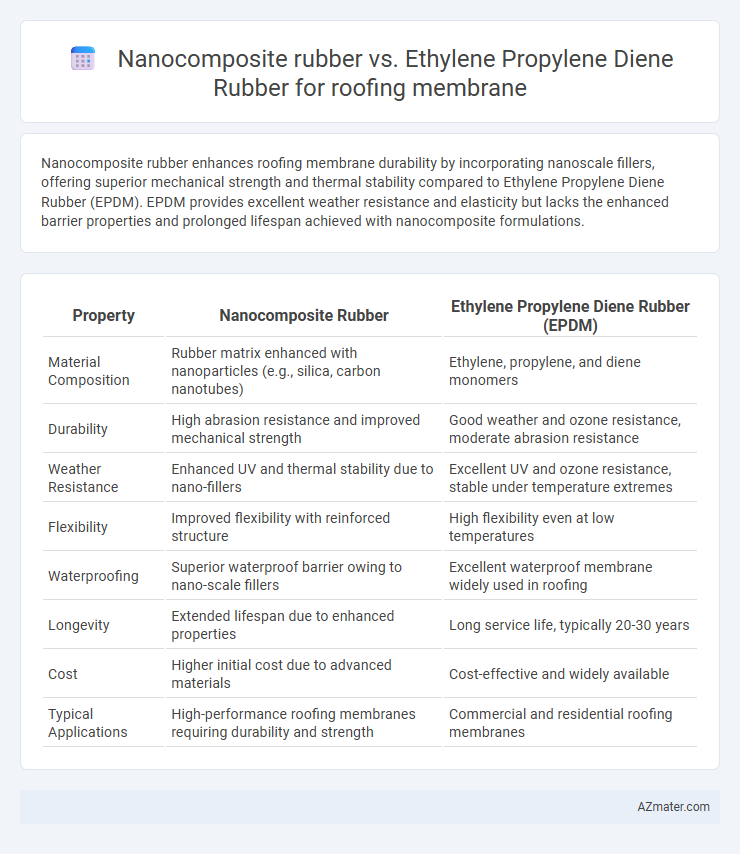
Nanocomposite rubber enhances roofing membrane durability by incorporating nanoscale fillers, offering superior mechanical strength and thermal stability compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM). EPDM provides excellent weather resistance and elasticity but lacks the enhanced barrier properties and prolonged lifespan achieved with nanocomposite formulations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanocomposite Rubber | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Rubber matrix enhanced with nanoparticles (e.g., silica, carbon nanotubes) | Ethylene, propylene, and diene monomers |
| Durability | High abrasion resistance and improved mechanical strength | Good weather and ozone resistance, moderate abrasion resistance |
| Weather Resistance | Enhanced UV and thermal stability due to nano-fillers | Excellent UV and ozone resistance, stable under temperature extremes |
| Flexibility | Improved flexibility with reinforced structure | High flexibility even at low temperatures |
| Waterproofing | Superior waterproof barrier owing to nano-scale fillers | Excellent waterproof membrane widely used in roofing |
| Longevity | Extended lifespan due to enhanced properties | Long service life, typically 20-30 years |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced materials | Cost-effective and widely available |
| Typical Applications | High-performance roofing membranes requiring durability and strength | Commercial and residential roofing membranes |
Introduction to Roofing Membranes
Roofing membranes serve as critical barriers that protect buildings from weather elements, with performance depending heavily on material properties. Nanocomposite rubber incorporates nanoparticles to enhance mechanical strength, durability, and UV resistance compared to traditional Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, which offers excellent weatherability and flexibility but may fall short in advanced reinforcement. Selecting nanocomposite rubber for roofing membranes can result in longer service life, improved tensile strength, and superior resistance to environmental degradation relative to standard EPDM options.
Overview of Nanocomposite Rubber
Nanocomposite rubber integrates nanoscale fillers such as clay, silica, or carbon nanotubes into a rubber matrix, enhancing mechanical strength, thermal stability, and UV resistance compared to conventional Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber used in roofing membranes. These nanoscale reinforcements improve impermeability and weathering durability, leading to prolonged membrane lifespan and reduced maintenance costs. The superior barrier properties and improved elasticity of nanocomposite rubber make it an advanced alternative for roofing applications demanding high performance under extreme environmental conditions.
Understanding Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) is widely used for roofing membranes due to its exceptional weather resistance, UV stability, and excellent elasticity over a broad temperature range. Nanocomposite rubber enhances traditional rubber by incorporating nanoscale fillers, improving mechanical strength, thermal stability, and durability compared to standard EPDM. EPDM remains favored for roofing because of its cost-effectiveness and proven long-term performance in resisting ozone, moisture, and temperature fluctuations.
Comparative Material Properties
Nanocomposite rubber exhibits enhanced mechanical strength, superior thermal stability, and improved UV resistance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it highly suitable for roofing membranes exposed to extreme weather conditions. EPDM offers excellent flexibility, ozone resistance, and cost-effectiveness but generally has lower tensile strength and thermal endurance than nanocomposite variants. The integration of nanoparticles in nanocomposite rubber significantly increases abrasion resistance and elongation properties, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance for roofing applications.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Nanocomposite rubber roofing membranes demonstrate superior durability due to enhanced tensile strength and resistance to cracking, outperforming standard Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber in long-term performance. The incorporation of nanomaterials in nanocomposite rubber significantly improves weather resistance by providing exceptional UV, ozone, and thermal stability, making it more resilient under harsh environmental conditions. EPDM membranes offer good weather resistance but typically show reduced mechanical properties and faster degradation compared to nanocomposite variants, especially in extreme climates.
Flexibility and Elasticity Performance
Nanocomposite rubber offers enhanced flexibility and elasticity compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber due to the uniform dispersion of nanoscale fillers that improve polymer chain mobility and stress distribution. EPDM exhibits good elasticity and weather resistance but can experience reduced flexibility at lower temperatures, while nanocomposite rubber maintains superior elasticity over a wider temperature range. The integration of nanofillers in nanocomposite rubber results in improved crack resistance and elongation performance, making it a more durable option for roofing membrane applications requiring long-term flexibility.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Nanocomposite rubber roofing membranes offer enhanced durability and flexibility compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), enabling easier installation on complex roof geometries and reducing the risk of tearing. EPDM membranes require specialized adhesives and seam tapes during installation, whereas nanocomposite rubber materials often utilize advanced self-adhesive technologies that simplify application and shorten project timelines. Maintenance of nanocomposite rubber membranes benefits from superior UV and chemical resistance, leading to fewer repairs and longer service life compared to EPDM, which may need more frequent inspections and patching to address weathering and surface degradation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanocomposite rubber roofing membranes exhibit enhanced durability and reduced permeability, leading to longer service life and minimized material replacement, which significantly lowers environmental impact compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber. EPDM membranes, while widely used and recyclable, often require more frequent replacement due to lower resistance to UV degradation and weathering, increasing waste and environmental footprint. The incorporation of nanomaterials in nanocomposite rubber improves thermal insulation and reduces heat island effects, contributing to greater sustainability in roofing applications.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Nanocomposite rubber roofing membranes exhibit superior durability and weather resistance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, leading to longer service life and reduced maintenance costs. While initial costs for nanocomposite rubber materials can be higher, their enhanced mechanical properties and UV resistance often result in lower total lifecycle expenses. EPDM remains a cost-effective choice for budget-sensitive projects due to its established manufacturing processes and widespread availability, despite higher susceptibility to degradation over time.
Future Trends in Roofing Membrane Materials
Nanocomposite rubber offers enhanced mechanical strength, UV resistance, and chemical stability compared to traditional Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, driving its growing adoption in roofing membranes. Innovations in nanomaterials enable the creation of lighter, more durable, and energy-efficient membranes that extend roof lifespan and reduce maintenance costs. Future trends indicate a shift toward multifunctional nanocomposite membranes integrating self-healing properties and advanced thermal insulation, surpassing the performance capabilities of conventional EPDM roofing solutions.
Infographic: Nanocomposite rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Roofing membrane
 azmater.com
azmater.com