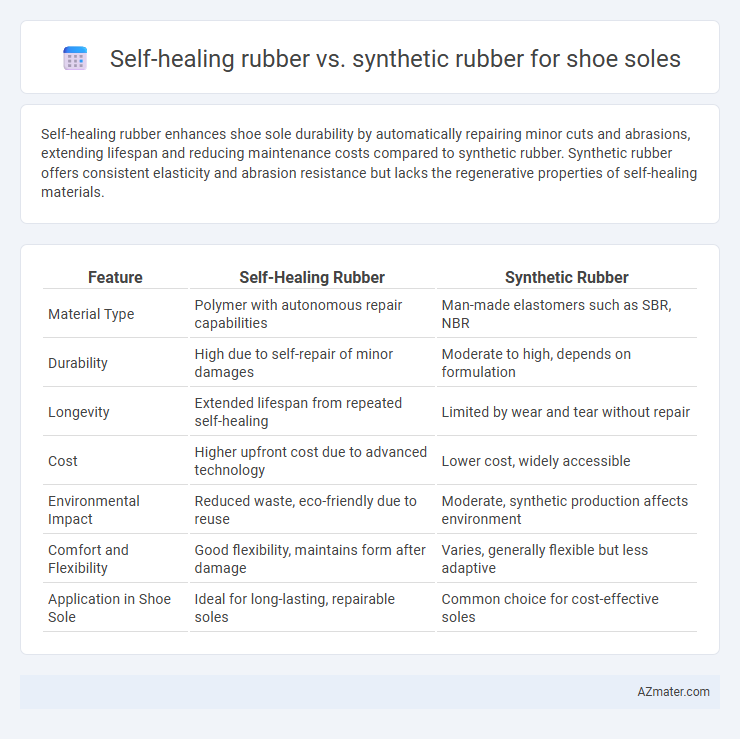
Self-healing rubber enhances shoe sole durability by automatically repairing minor cuts and abrasions, extending lifespan and reducing maintenance costs compared to synthetic rubber. Synthetic rubber offers consistent elasticity and abrasion resistance but lacks the regenerative properties of self-healing materials.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Self-Healing Rubber | Synthetic Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polymer with autonomous repair capabilities | Man-made elastomers such as SBR, NBR |
| Durability | High due to self-repair of minor damages | Moderate to high, depends on formulation |
| Longevity | Extended lifespan from repeated self-healing | Limited by wear and tear without repair |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost due to advanced technology | Lower cost, widely accessible |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced waste, eco-friendly due to reuse | Moderate, synthetic production affects environment |
| Comfort and Flexibility | Good flexibility, maintains form after damage | Varies, generally flexible but less adaptive |
| Application in Shoe Sole | Ideal for long-lasting, repairable soles | Common choice for cost-effective soles |
Introduction to Self-Healing and Synthetic Rubber
Self-healing rubber integrates microcapsules or reversible bonds that enable the material to autonomously repair cuts and abrasions, significantly extending the lifespan of shoe soles. Synthetic rubber, such as styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) or ethylene-propylene-diene monomer (EPDM), offers durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness but lacks inherent self-repair capabilities. Advances in polymer chemistry are driving the development of self-healing rubber compounds, aiming to combine resilience and sustainability for high-performance footwear applications.
Composition and Properties of Self-Healing Rubber
Self-healing rubber for shoe soles typically consists of specialized polymers such as polyurethane or silicone integrated with microcapsules or reversible covalent bonds that enable automatic repair after damage. This composition allows self-healing rubber to recover from cuts or abrasions, maintaining durability and elasticity over time, unlike traditional synthetic rubber which lacks such regenerative properties. Key properties include enhanced longevity, flexibility, and resistance to wear, making self-healing rubber an innovative alternative to conventional synthetic materials in footwear applications.
Key Characteristics of Synthetic Rubber for Shoe Soles
Synthetic rubber used in shoe soles offers excellent durability, abrasion resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for high-performance footwear. Its resistance to heat, oils, and ozone extends the sole's lifespan under various environmental conditions. The material's ability to maintain elasticity and provide strong traction ensures comfort and safety during prolonged use.
Durability Comparison: Self-Healing vs Synthetic Rubber
Self-healing rubber offers enhanced durability for shoe soles by autonomously repairing microcracks and surface damage, extending the lifespan compared to conventional synthetic rubber. Synthetic rubber, while durable and resistant to abrasion, lacks the intrinsic ability to recover from wear and tear, leading to faster degradation under repetitive stress. The self-healing mechanism significantly reduces maintenance needs and improves end-use performance, especially in high-impact and high-flex environments.
Flexibility and Comfort in Footwear Applications
Self-healing rubber offers enhanced durability by autonomously repairing micro-cracks, maintaining flexibility and prolonging comfort in shoe soles. Synthetic rubber provides consistent elasticity and cushioning, essential for shock absorption and foot support in footwear applications. The self-healing properties lead to longer-lasting flexibility, while synthetic rubber ensures reliable comfort during extended wear.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Self-healing rubber for shoe soles offers a significant reduction in environmental impact by extending product lifespan and minimizing waste compared to traditional synthetic rubber, which often relies on fossil fuel-derived materials with higher carbon footprints. The regenerative properties of self-healing rubber reduce the frequency of sole replacements, lowering the consumption of raw materials and energy throughout the product lifecycle. Synthetic rubber soles typically contribute to microplastic pollution and have limited recyclability, whereas self-healing alternatives promote sustainability through enhanced durability and potential for material reuse.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Self-healing rubber offers long-term cost-effectiveness by reducing the frequency of sole replacements, though its initial price remains higher than traditional synthetic rubber, which is widely available and more affordable for mass production. Synthetic rubber dominates the shoe sole market due to established supply chains and consistent performance, while self-healing rubber is gaining traction in niche, premium segments focused on durability and sustainability. Manufacturers balancing cost and innovation must evaluate the trade-offs between upfront investment in self-healing technology and ongoing expenses associated with synthetic rubber wear and tear.
Repair and Maintenance Benefits
Self-healing rubber significantly reduces shoe sole maintenance costs by automatically repairing minor cuts and abrasions, extending the lifespan of footwear compared to synthetic rubber, which requires manual patching or replacement. Its polymer network enables autonomous recovery from damage, minimizing downtime and maintaining sole integrity under daily wear conditions. Synthetic rubber, while durable, lacks intrinsic repair properties, leading to higher long-term expenses and environmental waste due to frequent sole replacements.
Consumer Preferences and Industry Trends
Self-healing rubber is emerging as a preferred material in shoe soles due to its ability to repair minor damages autonomously, extending product lifespan and enhancing consumer value. Synthetic rubber, widely used for its cost-effectiveness and versatility, remains dominant but faces growing competition as consumers prioritize sustainability and durability in footwear. Industry trends highlight increasing investments in self-healing polymer technologies, reflecting a shift towards innovative materials that meet evolving consumer demands for performance and eco-conscious products.
Future Prospects and Innovations in Shoe Sole Materials
Self-healing rubber in shoe soles offers significant future prospects by extending product lifespan and reducing environmental impact through autonomous damage repair, surpassing conventional synthetic rubber's durability constraints. Innovations include embedding microcapsules or reversible polymer networks that activate upon damage, paving the way for smarter, more sustainable footwear. This technology integration promises enhanced performance, cost efficiency, and eco-friendly solutions in the evolving shoe manufacturing industry.
Infographic: Self-healing rubber vs Synthetic rubber for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com