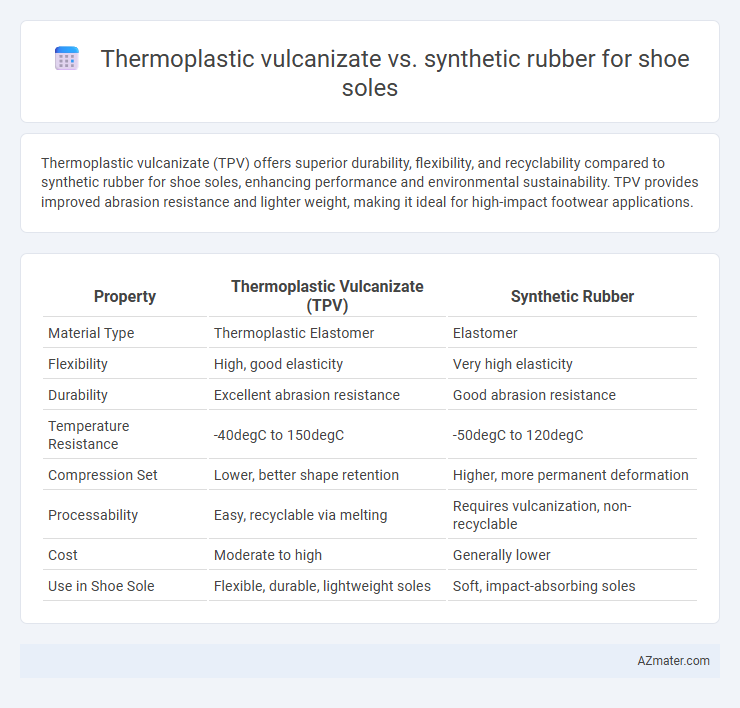
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior durability, flexibility, and recyclability compared to synthetic rubber for shoe soles, enhancing performance and environmental sustainability. TPV provides improved abrasion resistance and lighter weight, making it ideal for high-impact footwear applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV) | Synthetic Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Elastomer | Elastomer |
| Flexibility | High, good elasticity | Very high elasticity |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion resistance | Good abrasion resistance |
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 150degC | -50degC to 120degC |
| Compression Set | Lower, better shape retention | Higher, more permanent deformation |
| Processability | Easy, recyclable via melting | Requires vulcanization, non-recyclable |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower |
| Use in Shoe Sole | Flexible, durable, lightweight soles | Soft, impact-absorbing soles |
Introduction: Importance of Shoe Sole Materials
Shoe sole materials significantly impact comfort, durability, and performance, making the choice between thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) and synthetic rubber critical for footwear design. TPV offers enhanced flexibility, chemical resistance, and recyclability, while synthetic rubber provides superior abrasion resistance and elasticity. Selecting the appropriate material optimizes sole resilience, traction, and overall wear life in various environmental conditions.
Overview of Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV)
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) is a high-performance elastomer combining the flexibility of rubber with the processability of thermoplastics, making it ideal for shoe sole applications. TPVs offer excellent abrasion resistance, superior elasticity, and enhanced chemical stability compared to traditional synthetic rubber materials such as SBR or NBR. Their recyclable nature and ability to be molded repeatedly under heat provide manufacturers with cost-effective, durable, and sustainable options for producing comfortable and long-lasting shoe soles.
Overview of Synthetic Rubber
Synthetic rubber, commonly used for shoe soles, offers exceptional elasticity, abrasion resistance, and durability, making it suitable for demanding footwear applications. Unlike thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV), synthetic rubber maintains flexibility over a wide temperature range and provides superior grip on various surfaces. Popular types like styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and nitrile rubber (NBR) enhance outsole performance by resisting oil, chemicals, and wear.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) exhibit superior abrasion resistance and enhanced flexibility compared to conventional synthetic rubber, making them ideal for durable shoe soles. TPVs typically offer higher tensile strength and better elongation at break, ensuring prolonged wear and comfort during use. In contrast, synthetic rubber soles may provide better shock absorption but often lack the resilience and repeated deformation resistance characteristic of TPVs.
Flexibility and Comfort
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior flexibility and cushioning compared to synthetic rubber, making it ideal for shoe soles that require enhanced comfort and shock absorption. TPV materials combine the elasticity of vulcanized rubber with the processability of thermoplastics, resulting in lightweight soles that adapt well to foot movement and reduce fatigue. Synthetic rubber soles, while durable and resistant to abrasion, typically provide less flexibility and can feel stiffer during prolonged wear, impacting overall comfort.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior durability and wear resistance compared to synthetic rubber, making it ideal for shoe soles subjected to frequent abrasion and impact. TPV combines the elasticity of vulcanized rubber with the processability of thermoplastics, resulting in enhanced resistance to cracking, deformation, and chemical exposure. Synthetic rubber, while flexible, tends to exhibit faster wear and reduced lifespan under harsh conditions, limiting its effectiveness in high-performance footwear applications.
Production Process and Cost Efficiency
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) are produced through dynamic vulcanization, combining the processing advantages of thermoplastics with the elasticity of rubber, resulting in shorter cycle times and easier recyclability compared to synthetic rubber, which requires prolonged curing in molds. The TPV production process involves melt blending and dynamic cross-linking, enabling continuous manufacturing and reduced energy consumption, whereas synthetic rubber soles often necessitate batch vulcanization with higher labor and energy costs. Cost efficiency favors TPVs due to lower tooling expenses, faster turnaround, and improved material utilization, making them more suitable for high-volume shoe sole production.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) offer enhanced recyclability and lower carbon footprints compared to synthetic rubber, as they can be melted and reshaped multiple times, reducing waste in shoe sole production. Synthetic rubber soles, often derived from petrochemical processes, present significant environmental challenges due to their non-biodegradability and difficulty in recycling, contributing to landfill accumulation. Choosing TPVs for shoe soles supports sustainability efforts by minimizing resource consumption and promoting circular economy principles in footwear manufacturing.
Application Suitability in Footwear Industry
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) offer superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and recyclability compared to synthetic rubber, making them highly suitable for shoe soles requiring durability and lightweight comfort. Synthetic rubbers, such as styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), provide excellent abrasion resistance and elasticity, ideal for high-performance athletic footwear. The footwear industry increasingly favors TPVs for casual and sports shoes due to their ease of processing and sustainable lifecycle benefits, while synthetic rubber remains preferred in heavy-duty and specialized footwear applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Shoe Soles
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior flexibility, durability, and recyclability, making it ideal for eco-friendly, high-performance shoe soles. Synthetic rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and cost-efficiency but lacks the temperature resilience and ease of processing found in TPV. Selecting the right material depends on balancing performance requirements, environmental impact, and manufacturing considerations to ensure optimal shoe sole functionality.
Infographic: Thermoplastic vulcanizate vs Synthetic rubber for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com