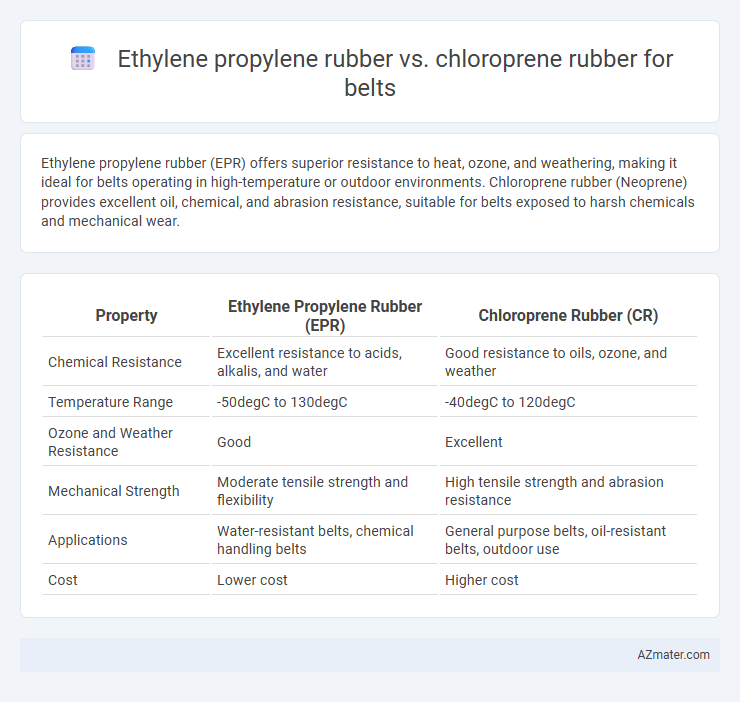
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for belts operating in high-temperature or outdoor environments. Chloroprene rubber (Neoprene) provides excellent oil, chemical, and abrasion resistance, suitable for belts exposed to harsh chemicals and mechanical wear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids, alkalis, and water | Good resistance to oils, ozone, and weather |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 130degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength and flexibility | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance |
| Applications | Water-resistant belts, chemical handling belts | General purpose belts, oil-resistant belts, outdoor use |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Rubber and Chloroprene Rubber
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it suitable for belts operating in harsh outdoor environments. Chloroprene rubber (CR), also known as neoprene, provides superior oil and chemical resistance along with good mechanical strength, ideal for belts exposed to oils and solvents. Both materials deliver durable performance, but EPR excels in thermal stability while CR stands out for chemical and abrasion resistance in belt applications.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) features a saturated hydrocarbon backbone with ethylene and propylene units, providing excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it highly durable for belt applications. Chloroprene rubber (CR) contains chlorine atoms in its polymer chain, imparting superior oil, chemical, and flame resistance while maintaining good mechanical strength and flexibility. The choice between EPR and CR belts depends on exposure conditions, with EPR favored for chemical inertness and CR preferred where oil resistance and flame retardancy are critical.
Mechanical Strength: EPDM vs Chloroprene in Belt Applications
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPDM) exhibits superior tensile strength and excellent resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for belt applications requiring durability and mechanical robustness. Chloroprene rubber (Neoprene) offers good elasticity and moderate mechanical strength but falls short in long-term abrasion resistance compared to EPDM. For heavy-duty belts subjected to continuous stress and wear, EPDM's enhanced mechanical strength and resistance to environmental factors provide a significant performance advantage over chloroprene rubber.
Resistance to Weathering and Ozone
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) exhibits superior resistance to weathering and ozone compared to chloroprene rubber, maintaining flexibility and performance in harsh outdoor environments. EPR's molecular structure resists degradation from UV radiation, ozone, and varying temperatures, making it ideal for belts exposed to prolonged environmental stress. Chloroprene rubber offers moderate resistance but tends to crack or harden under extended ozone exposure, reducing durability in outdoor applications.
Temperature Tolerance: Performance in Extreme Conditions
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) exhibits exceptional temperature tolerance, maintaining flexibility and resilience in extreme heat up to 130degC and cold down to -50degC, making it ideal for belts exposed to harsh environments. Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers moderate temperature resistance, functioning effectively between -40degC and 120degC, but may harden or degrade faster under prolonged high-temperature conditions. EPR's superior thermal stability ensures longer belt lifespan and consistent performance in extreme temperature fluctuations compared to chloroprene rubber.
Oil, Chemicals, and Solvent Resistance
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) exhibits superior resistance to acids, alkalis, and a wide range of aqueous chemicals, making it highly suitable for belts exposed to harsh chemicals and solvents. Chloroprene rubber (CR), known for moderate oil resistance, performs well against fuels and lubricants but degrades faster than EPR when exposed to aggressive solvents and strong chemicals. For applications demanding prolonged exposure to oils, solvents, and harsh chemical environments, EPR offers enhanced durability and longevity compared to chloroprene rubber belts.
Durability and Lifespan in Industrial Belts
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, contributing to its extended durability and longer lifespan in industrial belt applications. Chloroprene rubber (CR), known for its good abrasion resistance and flexibility, performs well in environments requiring moderate chemical resistance and mechanical wear. EPR generally outlasts CR in harsh conditions due to its enhanced aging properties, making it a preferred choice for belts exposed to extreme temperatures and oxidative environments.
Cost and Availability of EPDM vs Chloroprene
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPDM) typically offers lower cost and higher availability compared to chloroprene rubber (CR), making it a preferred choice for belts in budget-sensitive applications. EPDM's widespread production results in a stable supply chain and competitive pricing, whereas chloroprene rubber, despite its superior oil and weather resistance, is generally more expensive and less readily available. Manufacturers often select EPDM belts to optimize cost-efficiency without compromising essential performance criteria in general industrial uses.
Application Suitability: Which Rubber for Which Belt?
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) excels in applications requiring excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and water, making it ideal for conveyor belts exposed to outdoor environments and harsh chemicals. Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers superior abrasion resistance, oil resistance, and mechanical strength, fitting well for drive and timing belts in automotive and industrial machinery. Selecting EPR is optimal for belts in wet or corrosive conditions, while CR suits applications demanding durability against wear, oil exposure, and mechanical stress.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior sustainability due to its excellent resistance to weathering and ozone, enabling longer belt life and reduced material waste in industrial applications. Chloroprene rubber, while effective in mechanical durability and chemical resistance, relies on more energy-intensive manufacturing processes and contains chlorine, which can lead to hazardous byproducts during disposal. Choosing EPR belts supports eco-friendly practices by minimizing environmental impact through lower emissions and easier recycling options.
Infographic: Ethylene propylene rubber vs Chloroprene rubber for Belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com