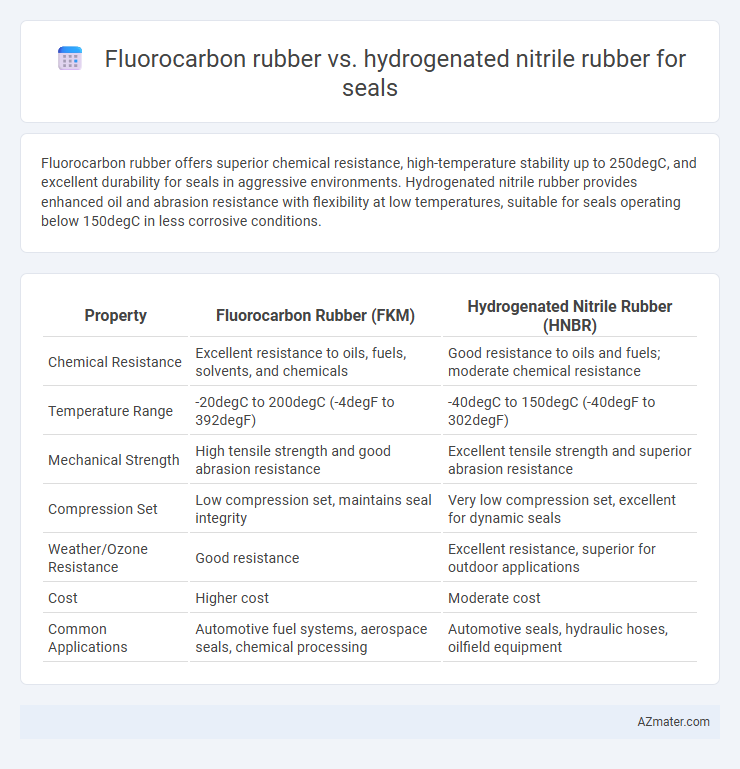
Fluorocarbon rubber offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 250degC, and excellent durability for seals in aggressive environments. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber provides enhanced oil and abrasion resistance with flexibility at low temperatures, suitable for seals operating below 150degC in less corrosive conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM) | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, solvents, and chemicals | Good resistance to oils and fuels; moderate chemical resistance |
| Temperature Range | -20degC to 200degC (-4degF to 392degF) | -40degC to 150degC (-40degF to 302degF) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and good abrasion resistance | Excellent tensile strength and superior abrasion resistance |
| Compression Set | Low compression set, maintains seal integrity | Very low compression set, excellent for dynamic seals |
| Weather/Ozone Resistance | Good resistance | Excellent resistance, superior for outdoor applications |
| Cost | Higher cost | Moderate cost |
| Common Applications | Automotive fuel systems, aerospace seals, chemical processing | Automotive seals, hydraulic hoses, oilfield equipment |
Introduction to Fluorocarbon and Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) is a synthetic elastomer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 200degC, and excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents, making it ideal for demanding sealing applications in aerospace and automotive industries. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior mechanical strength, resistance to heat (up to 150degC), ozone, and aging due to its hydrogenated molecular structure, providing enhanced durability in hydraulic seals and oilfield equipment. Both materials deliver unique properties tailored for sealing performance, with FKM excelling in aggressive chemical environments and HNBR offering robust wear resistance and elasticity.
Key Properties of Fluorocarbon Rubber Seals
Fluorocarbon rubber seals exhibit exceptional chemical resistance, maintaining stability in fuels, oils, and aggressive chemicals at temperatures ranging from -26degC to 204degC, making them ideal for automotive and aerospace applications. Their superior heat resistance and low gas permeability provide enhanced durability compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber seals, which perform well under lower temperature conditions (-40degC to 150degC) but have limited chemical exposure tolerance. Fluorocarbon seals also offer excellent compression set resistance, ensuring reliable long-term sealing performance in harsh environments.
Essential Characteristics of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber Seals
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) seals exhibit exceptional resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals, maintaining durability in temperatures ranging from -40degC to 150degC, which surpasses many fluorocarbon rubber capabilities. HNBR's superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance ensure longer service life and reliability in dynamic sealing applications, particularly in automotive and industrial environments. Its resistance to swell and compression set positions HNBR seals as cost-effective and high-performance alternatives to fluorocarbon rubber in demanding sealing conditions.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits superior chemical resistance to a wide range of aggressive fluids, including hydrocarbons, acids, oils, and solvents, making it ideal for harsh chemical environments. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and heat but is less resistant to aromatic and chlorinated solvents compared to FKM. For seals exposed to strong chemicals and high temperatures, fluorocarbon rubber provides a longer service life and enhanced durability over hydrogenated nitrile rubber.
Temperature Range and Performance
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits excellent resistance to high temperatures, typically operating between -26degC to 204degC, making it ideal for seals exposed to extreme heat and aggressive chemicals. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) performs well within a temperature range of -40degC to 150degC, offering superior mechanical properties and enhanced resistance to abrasion and compression set compared to standard nitriles. FKM seals maintain integrity in harsh chemical environments with stable elasticity at elevated temperatures, while HNBR seals provide durable performance in dynamic applications requiring flexibility and resistance to oils and fuels.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) exhibits superior mechanical strength with high tensile and tear resistance, making it ideal for seals exposed to harsh chemicals and extreme temperatures. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and maintains elasticity under high pressure, ensuring durability in dynamic sealing applications. FKM outperforms HNBR in oxidative and thermal stability, while HNBR excels in resistance to swelling from fuels and oils, influencing seal lifespan based on operating environment.
Cost Considerations for Seal Applications
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) typically presents higher initial costs compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR), driven by its superior chemical resistance and temperature tolerance in demanding seal applications. HNBR offers a cost-effective alternative with excellent resistance to oils, heat, and abrasion, making it suitable for moderate environments while maintaining economic efficiency. Evaluating the total lifecycle cost, including durability and maintenance, often reveals HNBR as a budget-friendly choice without compromising essential performance in less aggressive conditions.
Typical Applications of Fluorocarbon vs. HNBR Seals
Fluorocarbon rubber seals excel in high-temperature environments and exposure to aggressive chemicals, making them ideal for automotive fuel systems, aerospace components, and chemical processing equipment. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) seals offer superior resistance to abrasion, heat, and oil, commonly used in automotive engine seals, oilfield equipment, and industrial hydraulic systems. Choosing between fluorocarbon and HNBR seals depends on the specific application requirements for chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and mechanical durability.
Pros and Cons: Fluorocarbon Rubber vs. HNBR
Fluorocarbon rubber offers excellent chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 200degC, and superior resistance to oils and fuels, making it ideal for harsh automotive and aerospace sealing applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides good mechanical strength, improved abrasion resistance, and operates effectively between -40degC and 150degC but has lower chemical resistance compared to fluorocarbon rubber. While fluorocarbon rubber is more expensive and can be less flexible at low temperatures, HNBR delivers cost-efficiency and better cold temperature flexibility but may degrade faster in aggressive chemical environments.
Choosing the Right Seal Material for Your Needs
Fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) offers exceptional chemical resistance, high temperature tolerance up to 200-250degC, and excellent durability, making it ideal for sealing applications in harsh environments with exposure to oils, fuels, and solvents. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior abrasion resistance, good resistance to heat up to 150-160degC, and excellent mechanical properties, suitable for dynamic seals in automotive and industrial applications requiring high resilience and oxidative stability. Selecting the right seal material depends on specific operating conditions such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress to ensure optimal performance and seal longevity.
Infographic: Fluorocarbon rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile rubber for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com