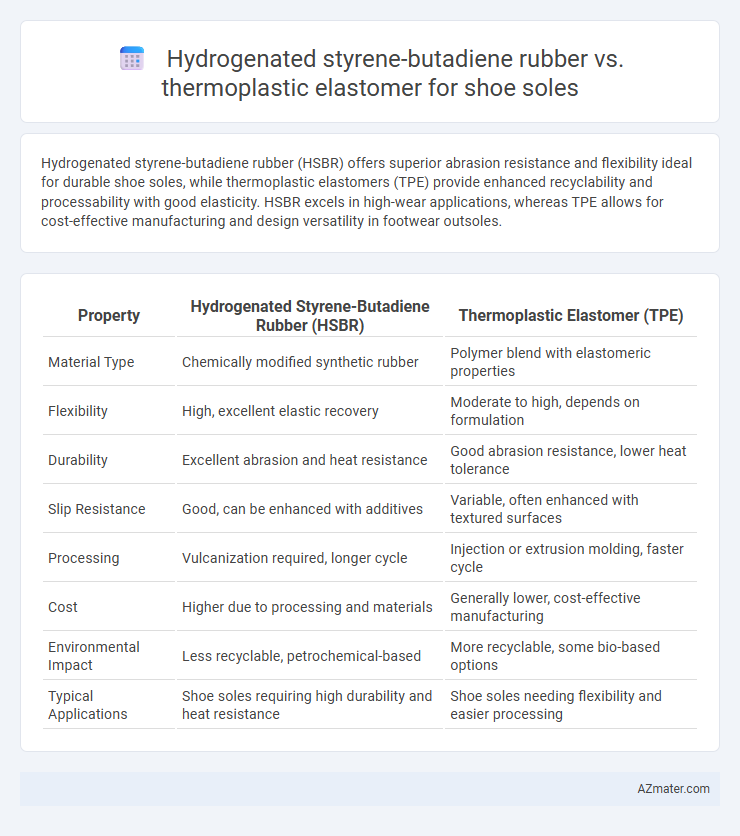
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and flexibility ideal for durable shoe soles, while thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) provide enhanced recyclability and processability with good elasticity. HSBR excels in high-wear applications, whereas TPE allows for cost-effective manufacturing and design versatility in footwear outsoles.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) | Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Chemically modified synthetic rubber | Polymer blend with elastomeric properties |
| Flexibility | High, excellent elastic recovery | Moderate to high, depends on formulation |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion and heat resistance | Good abrasion resistance, lower heat tolerance |
| Slip Resistance | Good, can be enhanced with additives | Variable, often enhanced with textured surfaces |
| Processing | Vulcanization required, longer cycle | Injection or extrusion molding, faster cycle |
| Cost | Higher due to processing and materials | Generally lower, cost-effective manufacturing |
| Environmental Impact | Less recyclable, petrochemical-based | More recyclable, some bio-based options |
| Typical Applications | Shoe soles requiring high durability and heat resistance | Shoe soles needing flexibility and easier processing |
Overview of Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) and Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
Hydrogenated Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance, enhanced heat aging properties, and excellent flexibility, making it ideal for durable and long-lasting shoe soles. Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) combine the flexibility and resilience of rubber with the processability of plastics, providing good cushioning, lightweight characteristics, and ease of recycling for eco-friendly footwear design. Both materials offer distinct advantages in shoe sole manufacturing, with HSBR favoring performance and durability, while TPE emphasizes versatility and sustainability.
Key Chemical and Structural Differences
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) features a saturated backbone from hydrogenation, enhancing its resistance to heat, oxidation, and aging compared to conventional SBR. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) consist of a block copolymer structure combining rubbery and thermoplastic segments, enabling melt processability and recyclability, unlike the crosslinked, vulcanized network in HSBR. Key chemical differences include HSBR's saturated polymer chains versus TPE's phase-separated morphology, resulting in distinct mechanical properties and processing methods suitable for durable, flexible shoe soles.
Durability and Wear Resistance Comparison
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior durability and wear resistance compared to thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) due to its enhanced chemical stability and abrasion resistance, making HSBR ideal for high-performance shoe soles subjected to rigorous use. TPE provides flexibility and ease of processing but generally exhibits lower resistance to wear and environmental degradation, resulting in reduced longevity under heavy or abrasive conditions. Performance testing indicates HSBR soles maintain structural integrity and cushioning properties longer, supporting extended shoe lifespan in demanding environments.
Flexibility and Comfort in Shoe Sole Applications
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance, making it highly suitable for durable shoe soles that require long-lasting comfort. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) provide superior elastic recovery and cushioning, enhancing shock absorption and overall comfort in footwear applications. Compared to HSBR, TPEs allow for more design versatility and lightweight comfort while maintaining adequate flexibility for everyday shoe sole performance.
Traction and Slip Resistance Performance
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior traction and slip resistance for shoe soles due to its enhanced abrasion resistance and flexibility under various temperatures, providing consistent grip on wet and dry surfaces. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) provide moderate slip resistance with good elasticity but generally lack the durability and firm surface contact that HSBR compounds achieve, especially in high-friction environments. The higher wear resistance and resilience of HSBR make it more effective for outsoles requiring reliable traction and long-term slip performance.
Weight and Design Versatility
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers a lightweight option for shoe soles with enhanced durability and resistance to wear and heat, contributing to longer-lasting performance. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) provide superior design versatility through easy molding and customization, allowing for intricate patterns and multiple color options that improve aesthetic appeal. While HSBR emphasizes durability and consistent lightweight properties, TPE excels in producing complex, flexible designs without significantly increasing the sole's weight.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for shoe soles requiring durability and comfort, while demanding complex vulcanization processes that increase production time and cost. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) provide easier processing through injection molding and recyclability, enabling faster manufacturing cycles and reduced waste, but may offer lower abrasion resistance compared to HSBR. Selecting between HSBR and TPE requires balancing manufacturing speed and cost-effectiveness against performance criteria such as wear resistance and flexibility in shoe sole applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) exhibits durability and chemical resistance but is derived from non-renewable petroleum resources, contributing to environmental concerns due to limited biodegradability and challenges in recycling. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), often containing varied polymer blends, offer improved recyclability and potential for lower environmental impact through easier reprocessing and reduced waste generation in shoe sole production. Choosing TPE can enhance sustainability efforts by enabling circular material use, whereas HSBR soles may contribute to longer product lifespans but at the cost of end-of-life ecological considerations.
Cost-effectiveness in Large-scale Production
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it a preferred material in high-performance shoe soles, but its production cost is generally higher than thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) due to complex hydrogenation processes. Thermoplastic elastomers provide cost-effective manufacturing benefits in large-scale production through faster molding cycles and recyclability, reducing overall material waste and energy consumption. For large-scale shoe sole manufacturing, TPEs deliver better cost-efficiency, whereas HSBR justifies higher expenses with enhanced durability and performance in premium footwear applications.
Best Applications and Market Trends for Shoe Soles
Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber (HSBR) offers superior abrasion resistance, flexibility, and heat stability, making it ideal for high-performance athletic and industrial shoe soles requiring durability and impact absorption. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) provide lightweight, eco-friendly, and recyclable properties, favored in casual and fashion footwear due to their easy processing and design versatility. Market trends emphasize increased demand for sustainable materials like TPEs while maintaining performance standards, positioning HSBR for specialized use in heavy-duty and sports applications.
Infographic: Hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber vs Thermoplastic elastomer for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com