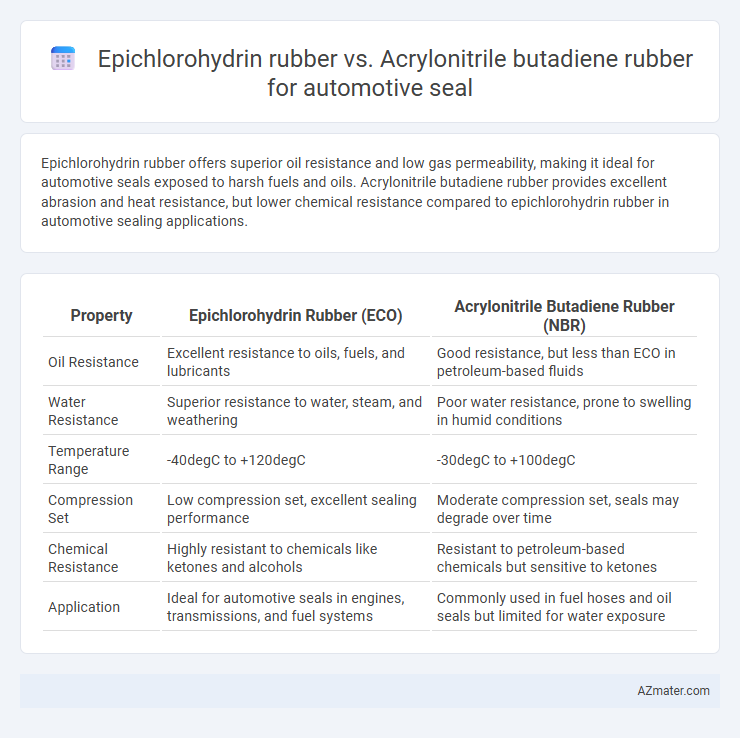
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil resistance and low gas permeability, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh fuels and oils. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber provides excellent abrasion and heat resistance, but lower chemical resistance compared to epichlorohydrin rubber in automotive sealing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and lubricants | Good resistance, but less than ECO in petroleum-based fluids |
| Water Resistance | Superior resistance to water, steam, and weathering | Poor water resistance, prone to swelling in humid conditions |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to +120degC | -30degC to +100degC |
| Compression Set | Low compression set, excellent sealing performance | Moderate compression set, seals may degrade over time |
| Chemical Resistance | Highly resistant to chemicals like ketones and alcohols | Resistant to petroleum-based chemicals but sensitive to ketones |
| Application | Ideal for automotive seals in engines, transmissions, and fuel systems | Commonly used in fuel hoses and oil seals but limited for water exposure |
Introduction to Automotive Seal Materials
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers excellent resistance to heat, oils, and weathering, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh conditions like engine compartments. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) provides superior resistance to petroleum-based fuels and lubricants, commonly used in fuel system seals and gaskets. Selecting between ECO and NBR depends on the specific chemical exposure and temperature ranges encountered in automotive sealing applications.
Overview of Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO)
Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) offers superior resistance to heat, oils, and weathering, making it ideal for automotive seals requiring durability in harsh environments. Its low permeability to gases and excellent flexibility at low temperatures outperform Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) in sealing applications exposed to extreme conditions. ECO's enhanced chemical stability and aging resistance contribute to longer service life in engine and transmission seals compared to traditional NBR materials.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) is widely used in automotive seals due to its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and other chemicals, making it ideal for engine and fuel system components. Its superior abrasion resistance and flexibility at low temperatures enhance durability and maintain effective sealing under dynamic conditions. Compared to Epichlorohydrin rubber, NBR offers better performance in high-temperature applications and exposure to hydrocarbons, which is critical for maintaining seal integrity in automotive environments.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone, making it highly suitable for automotive seals exposed to harsh chemical environments. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) offers excellent resistance to petroleum-based fluids but performs less effectively against ozone and weathering compared to epichlorohydrin. The chemical resistance profile of epichlorohydrin rubber ensures longer seal integrity in applications involving exposure to aggressive solvents and automotive fluids.
Temperature Performance and Stability
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) exhibits superior temperature resistance, maintaining flexibility and sealing properties between -40degC to 120degC, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to extreme thermal fluctuations. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) offers good resistance up to 100degC but tends to harden or crack under prolonged heat exposure, limiting its stability in high-temperature environments. ECO also delivers enhanced resistance to ozone, weathering, and chemical degradation, ensuring longer-lasting seal performance compared to NBR in demanding automotive applications.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and various fluids, making it highly durable for automotive seals that require chemical stability and low permeability. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) offers excellent oil and fuel resistance combined with good mechanical strength, but its performance diminishes under prolonged heat exposure compared to epichlorohydrin. While epichlorohydrin provides enhanced elasticity and tensile strength with better compression set resistance, NBR is favored for applications demanding higher resistance to petroleum-based fluids and abrasion.
Weathering and Ozone Resistance
Epichlorohydrin rubber demonstrates superior weathering and ozone resistance compared to Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh outdoor conditions. Effective resistance to ozone-induced cracking enhances Epichlorohydrin's durability in fluctuating temperatures and UV radiation environments. In contrast, NBR offers moderate ozone resistance but tends to degrade faster under prolonged weathering stress, reducing service life in demanding automotive applications.
Cost and Availability Factors
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers moderate cost and good resistance to oil and weathering, making it suitable for automotive seals requiring durability, though it is less available globally compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR). Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber is generally more cost-effective and widely available due to extensive production, providing excellent resistance to fuels and oils, which is critical for automotive sealing applications. Cost efficiency and supply chain reliability make NBR the preferred choice over epichlorohydrin rubber in mass-produced automotive seals.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers superior chemical resistance and low permeability, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh fuels and oils, with excellent ozone and weather resistance that enhances durability and reduces environmental waste from frequent replacements. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) is widely used due to its strong resistance to petroleum products and good mechanical properties but can release hazardous nitrile and butadiene compounds during production and disposal, posing environmental and health risks. Choosing ECO minimizes toxic emissions and improves occupant safety through enhanced seal reliability, while NBR requires careful handling to mitigate its environmental footprint.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Rubber for Automotive Seals
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and a wide range of oils, making it highly suitable for automotive seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions and chemical exposure. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) excels in fuel and oil resistance, providing excellent sealing performance in engines and fuel systems but has lower resistance to ozone and weathering compared to epichlorohydrin rubber. Selecting between Epichlorohydrin and NBR depends on specific automotive seal requirements, balancing exposure to fuels, oils, temperature ranges, and environmental factors for optimal durability and performance.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber for Automotive seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com