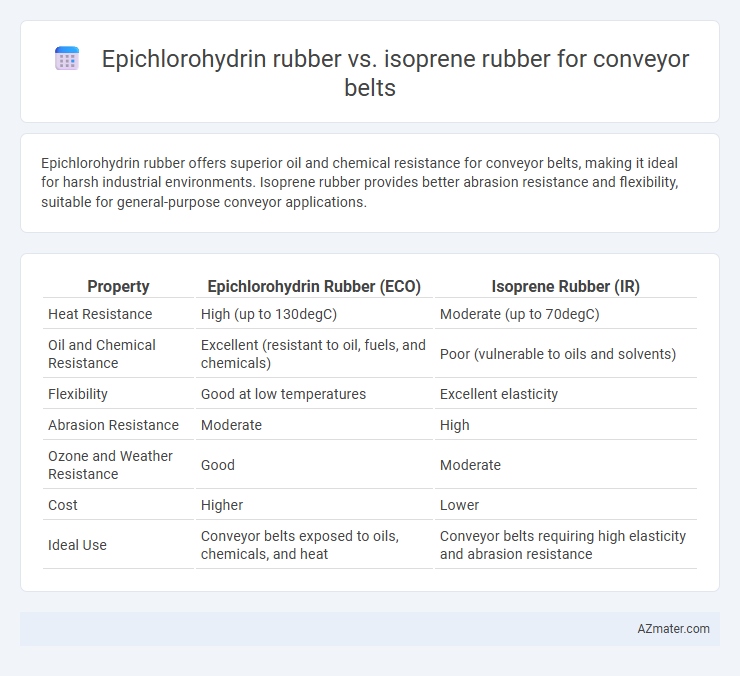
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil and chemical resistance for conveyor belts, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments. Isoprene rubber provides better abrasion resistance and flexibility, suitable for general-purpose conveyor applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Isoprene Rubber (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | High (up to 130degC) | Moderate (up to 70degC) |
| Oil and Chemical Resistance | Excellent (resistant to oil, fuels, and chemicals) | Poor (vulnerable to oils and solvents) |
| Flexibility | Good at low temperatures | Excellent elasticity |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Good | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Ideal Use | Conveyor belts exposed to oils, chemicals, and heat | Conveyor belts requiring high elasticity and abrasion resistance |
Overview of Conveyor Belt Materials
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent oil, abrasion, and heat resistance, making it ideal for conveyor belts used in harsh industrial environments such as automotive and chemical sectors. Isoprene rubber, derived from natural sources, provides superior flexibility and resilience, suitable for applications requiring high tensile strength and low-temperature performance. Choosing between these materials depends on the conveyor belt's operating conditions, including exposure to chemicals, temperature ranges, and mechanical stress.
Introduction to Epichlorohydrin Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber, known for its exceptional resistance to oil, ozone, and weathering, is widely used in conveyor belts operating in harsh industrial environments. Its unique polymer structure provides superior flexibility and tensile strength compared to isoprene rubber, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and chemical resistance. In contrast, isoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance but lacks the same level of oil and heat resistance found in epichlorohydrin, limiting its suitability for heavy-duty conveyor systems.
Introduction to Isoprene Rubber
Isoprene rubber, a synthetic elastomer closely resembling natural rubber, offers superior tensile strength and elasticity essential for durable conveyor belts. Compared to Epichlorohydrin rubber, Isoprene rubber exhibits enhanced abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for heavy-duty, high-friction environments. Its chemical stability and resilience against wear contribute to longer conveyor belt lifespan and reduced maintenance costs.
Key Physical Properties Compared
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior oil and chemical resistance, with a tensile strength ranging from 15 to 25 MPa and elongation at break between 350% to 550%, making it highly durable for conveyor belts exposed to harsh environments. In contrast, Isoprene rubber offers excellent resilience and abrasion resistance, featuring tensile strength around 20 to 25 MPa and elongation typically between 400% to 600%, ideal for general-purpose conveyor belts requiring flexibility and impact resistance. Both rubbers provide distinct advantages; Epichlorohydrin's low gas permeability suits aggressive chemical exposure, while Isoprene's natural elasticity enhances mechanical performance under continuous stress.
Chemical Resistance: Epichlorohydrin vs Isoprene
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to isoprene rubber, particularly against oils, ozone, and fuels, making it ideal for conveyor belts exposed to harsh chemicals. Isoprene rubber offers limited resistance to hydrocarbons and degrades faster when in contact with oils and solvents, reducing its durability in industrial applications. The enhanced chlorine content in epichlorohydrin rubber contributes to its resilience against chemical attacks, ensuring longer service life in chemically aggressive environments.
Temperature Performance in Conveyor Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to heat aging and maintains flexibility at temperatures ranging from -40degC to 115degC, making it ideal for conveyor belts operating in harsh thermal environments. Isoprene rubber exhibits good low-temperature flexibility down to -50degC but degrades faster at temperatures above 80degC, limiting its use in high-temperature conveyor applications. Temperature performance in conveyor belts is critical for durability; therefore, Epichlorohydrin rubber is preferred when continuous exposure to elevated temperatures and aging resistance are required.
Wear and Abrasion Resistance
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior wear and abrasion resistance compared to Isoprene rubber, making it more suitable for conveyor belts operating in harsh environments. Its unique molecular structure provides enhanced chemical resistance and durability, reducing maintenance costs and improving belt longevity. Isoprene rubber, while flexible and resilient, tends to wear faster under abrasive conditions, limiting its effectiveness in heavy-duty conveyor applications.
Cost and Availability Factors
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers moderate cost and is readily available due to its widespread industrial production, making it a cost-effective choice for conveyor belts in chemical and oil industries. Isoprene rubber, while providing excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance for conveyor applications, is typically more expensive and less available because it is sourced primarily from natural rubber production. Cost efficiency and availability often favor epichlorohydrin rubber in large-scale conveyor belt manufacturing where consistent supply and budget constraints are critical.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers superior chemical resistance and oil resistance but involves chlorine-containing compounds that generate hazardous byproducts during production and disposal, raising environmental concerns. Isoprene rubber, being a natural or synthetic polymer based on renewable isoprene units, provides better biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint, enhancing sustainability in conveyor belt applications. Selecting isoprene rubber reduces ecological impact through safer degradation and less toxic emissions compared to epichlorohydrin rubber, aligning with sustainable manufacturing goals.
Choosing the Best Rubber for Conveyor Belts
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering, making it ideal for conveyor belts operating in harsh industrial environments. Isoprene rubber provides excellent flexibility, abrasion resistance, and heat stability, which suits conveyor belts in applications requiring high mechanical performance and resilience. Choosing the best rubber depends on the specific operational demands, with epichlorohydrin preferred for chemical exposure and isoprene favored for dynamic mechanical stress and durability.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Isoprene rubber for Conveyor belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com