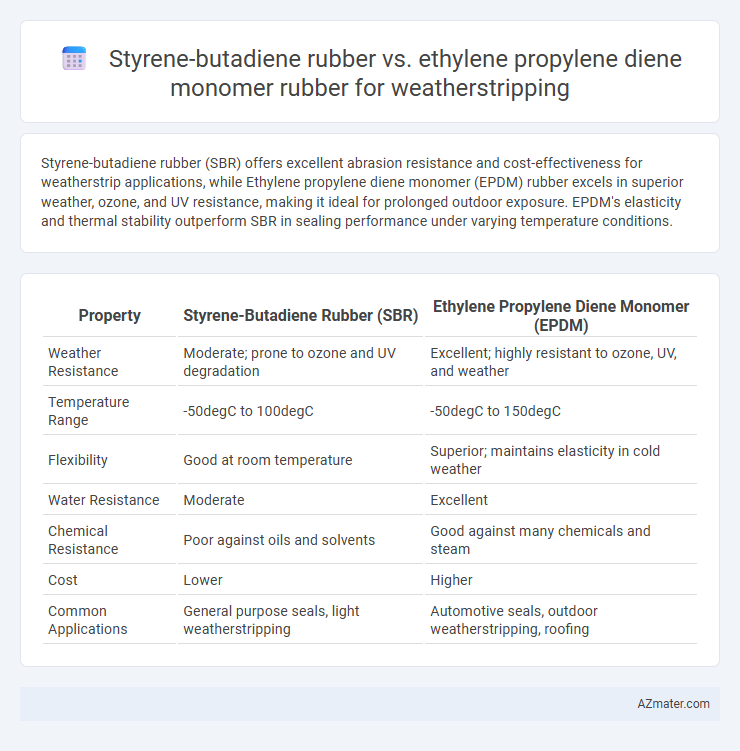
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness for weatherstrip applications, while Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in superior weather, ozone, and UV resistance, making it ideal for prolonged outdoor exposure. EPDM's elasticity and thermal stability outperform SBR in sealing performance under varying temperature conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Weather Resistance | Moderate; prone to ozone and UV degradation | Excellent; highly resistant to ozone, UV, and weather |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 100degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Flexibility | Good at room temperature | Superior; maintains elasticity in cold weather |
| Water Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Poor against oils and solvents | Good against many chemicals and steam |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Applications | General purpose seals, light weatherstripping | Automotive seals, outdoor weatherstripping, roofing |
Introduction to Weatherstrip Materials
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) exhibits excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it a common choice for weatherstrip materials in automotive and industrial applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers superior resistance to ozone, UV rays, and extreme weather conditions, ensuring long-lasting performance in outdoor sealing applications. EPDM's enhanced flexibility and resistance to aging make it ideal for weatherstrips exposed to harsh environmental elements.
Overview of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic elastomer widely used in weatherstripping due to its excellent abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making it durable against mechanical stress. Its composition of styrene and butadiene monomers provides good aging stability and resistance to heat and ozone, essential for maintaining weatherstrip integrity in varying environmental conditions. Compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, SBR offers superior wear resistance but typically has lower resistance to UV radiation and weathering, influencing its suitability depending on exposure scenarios.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Rubber
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber is a synthetic elastomer prized for its exceptional resistance to weathering, ozone, UV rays, and extreme temperatures, making it ideal for weatherstrip applications. Compared to Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), EPDM offers superior durability and elasticity in outdoor environments, ensuring long-lasting sealing and insulation. Its excellent water and steam resistance further enhance performance in automotive and construction weatherstripping, where exposure to harsh elements is common.
Weather Resistance: SBR vs EPDM
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) exhibits moderate weather resistance but tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to UV radiation, ozone, and oxidation, making it less suitable for outdoor weatherstrip applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber (EPDM), renowned for its exceptional resistance to UV rays, ozone, oxidation, and extreme temperatures, provides superior durability and longevity in weatherstripping. Consequently, EPDM is the preferred material for weatherstrips requiring high performance in harsh environmental conditions.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate durability with good abrasion resistance but is more susceptible to weathering and ozone degradation, limiting its longevity in outdoor weatherstripping applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in weather resistance, UV stability, and ozone resistance, resulting in superior durability and extended lifespan for weatherstrips exposed to harsh environmental conditions. EPDM's molecular structure provides excellent elasticity retention over time, making it the preferred choice for long-lasting weatherstripping solutions.
Flexibility and Compression Set Performance
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate flexibility with good abrasion resistance, but exhibits higher compression set values, making it less ideal for weatherstrips requiring long-term elasticity. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides superior flexibility and significantly lower compression set, ensuring excellent weather resistance and shape retention under repetitive compression in sealing applications. EPDM's enhanced resistance to ozone, UV, and temperature extremes further improves the durability of weatherstrips compared to SBR.
Cost Efficiency: SBR vs EPDM for Weatherstrips
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers a lower initial cost compared to Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it attractive for budget-sensitive weatherstrip applications. However, EPDM provides superior weather resistance, ozone resistance, and durability, which translates to longer service life and lower replacement frequency, resulting in better long-term cost efficiency. The choice between SBR and EPDM depends on balancing upfront material expenses against maintenance and replacement costs in varying environmental conditions.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers easier installation for weatherstrips due to its higher rigidity, providing a firmer fit in door and window frames. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber demands more careful handling during installation because of its superior flexibility and elasticity, which enhances long-term sealing performance but may require precise positioning to avoid deformation. Maintenance of EPDM is generally lower since it resists UV radiation, ozone, and extreme weather better than SBR, which tends to deteriorate faster under harsh environmental conditions, necessitating more frequent replacement or repairs.
Typical Applications and Industry Preferences
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is commonly used in weatherstripping for automotive door seals and window gaskets due to its good abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, particularly favored in automotive and construction industries. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in weatherstripping applications exposed to extreme weather conditions, ozone, and UV radiation, making it preferred in outdoor, roofing, and HVAC industries. Industry preferences typically lean toward EPDM for superior durability and weather resistance in outdoor environments, while SBR is chosen for moderate climates and budget-sensitive projects.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Weatherstrip Needs
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for general-purpose weatherstripping applications exposed to moderate weather conditions. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in ozone, UV, and extreme temperature resistance, ideal for harsh outdoor environments requiring long-term durability and flexibility. Selecting between SBR and EPDM depends on the specific weatherstrip exposure, with EPDM preferred for prolonged exposure to sunlight and SBR chosen for economical solutions in less demanding settings.
Infographic: Styrene-butadiene rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber for Weatherstrip
 azmater.com
azmater.com