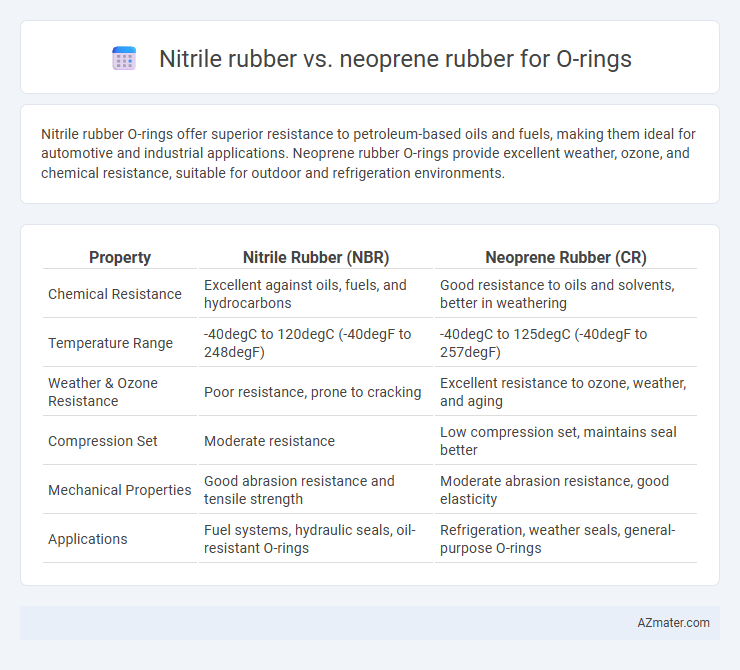
Nitrile rubber O-rings offer superior resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels, making them ideal for automotive and industrial applications. Neoprene rubber O-rings provide excellent weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, suitable for outdoor and refrigeration environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Neoprene Rubber (CR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons | Good resistance to oils and solvents, better in weathering |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) | -40degC to 125degC (-40degF to 257degF) |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Poor resistance, prone to cracking | Excellent resistance to ozone, weather, and aging |
| Compression Set | Moderate resistance | Low compression set, maintains seal better |
| Mechanical Properties | Good abrasion resistance and tensile strength | Moderate abrasion resistance, good elasticity |
| Applications | Fuel systems, hydraulic seals, oil-resistant O-rings | Refrigeration, weather seals, general-purpose O-rings |
Introduction to Nitrile and Neoprene Rubber
Nitrile rubber, also known as Buna-N, is a synthetic elastomer renowned for its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for O-ring applications in automotive and industrial settings. Neoprene rubber, or polychloroprene, offers superior weathering, ozone, and chemical resistance, which enhances its performance in outdoor and marine O-ring uses. Both materials exhibit distinct mechanical properties, with nitrile excelling in hydrocarbon environments and neoprene favored for durability in harsh atmospheric conditions.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Nitrile rubber O-rings are composed primarily of acrylonitrile and butadiene, offering excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels due to polar nitrile groups enhancing chemical stability. Neoprene rubber O-rings consist of polychloroprene polymers, characterized by chlorine atoms in their structure that provide superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and mild acids. The chemical composition differences influence their molecular backbone flexibility and cross-link density, impacting their compatibility with various chemicals in sealing applications.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels, with an oil resistance rating of 70-100, making it ideal for automotive and industrial O-rings exposed to hydrocarbons. Neoprene rubber excels in weather, ozone, and moderate chemical resistance, featuring a durometer hardness range of 40-90 Shore A and maintaining flexibility in temperatures from -40degC to 120degC. Both materials possess excellent tensile strength and abrasion resistance, but nitrile generally provides higher resistance to wear and compression set, essential for dynamic sealing applications in harsh environments.
Temperature Resistance: Nitrile vs Neoprene
Nitrile rubber O-rings exhibit temperature resistance typically ranging from -40degC to 120degC, making them suitable for applications involving oils and fuels at moderate temperatures. Neoprene rubber O-rings withstand a wider temperature range, approximately -40degC to 125degC, with enhanced resistance to weathering, ozone, and moderate chemical exposure. For high-temperature applications or those requiring resistance to environmental degradation, neoprene offers superior performance compared to nitrile.
Chemical Compatibility and Resistance
Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and many hydraulic fluids, making it ideal for O-rings in automotive and industrial applications involving hydrocarbons. Neoprene rubber exhibits superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and a broader range of chemicals including refrigerants, mild acids, and alkalis, enhancing its suitability for outdoor and refrigeration sealing uses. Chemical compatibility charts highlight nitrile's limitations with ketones and aromatic hydrocarbons, while neoprene demonstrates better performance against corrosive agents and chlorinated solvents.
Durability and Wear Performance
Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to oils and fuels, making it highly durable for O-ring applications in automotive and industrial environments. Neoprene rubber provides superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and moderate chemicals, enhancing wear performance in outdoor and refrigeration seals. Both materials deliver robust durability, with nitrile excelling in oil exposure and neoprene outperforming in environmental and chemical abrasion.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Nitrile rubber O-rings offer superior cost efficiency due to their lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making them widely available in various industrial markets. Neoprene rubber O-rings, while typically more expensive, provide enhanced chemical resistance and durability, which can justify the higher initial cost in specialized applications. Availability of nitrile rubber is broader globally, ensuring faster supply chains and lower procurement costs compared to neoprene, which is less prevalent and often sourced from more limited suppliers.
Typical Applications and Industry Usage
Nitrile rubber (NBR) O-rings are widely used in the automotive, petroleum, and pneumatic industries due to their excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons, making them ideal for fuel systems, oil seals, and hydraulic components. Neoprene rubber (CR) O-rings find typical application in refrigeration, chemical processing, and marine industries because of their superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and moderate oils. Industry usage favors nitrile for dynamic sealing in fuel systems, while neoprene is preferred for static sealing in refrigeration compressors and outdoor equipment exposed to environmental factors.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Nitrile rubber O-rings offer superior resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels, making them suitable for industrial environments with hydrocarbon exposure, but they may release harmful nitrile fumes during combustion. Neoprene rubber O-rings provide enhanced resistance to weathering, ozone, and flame, making them safer for outdoor and chemical exposure applications with lower toxicity upon degradation. Both materials require proper handling and disposal to minimize environmental impact, with neoprene generally favored for its broader chemical stability and reduced risk of hazardous emissions.
Choosing the Right O-Ring Material: Nitrile or Neoprene
Nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and synthetic oils, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications requiring high oil resistance. Neoprene rubber provides excellent weather, ozone, and moderate chemical resistance, suitable for outdoor and refrigeration environments where durability and flexibility are critical. Selecting between nitrile and neoprene O-rings depends on the specific exposure conditions, temperature range, and chemical compatibility to ensure optimal sealing performance and longevity.
Infographic: Nitrile rubber vs Neoprene rubber for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com