Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent adhesion for seals, enhancing durability in dynamic applications. Nitrile rubber provides exceptional resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for seals exposed to harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
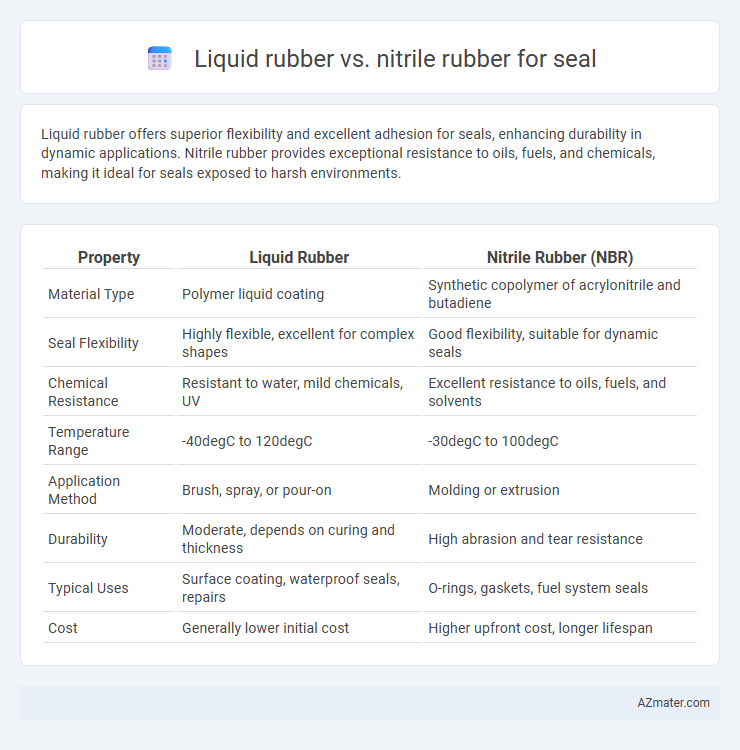
| Property | Liquid Rubber | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polymer liquid coating | Synthetic copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene |
| Seal Flexibility | Highly flexible, excellent for complex shapes | Good flexibility, suitable for dynamic seals |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to water, mild chemicals, UV | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -30degC to 100degC |
| Application Method | Brush, spray, or pour-on | Molding or extrusion |
| Durability | Moderate, depends on curing and thickness | High abrasion and tear resistance |
| Typical Uses | Surface coating, waterproof seals, repairs | O-rings, gaskets, fuel system seals |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher upfront cost, longer lifespan |
Introduction to Liquid Rubber and Nitrile Rubber
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent waterproof sealing properties, making it ideal for dynamic environments requiring durable protection against moisture. Nitrile rubber, known for its exceptional resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, is widely used in industrial seals exposed to harsh substances. Both materials provide reliable sealing solutions, with liquid rubber favored for versatile coatings and nitrile rubber preferred for robust mechanical seals in automotive and aerospace applications.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Liquid rubber primarily consists of synthetic polymers like styrene-butadiene or polyurethane, characterized by a flexible, elastic molecular network that cures into a seamless, adaptable coating. Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, with its chemical composition providing excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals due to the polar nitrile groups in its structure. The molecular structure of nitrile rubber offers superior impermeability and mechanical strength compared to liquid rubber, making it more suitable for seals requiring robust chemical and abrasion resistance.
Key Physical Properties for Sealing Applications
Liquid rubber exhibits excellent elasticity and superior adhesion, making it ideal for flexible, waterproof seals requiring dynamic movement. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers exceptional resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, with robust tensile strength and abrasion resistance, suitable for heavy-duty sealing in harsh environments. Both materials provide effective sealing, but liquid rubber excels in flexibility and ease of application, while nitrile rubber is preferred for durability and chemical resistance.
Durability and Longevity in Harsh Environments
Liquid rubber exhibits superior flexibility and excellent resistance to extreme temperatures, UV radiation, and chemical exposure, making it highly durable for seals in harsh environments. Nitrile rubber offers strong resistance to oils, fuels, and abrasion, ensuring long-lasting performance in industrial applications prone to mechanical wear. Both materials provide exceptional longevity, but liquid rubber is preferable for dynamic conditions requiring strong environmental resilience, while nitrile rubber excels in oil-rich, abrasive settings.
Chemical and Oil Resistance: A Detailed Analysis
Liquid rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance due to its flexible polymer chains, making it highly effective against a broad spectrum of solvents, acids, and alkalis frequently encountered in industrial seals. Nitrile rubber (NBR), renowned for its exceptional oil and fuel resistance, performs well in environments with petroleum-based fluids but may degrade faster when exposed to strong acids or solvents outside its optimal range. Selecting between liquid rubber and nitrile rubber for seals hinges on the specific chemical exposure profile, with liquid rubber favored for aggressive chemical environments and nitrile rubber preferred for oil-rich applications.
Temperature Range and Performance Limits
Liquid rubber offers excellent flexibility and maintains performance in temperatures ranging from -50degC to 120degC, making it ideal for dynamic sealing applications with moderate thermal exposure. Nitrile rubber excels in oil resistance and performs well between -40degC and 120degC, but its effectiveness diminishes outside this range due to brittleness at low temperatures and degradation at high heat. For seals subjected to wide temperature fluctuations and abrasive environments, liquid rubber provides superior elasticity, while nitrile rubber is preferred for oil-heavy conditions within its temperature limits.
Flexibility and Elasticity for Sealing Efficiency
Liquid rubber exhibits superior flexibility and elasticity compared to nitrile rubber, enhancing its ability to conform to irregular surfaces and maintain an effective seal under dynamic conditions. Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to oils and fuels but tends to be less flexible, potentially compromising sealing efficiency in applications requiring frequent movement or deformation. The enhanced elasticity of liquid rubber ensures longer-lasting seals by accommodating mechanical stresses and preventing leaks more effectively.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Liquid rubber offers cost-effective sealing solutions due to lower application and curing expenses, making it ideal for custom or small-scale projects. Nitrile rubber, widely available and mass-produced, provides durable seals with competitive pricing in large-volume manufacturing. Both materials balance cost-effectiveness and availability depending on project scale and specific sealing requirements.
Typical Seal Applications for Each Material
Liquid rubber excels in flexible, custom-shaped seals for applications such as waterproof coatings, automotive gaskets, and pipe linings due to its excellent adhesion and corrosion resistance. Nitrile rubber, known for its superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, is typically used in O-rings, fuel seals, and hydraulic system components where durability against petroleum-based fluids is critical. Both materials serve essential roles in sealing technologies, with liquid rubber favored for protective layers and nitrile rubber for dynamic mechanical seals in industrial equipment.
Choosing the Best Rubber for Your Sealing Needs
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and easy application for complex seals, making it ideal for irregular or hard-to-reach surfaces, while nitrile rubber excels in chemical resistance and durability, particularly against oils, fuels, and abrasives. Selecting the best rubber depends on the specific sealing environment; nitrile rubber seals outperform in automotive and industrial machinery due to their resilience under pressure and temperature variations. For waterproofing or coating irregular shapes, liquid rubber provides a seamless, durable barrier, whereas nitrile rubber is preferred when exposure to hydrocarbons and mechanical stress is a primary concern.
Infographic: Liquid rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com