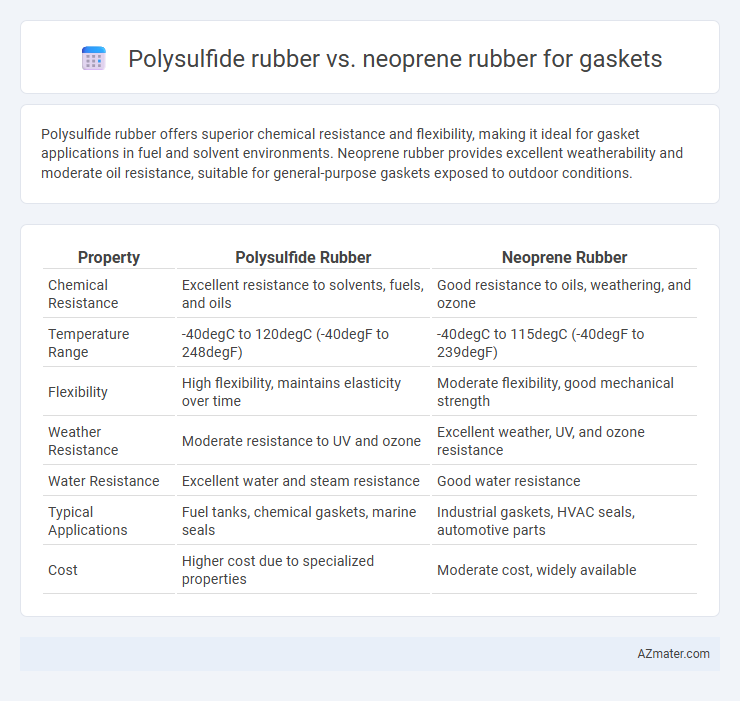
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for gasket applications in fuel and solvent environments. Neoprene rubber provides excellent weatherability and moderate oil resistance, suitable for general-purpose gaskets exposed to outdoor conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfide Rubber | Neoprene Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to solvents, fuels, and oils | Good resistance to oils, weathering, and ozone |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) | -40degC to 115degC (-40degF to 239degF) |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, maintains elasticity over time | Moderate flexibility, good mechanical strength |
| Weather Resistance | Moderate resistance to UV and ozone | Excellent weather, UV, and ozone resistance |
| Water Resistance | Excellent water and steam resistance | Good water resistance |
| Typical Applications | Fuel tanks, chemical gaskets, marine seals | Industrial gaskets, HVAC seals, automotive parts |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized properties | Moderate cost, widely available |
Introduction to Polysulfide and Neoprene Rubbers
Polysulfide rubber is a high-performance elastomer known for its excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and strong adhesion, making it ideal for gasket applications in aerospace, automotive, and marine industries. Neoprene rubber offers good weather, ozone, and chemical resistance with moderate flexibility, commonly used in gaskets for refrigeration, HVAC, and industrial sealing purposes. Both materials provide durable sealing solutions, but polysulfide excels in solvent and fuel resistance, whereas neoprene performs well under varied temperature and weather conditions.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Polysulfide rubber features a polymer chain with recurring sulfur-sulfur linkages, providing excellent chemical resistance to fuels, oils, and solvents, making it ideal for gaskets exposed to harsh chemicals. Neoprene rubber, a polychloroprene polymer, contains chlorine atoms within its backbone, which enhances its resistance to ozone, weathering, and mild acids. The sulfur-based crosslinking in polysulfide rubber offers superior solvent and chemical stability, whereas neoprene's chlorinated structure provides balanced mechanical strength and moderate chemical resistance.
Performance in Sealing Applications
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance and excellent fuel and solvent sealing properties, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments where long-term durability is crucial. Neoprene rubber provides balanced resistance to oils, weathering, and ozone, ensuring reliable sealing in automotive and marine gasket applications. Polysulfide's flexibility and low permeability enhance sealing performance under dynamic conditions, while neoprene excels in moderate temperature ranges with good mechanical strength.
Resistance to Chemicals and Solvents
Polysulfide rubber exhibits superior resistance to a broad spectrum of chemicals and solvents, including fuels, oils, and diluted acids, making it ideal for gaskets in harsh chemical environments. Neoprene rubber offers moderate chemical resistance but performs best against ozone, weathering, and mild acids rather than aggressive solvents. Choosing polysulfide rubber ensures enhanced durability and leak prevention in applications exposed to strong chemical agents, whereas neoprene suits environments with lighter chemical exposure and higher flexibility demands.
Temperature Tolerance and Thermal Stability
Polysulfide rubber exhibits excellent temperature tolerance, maintaining flexibility and sealing performance in environments ranging from -40degC to 120degC, with superior resistance to heat aging and thermal degradation. Neoprene rubber offers a slightly narrower temperature range, typically between -40degC and 100degC, and while it provides good thermal stability, it is more prone to hardening and cracking under prolonged high-temperature exposure. For gasket applications requiring prolonged exposure to higher temperatures and enhanced thermal stability, polysulfide rubber is generally the preferred choice.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Polysulfide rubber exhibits excellent mechanical properties such as high tensile strength and elongation, making it highly resistant to deformation under pressure, which enhances gasket performance in dynamic sealing applications. Neoprene rubber offers robust resistance to compression set and moderate tensile strength, providing durability in environments exposed to oil, weather, and ozone. Polysulfide's superior chemical resistance and flexibility contribute to longer gasket lifespan compared to neoprene, particularly in applications involving solvents and fluctuating temperatures.
Flexibility and Compression Set
Polysulfide rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent resistance to compression set, making it ideal for gaskets subjected to continuous deformation and dynamic sealing conditions. Neoprene rubber, while providing good flexibility, tends to exhibit a higher compression set, which can lead to gasket deformation and reduced sealing effectiveness over time. The low compression set of polysulfide rubber ensures long-term durability and reliable sealing performance in applications exposed to varying pressures and temperatures.
Environmental and Weather Resistance
Polysulfide rubber exhibits excellent resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and prolonged weather exposure, making it ideal for gaskets in harsh environmental conditions. Neoprene rubber offers strong resistance to oils, chemicals, and moderate weathering but can degrade faster under intense sunlight and oxidation. Polysulfide's superior permeability resistance to fuels and solvents provides enhanced durability in aggressive outdoor environments compared to neoprene.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Polysulfide rubber offers a moderate cost profile and exhibits good chemical resistance, making it a cost-effective option for gaskets used in fuel and solvent environments, though its availability can be limited compared to more common materials. Neoprene rubber, widely produced and readily available, generally incurs higher costs but provides superior resistance to oil, weathering, and ozone, making it suitable for harsh industrial gasket applications. Cost analysis favors polysulfide rubber when budget constraints prioritize chemical compatibility at a lower price point, while neoprene's widespread availability supports large-scale manufacturing with consistent quality.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Gasket Applications
Polysulfide rubber offers excellent fuel and chemical resistance, making it ideal for gaskets exposed to harsh solvents and oils, while neoprene rubber provides superior weather, ozone, and moderate chemical resistance suited for outdoor and marine gasket applications. Selecting the right rubber gasket depends on specific environmental factors such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress. Polysulfide excels in sealing fuel tanks and chemical containers, whereas neoprene is preferred for HVAC systems, refrigeration, and gasketing in moderate chemical environments.
Infographic: Polysulfide rubber vs Neoprene rubber for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com