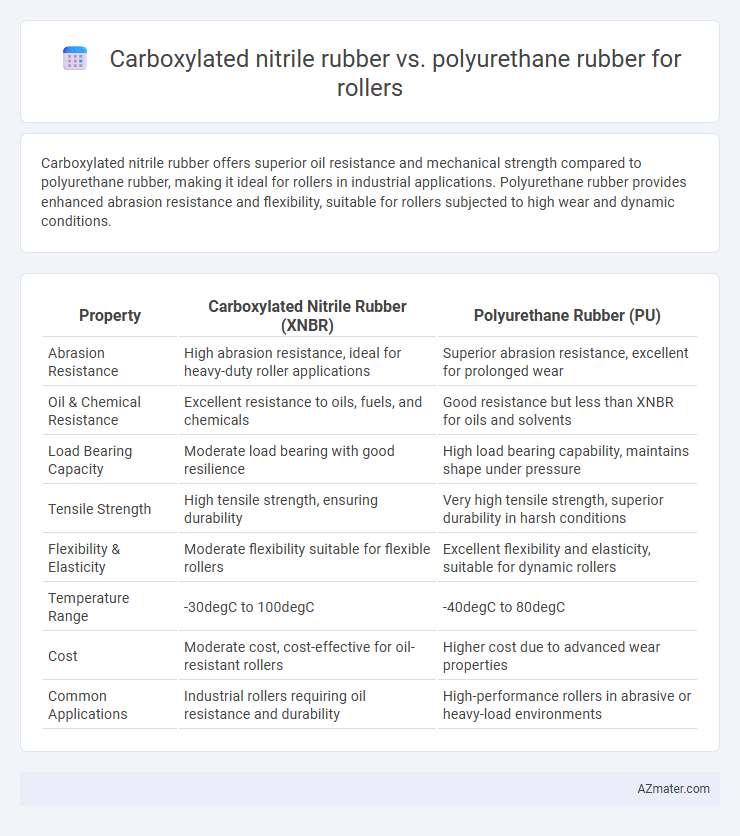
Carboxylated nitrile rubber offers superior oil resistance and mechanical strength compared to polyurethane rubber, making it ideal for rollers in industrial applications. Polyurethane rubber provides enhanced abrasion resistance and flexibility, suitable for rollers subjected to high wear and dynamic conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Abrasion Resistance | High abrasion resistance, ideal for heavy-duty roller applications | Superior abrasion resistance, excellent for prolonged wear |
| Oil & Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Good resistance but less than XNBR for oils and solvents |
| Load Bearing Capacity | Moderate load bearing with good resilience | High load bearing capability, maintains shape under pressure |
| Tensile Strength | High tensile strength, ensuring durability | Very high tensile strength, superior durability in harsh conditions |
| Flexibility & Elasticity | Moderate flexibility suitable for flexible rollers | Excellent flexibility and elasticity, suitable for dynamic rollers |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 100degC | -40degC to 80degC |
| Cost | Moderate cost, cost-effective for oil-resistant rollers | Higher cost due to advanced wear properties |
| Common Applications | Industrial rollers requiring oil resistance and durability | High-performance rollers in abrasive or heavy-load environments |
Introduction to Roller Material Selection
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, abrasion durability, and temperature tolerance, making it ideal for rollers operating in harsh industrial environments. Polyurethane rubber excels in wear resistance, load-bearing capacity, and elasticity, which enhances roller performance in applications requiring high mechanical strength and resilience. Selecting the appropriate roller material depends on specific operational demands such as exposure to oils, chemicals, and mechanical stress to optimize roller lifespan and efficiency.
Overview of Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance and improved tensile strength compared to standard nitrile rubber, making it ideal for roller applications subjected to high mechanical stress. The presence of carboxyl groups increases crosslink density, resulting in superior oil resistance, low gas permeability, and increased durability under harsh chemical environments. XNBR rollers provide excellent performance in industries such as printing, packaging, and automotive, where resistance to fuels, oils, and solvents is critical.
Key Properties of Polyurethane Rubber
Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and elasticity compared to carboxylated nitrile rubber, making it ideal for rollers in high-wear applications. Its excellent load-bearing capacity and resistance to oils, chemicals, and temperature variations enhance roller durability and performance in industrial environments. The material's ability to maintain dimensional stability under stress further solidifies its advantage for long-term roller usage.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) demonstrates superior chemical resistance against aliphatic hydrocarbons, oils, and fuels compared to polyurethane rubber, making it ideal for applications exposed to aggressive chemical environments. Polyurethane rubber excels in resistance to abrasives, solvents, and has better performance against aromatic hydrocarbons but is less resistant to oils and greases than XNBR. Selecting between XNBR and polyurethane rollers depends on the specific chemical exposure, with XNBR preferred for oil and fuel-rich conditions and polyurethane favored for wear resistance and solvent exposure.
Abrasion and Wear Performance
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior abrasion resistance compared to polyurethane rubber, making it ideal for rollers subjected to high friction and mechanical stress. XNBR's enhanced wear performance is due to its chemical crosslinking and polar carboxyl groups, which improve tensile strength and resilience. Polyurethane rubber offers good abrasion resistance but generally wears faster under continuous heavy load and abrasive conditions compared to carboxylated nitrile rubber.
Load-Bearing Capacity Differences
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior load-bearing capacity compared to polyurethane rubber due to its enhanced tensile strength and stiffness, making it ideal for heavy-duty roller applications. Polyurethane rubber offers excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility but generally has lower compressive strength, limiting its performance under high static loads. For rollers requiring sustained heavy loads and impact resistance, XNBR provides greater durability and load-bearing efficiency than polyurethane counterparts.
Temperature Tolerance and Stability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers excellent temperature tolerance with operational ranges typically from -40degC to 120degC, maintaining superior mechanical stability in high-temperature environments. Polyurethane rubber excels in higher temperature resistance, often enduring continuous use up to 130degC and providing exceptional abrasion resistance and dimensional stability under thermal stress. For roller applications requiring consistent performance in elevated temperatures and mechanical wear, polyurethane rubber generally delivers enhanced thermal stability and durability compared to carboxylated nitrile rubber.
Cost-Effectiveness and Longevity
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to polyurethane rubber, making it a cost-effective choice for rollers in harsh industrial environments. XNBR rollers typically require less frequent replacement due to enhanced wear and abrasion resistance, resulting in lower long-term maintenance costs. Polyurethane rubber, while initially cheaper, tends to degrade faster under mechanical stress, reducing its overall lifespan and increasing total cost of ownership.
Application Suitability in Industrial Rollers
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers excellent oil resistance and mechanical strength, making it highly suitable for rollers in heavy industrial environments such as oil processing and automotive manufacturing. Polyurethane rubber excels in abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, ideal for high-wear applications like printing presses and conveyor rollers. The choice between XNBR and polyurethane depends on factors such as chemical exposure and mechanical stress specific to industrial roller applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Rollers
Carboxylated nitrile rubber offers excellent oil and chemical resistance, making it ideal for rollers exposed to harsh industrial environments. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, suited for applications requiring durability and impact resistance. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific operational demands, balancing chemical exposure with mechanical wear to optimize roller performance and longevity.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Roller
 azmater.com
azmater.com