Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength compared to nitrile rubber, making it ideal for high-wear O-ring applications. Nitrile rubber excels in oil and fuel resistance, providing better performance in environments involving petroleum-based fluids.
Table of Comparison
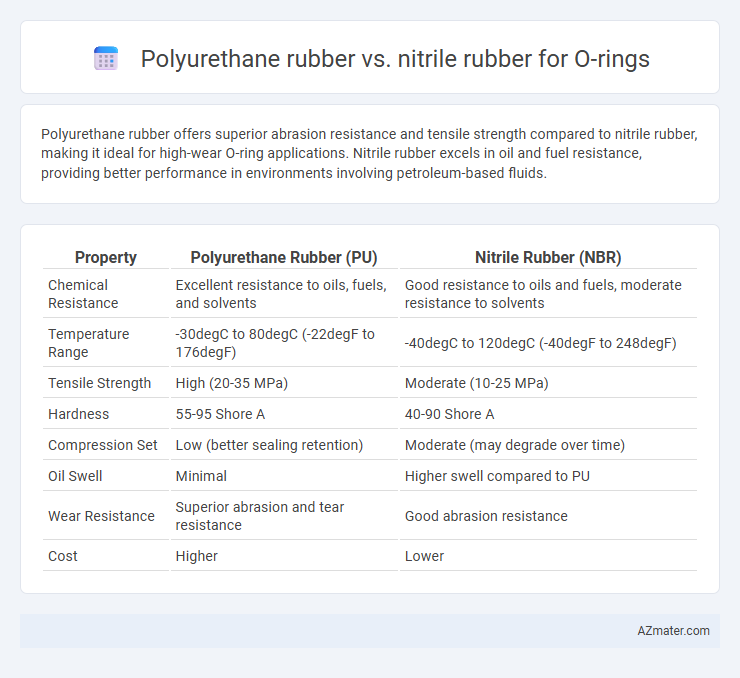
| Property | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents | Good resistance to oils and fuels, moderate resistance to solvents |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 80degC (-22degF to 176degF) | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) |
| Tensile Strength | High (20-35 MPa) | Moderate (10-25 MPa) |
| Hardness | 55-95 Shore A | 40-90 Shore A |
| Compression Set | Low (better sealing retention) | Moderate (may degrade over time) |
| Oil Swell | Minimal | Higher swell compared to PU |
| Wear Resistance | Superior abrasion and tear resistance | Good abrasion resistance |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to O-Ring Materials
O-rings are critical sealing components, and the choice between polyurethane rubber and nitrile rubber significantly impacts performance and durability. Polyurethane rubber offers exceptional abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making it ideal for dynamic sealing applications subjected to mechanical stress. Nitrile rubber, known for its excellent oil and fuel resistance, is preferred in environments where chemical compatibility and temperature resilience up to 120degC are essential.
Overview of Polyurethane Rubber
Polyurethane rubber offers exceptional abrasion resistance and high tensile strength, making it ideal for O-rings in dynamic sealing applications where durability is critical. Its superior resistance to oil, grease, and hydraulic fluids provides enhanced performance in demanding environments compared to nitrile rubber. Polyurethane's elasticity and tear resistance enable longer service life and reliable sealing under high pressure and mechanical stress.
Overview of Nitrile Rubber
Nitrile rubber, also known as Buna-N, is a synthetic elastomer widely used for O-rings due to its excellent resistance to oil, fuel, and chemicals, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications. It has superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and temperature tolerance ranging from -40degC to 120degC, outperforming many other elastomers in sealing performance. Compared to polyurethane rubber, nitrile offers better resistance to petroleum-based fluids but has lower mechanical strength and wear resistance.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Polyurethane rubber offers excellent resistance to abrasion and tear, but its chemical resistance is limited against acids, ketones, and aromatic hydrocarbons, making it less suitable for aggressive chemical environments. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in resistance to oils, fuels, and many hydrocarbons, providing superior chemical stability for O-rings exposed to petroleum-based fluids. When selecting O-rings for chemical applications, nitrile rubber is generally preferred for oil and fuel resistance, while polyurethane suits mechanical wear scenarios but struggles with harsh chemical exposure.
Temperature Tolerance and Environmental Performance
Polyurethane rubber O-rings exhibit excellent abrasion resistance and maintain functional integrity in temperature ranges from -40degF to 200degF, making them suitable for high wear applications with moderate thermal demands. Nitrile rubber O-rings offer superior temperature tolerance, typically from -40degF up to 250degF, and demonstrate excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and many chemicals, enhancing their environmental performance in harsh conditions. While polyurethane excels in mechanical durability, nitrile's broader temperature range and chemical resistance make it a preferred choice for applications requiring robust environmental tolerance.
Mechanical Properties and Wear Resistance
Polyurethane rubber offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to nitrile rubber, making it ideal for high-wear applications in O-rings. Nitrile rubber excels in oil resistance and flexibility at low temperatures but exhibits lower mechanical strength and wear resistance than polyurethane. Selecting between polyurethane and nitrile depends on the operational environment, with polyurethane preferred for heavy-duty mechanical stress and nitrile for oil-exposed seals.
Applications and Industry Suitability
Polyurethane rubber O-rings excel in applications requiring high abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, making them ideal for hydraulic systems, automotive seals, and heavy machinery components. Nitrile rubber O-rings offer superior chemical resistance, especially against oils, fuels, and solvents, suiting them for the petroleum, aerospace, and food processing industries. Selection between these materials depends on the specific environmental exposure and mechanical stress demands of the application.
Cost-Efficiency and Longevity
Polyurethane rubber O-rings offer superior abrasion resistance and longer service life, making them highly cost-efficient in applications subjected to mechanical wear. Nitrile rubber O-rings provide excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids, offering reliable performance at a lower initial cost but typically have shorter longevity under harsh mechanical conditions. Selecting polyurethane or nitrile for O-rings depends on balancing upfront material cost against durability requirements to optimize overall lifecycle expenses.
Pros and Cons of Polyurethane vs Nitrile O-Rings
Polyurethane O-rings offer superior abrasion resistance and high tensile strength, making them ideal for dynamic applications involving repetitive motion or exposure to harsh environments. Nitrile O-rings provide excellent oil and fuel resistance with good mechanical properties, but their performance deteriorates in extreme temperature ranges and they are less resistant to abrasion compared to polyurethane. Polyurethane O-rings tend to have lower chemical resistance and cost more, while nitrile O-rings are more cost-effective and versatile for general-purpose sealing applications.
Choosing the Right O-Ring Material for Your Needs
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making it ideal for high-wear environments requiring durable O-rings. Nitrile rubber excels in oil and fuel resistance, providing reliable sealing performance in automotive and industrial applications exposed to petroleum-based fluids. Selecting the right O-ring material depends on specific factors such as chemical compatibility, temperature range, and mechanical stress to ensure optimal sealing efficiency and longevity.
Infographic: Polyurethane rubber vs Nitrile rubber for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com