to stiffen and lose flexibility at low temperatures, limiting its effectiveness for weatherstripping in colder environments. CPE's enhanced thermal stability and resistance to weathering outperform SBR, ensuring longer-lasting seals and better performance in temperature fluctuations.
Chemical Resistance: How CPE and SBR Perform
Chlorinated polyethylene rubber (CPE) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), especially against oils, acids, and alkalis, making it ideal for weatherstrip applications exposed to harsh environmental chemicals. SBR offers moderate resistance but tends to degrade faster when exposed to ozone, oils, and hydrocarbons, limiting its performance in chemically aggressive conditions. The enhanced molecular structure of CPE provides better durability and longevity, ensuring effective sealing and protection in weatherstrips subjected to industrial pollutants and chemical exposure.
Durability and Longevity in Outdoor Applications
Chlorinated polyethylene rubber (CPE) exhibits superior resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and chemical exposure, making it highly durable for outdoor weatherstrip applications. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers good abrasion resistance but degrades faster under prolonged sunlight and ozone exposure, limiting its longevity in harsh outdoor environments. Therefore, CPE outperforms SBR in maintaining structural integrity and flexibility over extended outdoor use, ensuring longer service life in weatherstripping.
Cost Considerations and Economic Impact
Chlorinated polyethylene rubber (CPE) generally offers a higher initial material cost compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), but its superior weather resistance and durability can reduce long-term maintenance and replacement expenses in weatherstrip applications. SBR presents a more cost-effective option upfront due to lower raw material prices but may incur higher lifecycle costs from faster degradation under UV and ozone exposure. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that CPE's economic impact favors environments demanding extended weatherstrip longevity despite higher initial investment.
Environmental and Safety Aspects
Chlorinated polyethylene rubber (CPE) offers superior chemical resistance and UV stability in weatherstripping applications, reducing the risk of degradation and environmental release of harmful compounds compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR). CPE's low permeability to gases and resistance to ozone contribute to longer service life, enhancing safety by minimizing maintenance frequency and exposure to replacement materials. In contrast, SBR can emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during aging, posing environmental and health concerns, making CPE a more sustainable and safer choice for weatherstrips.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Weatherstrip Applications
Chlorinated polyethylene rubber (CPE) offers superior resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and various weather conditions, making it ideal for weatherstrip applications exposed to harsh environments. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility but is less resistant to ozone and UV damage, limiting its durability in outdoor weatherstrips. Selecting the right rubber involves prioritizing CPE for long-term outdoor performance and SBR for applications requiring cost-effective flexibility and wear resistance.
Infographic: Chlorinated polyethylene rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Weatherstrip
 azmater.com
azmater.com