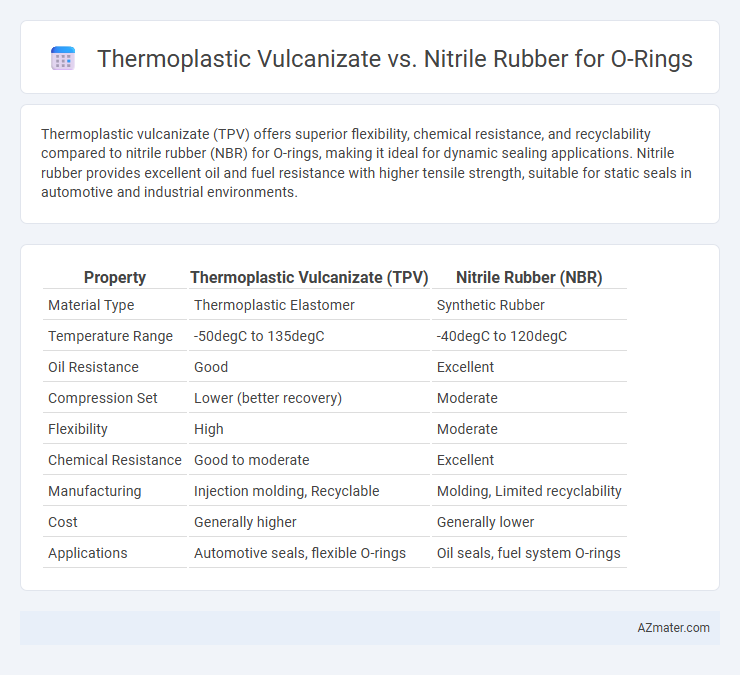
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and recyclability compared to nitrile rubber (NBR) for O-rings, making it ideal for dynamic sealing applications. Nitrile rubber provides excellent oil and fuel resistance with higher tensile strength, suitable for static seals in automotive and industrial environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Elastomer | Synthetic Rubber |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 135degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Oil Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Compression Set | Lower (better recovery) | Moderate |
| Flexibility | High | Moderate |
| Chemical Resistance | Good to moderate | Excellent |
| Manufacturing | Injection molding, Recyclable | Molding, Limited recyclability |
| Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
| Applications | Automotive seals, flexible O-rings | Oil seals, fuel system O-rings |
Introduction to O-Ring Materials
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) and nitrile rubber (NBR) are common materials used in O-ring manufacturing, each offering distinct benefits based on application requirements. TPV combines the elasticity of rubber with the processability of thermoplastics, providing excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and durability at a wide temperature range (-40degC to 135degC). Nitrile rubber, known for its superior resistance to oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons, excels in sealing applications exposed to petroleum-based fluids and temperatures typically between -30degC and 120degC.
Overview of Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV)
Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV) is a blend of vulcanized rubber particles dispersed within a thermoplastic matrix, offering excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability for O-ring applications. TPVs provide superior heat resistance up to 300degF (150degC) and excellent resistance to oils, greases, and weathering, making them suitable for dynamic sealing environments. In comparison to Nitrile Rubber (NBR), TPVs combine elastomeric performance with thermoplastic processing advantages, enabling faster manufacturing cycles and recyclability.
Overview of Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Nitrile Rubber (NBR) is a synthetic elastomer widely used for O-rings due to its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications. Its high tensile strength and ability to maintain flexibility over a temperature range from -40degC to 120degC ensure reliable sealing performance under varying conditions. Compared to Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV), NBR offers superior chemical resistance and durability in aggressive fluid environments.
Key Physical Properties: TPV vs Nitrile Rubber
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior flexibility and excellent resistance to compression set compared to nitrile rubber, making it ideal for dynamic O-ring applications requiring long-term sealing performance. Nitrile rubber provides superior resistance to oils, fuels, and petroleum-based fluids, with higher tensile strength and better abrasion resistance, which ensures durability in harsh chemical environments. TPV exhibits better thermal stability and can withstand a wider temperature range from -40degC to 150degC, whereas nitrile typically operates effectively between -30degC and 120degC.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) offer superior chemical resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), making them ideal for harsh chemical environments. Nitrile rubber provides excellent resistance to hydrocarbons and petroleum-based fluids but tends to degrade faster when exposed to solvents and acids. For applications requiring prolonged exposure to aggressive chemicals, TPVs maintain their elasticity and structural integrity better than conventional nitrile O-rings.
Temperature Range and Environmental Suitability
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) O-rings typically withstand temperatures ranging from -40degC to 135degC, offering excellent flexibility and weather resistance suitable for automotive and HVAC applications. Nitrile rubber (NBR) O-rings have a narrower temperature range of -40degC to 120degC but excel in oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, making them ideal for industrial and hydraulic environments. TPV demonstrates superior resistance to ozone, UV exposure, and aging, while NBR provides better performance in oils and fuels, affecting choice based on specific environmental conditions.
Durability and Mechanical Performance
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) offers superior durability and abrasion resistance compared to nitrile rubber (NBR) in O-ring applications, making it ideal for environments with repeated mechanical stress. TPV exhibits excellent compression set resistance and thermal stability, maintaining performance in temperatures ranging from -40degC to 120degC, while NBR typically operates effectively between -35degC to 100degC but degrades faster under prolonged heat exposure. Mechanical performance-wise, TPV provides enhanced elasticity and resilience, resulting in longer service life and improved sealing reliability under dynamic conditions compared to the relatively rigid and less resistant nitrile rubber.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) offer greater cost-effectiveness than nitrile rubber (NBR) for O-ring applications due to their easier processability and recyclability, reducing manufacturing expenses. Nitrile rubber remains widely available and is preferred for oil resistance, but its higher raw material cost and complex curing process increase overall expenses. TPVs combine the elasticity of rubber with the manufacturing efficiency of thermoplastics, making them a competitive choice where budget and production speed are critical.
Industry-Specific Applications
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) O-rings excel in automotive fuel and coolant systems due to their outstanding chemical resistance and flexibility at extreme temperatures, making them ideal for dynamic sealing applications. Nitrile rubber (NBR) O-rings dominate hydraulic systems and oil handling industries, providing superior resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and abrasion under high pressure. Selecting between TPV and NBR depends on specific industry requirements such as temperature range, fluid compatibility, and mechanical stress.
Selecting the Right Material for Your O-Ring Needs
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) offer excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and ease of processing, making them ideal for O-rings in automotive and industrial applications requiring resilience to repeated compression. Nitrile rubber (NBR) is highly valued for its superior oil, fuel, and abrasion resistance, often preferred for sealing components exposed to petroleum-based products and extreme temperatures. Selecting the right O-ring material depends on the specific environmental conditions, chemical exposure, and mechanical demands of the application, with TPVs excelling in dynamic sealing scenarios and NBR providing robust performance against hydrocarbon-based fluids.
Infographic: Thermoplastic vulcanizate vs Nitrile Rubber for O-Ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com