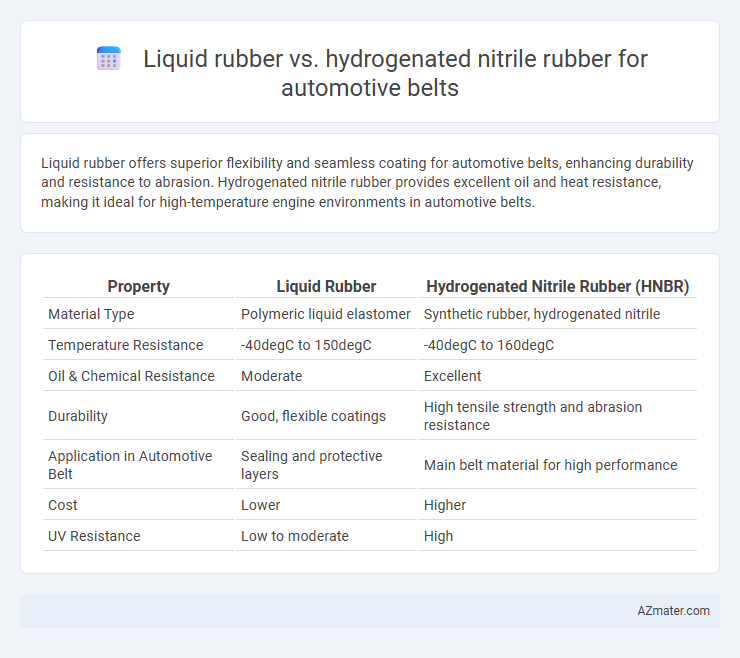
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and seamless coating for automotive belts, enhancing durability and resistance to abrasion. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber provides excellent oil and heat resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature engine environments in automotive belts.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Rubber | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polymeric liquid elastomer | Synthetic rubber, hydrogenated nitrile |
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 150degC | -40degC to 160degC |
| Oil & Chemical Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Durability | Good, flexible coatings | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance |
| Application in Automotive Belt | Sealing and protective layers | Main belt material for high performance |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| UV Resistance | Low to moderate | High |
Introduction to Automotive Belt Materials
Liquid rubber and hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) are both advanced materials widely used in automotive belt manufacturing due to their superior mechanical properties. Liquid rubber offers excellent flexibility and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for dynamic applications where vibration dampening is critical, while HNBR provides exceptional heat, oil, and chemical resistance crucial for prolonged durability in engine environments. Selecting between these materials depends on specific automotive belt requirements such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and expected lifespan.
Overview of Liquid Rubber
Liquid rubber offers exceptional flexibility and seamless application for automotive belts, providing superior resistance to abrasion, weathering, and chemicals compared to traditional hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR). Its ability to form a uniform, durable coating enhances belt longevity and performance under extreme temperature fluctuations typical in automotive environments. This innovative material improves belt elasticity and reduces maintenance, making it a cost-effective solution in automotive manufacturing.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) offers exceptional resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals, making it highly suitable for automotive belt applications where durability and performance under harsh conditions are critical. Unlike Liquid Rubber, HNBR maintains its elasticity and mechanical strength at temperatures up to 150degC, enhancing the belt's longevity and reliability. Its superior abrasion resistance and low compression set contribute to consistent tensioning and reduced maintenance in automotive systems.
Key Performance Properties: Liquid Rubber vs HNBR
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent resistance to abrasion and weathering, making it ideal for automotive belts exposed to dynamic environmental conditions. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides enhanced heat resistance up to 150degC, exceptional oil and chemical resistance, and high tensile strength, ensuring durability in high-temperature engine environments. Key performance properties favor liquid rubber for flexibility and environmental resilience, while HNBR excels in thermal stability and chemical resistance for demanding automotive applications.
Durability and Wear Resistance Comparison
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent wear resistance in automotive belt applications, providing enhanced durability under continuous dynamic stress and temperature variations. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits outstanding resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion, maintaining structural integrity and extending belt lifespan in harsh engine environments. Comparative testing indicates HNBR generally outperforms liquid rubber in long-term wear resistance and durability, especially in high-temperature and chemically aggressive conditions.
Heat and Chemical Resistance in Automotive Applications
Liquid rubber exhibits superior heat resistance, maintaining elasticity and performance in temperatures up to 200degC, making it highly effective for automotive belts exposed to engine heat. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides excellent chemical resistance, especially against oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids, crucial for durability in automotive environments. Combining both materials can optimize performance by balancing thermal stability and chemical resistance for enhanced automotive belt longevity.
Flexibility and Low-Temperature Performance
Liquid rubber exhibits superior flexibility and maintains elasticity at low temperatures, making it ideal for automotive belts exposed to cold climates. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers excellent chemical resistance and high-temperature stability but tends to be less flexible and more rigid in sub-zero conditions. For automotive belts requiring consistent performance in extreme cold, liquid rubber provides enhanced low-temperature flexibility and durability compared to HNBR.
Cost Analysis: Liquid Rubber vs HNBR Belts
Liquid rubber automotive belts often present lower upfront material costs compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) belts, making them attractive for budget-conscious applications. HNBR belts, while more expensive initially, offer superior durability, chemical resistance, and high-temperature performance, potentially reducing replacement frequency and long-term maintenance expenses. Analyzing total cost of ownership usually favors HNBR belts in demanding automotive environments due to their extended service life and reliability despite higher initial investment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Liquid rubber offers superior environmental benefits for automotive belts due to its lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and enhanced recyclability compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR). Hydrogenated nitrile rubber, while chemically resistant and durable, involves more energy-intensive production processes and generates higher carbon footprints. Optimizing automotive belts with liquid rubber can significantly reduce ecological impact and enhance sustainability in the automotive industry.
Choosing the Right Material for Automotive Belt Design
Liquid rubber offers excellent flexibility and strong adhesion properties, making it ideal for complex automotive belt designs requiring seamless coating and enhanced durability. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior heat, oil, and abrasion resistance, extending belt lifespan in high-performance engines exposed to harsh environments. Selecting between liquid rubber and HNBR depends on the specific requirements for flexibility, chemical resistance, and thermal stability in automotive belt applications.
Infographic: Liquid rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile rubber for Automotive belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com