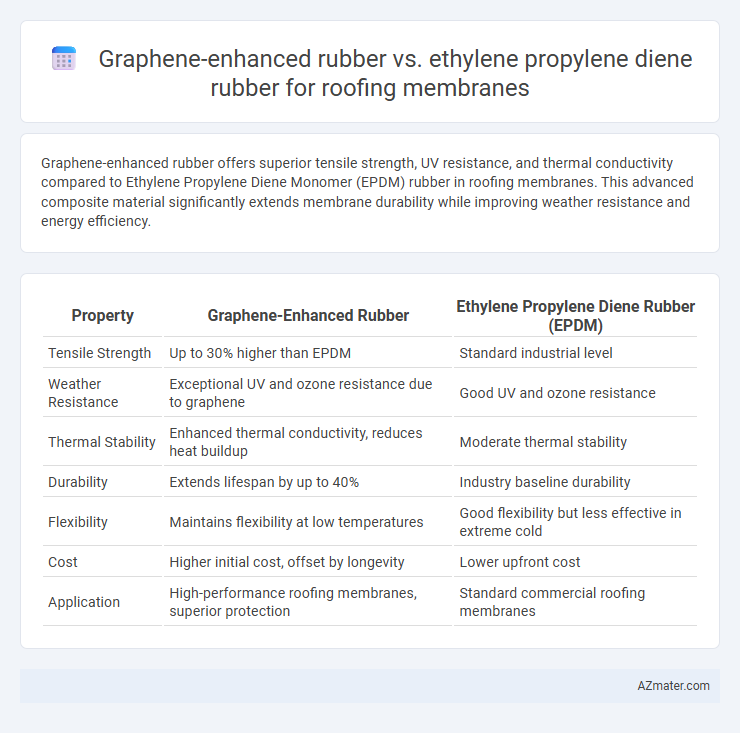
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior tensile strength, UV resistance, and thermal conductivity compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber in roofing membranes. This advanced composite material significantly extends membrane durability while improving weather resistance and energy efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Graphene-Enhanced Rubber | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Up to 30% higher than EPDM | Standard industrial level |
| Weather Resistance | Exceptional UV and ozone resistance due to graphene | Good UV and ozone resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Enhanced thermal conductivity, reduces heat buildup | Moderate thermal stability |
| Durability | Extends lifespan by up to 40% | Industry baseline durability |
| Flexibility | Maintains flexibility at low temperatures | Good flexibility but less effective in extreme cold |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, offset by longevity | Lower upfront cost |
| Application | High-performance roofing membranes, superior protection | Standard commercial roofing membranes |
Introduction to Roofing Membranes
Roofing membranes are essential for waterproofing and protecting building structures, with materials like Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber widely used for their durability and UV resistance. Graphene-enhanced rubber introduces superior mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and weather resistance, offering potential improvements over traditional EPDM in roofing applications. Integrating graphene into rubber membranes enhances their lifespan and performance under extreme environmental conditions, making them an advanced option for modern roofing solutions.
Overview of Graphene-Enhanced Rubber
Graphene-enhanced rubber improves roofing membranes by integrating graphene's exceptional tensile strength and thermal conductivity, resulting in superior durability, flexibility, and weather resistance compared to traditional Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber. The incorporation of graphene enhances UV resistance and reduces permeability, extending the lifespan of roofing membranes under harsh environmental conditions. This advanced material offers a lightweight and eco-friendly alternative that maintains structural integrity while improving efficiency in insulation and waterproofing.
Properties of Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber is a highly durable synthetic elastomer widely used in roofing membranes due to its excellent weather, ozone, and UV resistance, maintaining flexibility in extreme temperatures ranging from -40degC to 150degC. Its superior tensile strength and resistance to water, steam, and chemicals make EPDM an ideal material for long-lasting waterproof roofing applications. Compared to graphene-enhanced rubber, EPDM offers proven performance with cost-effectiveness and ease of installation in large-scale commercial roofing projects.
Durability Comparison: Graphene-Enhanced vs EPDM
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits superior durability compared to traditional Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) in roofing membranes, showcasing enhanced resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and extreme weather conditions. The incorporation of graphene nanoparticles significantly improves tensile strength and elongation at break, resulting in extended service life and reduced maintenance costs. EPDM remains widely used for its elasticity and cost-effectiveness, but graphene-enhanced variants offer a robust alternative with improved mechanical properties and environmental resilience.
Waterproofing Performance and Reliability
Graphene-enhanced rubber roofing membranes exhibit superior waterproofing performance due to graphene's exceptional hydrophobic properties and enhanced tensile strength, reducing water permeability and increasing durability. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers reliable waterproofing with excellent ozone and weather resistance but typically lacks the advanced mechanical reinforcement provided by graphene composites. Graphene integration significantly improves membrane reliability by enhancing thermal stability and resistance to cracking, extending the roof's service life compared to conventional EPDM materials.
Thermal Resistance and Energy Efficiency
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, maintaining structural integrity and elasticity at elevated temperatures up to 200degC. The high thermal conductivity and insulating properties of graphene significantly improve energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer through roofing membranes, thereby lowering cooling costs in buildings. EPDM, while durable and UV resistant, typically lacks the advanced thermal modulation capabilities found in graphene composites, making graphene-enhanced rubber a cutting-edge choice for energy-efficient roofing solutions.
Flexibility and Installation Considerations
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits superior flexibility compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, allowing for easier conforming to complex roof contours and reducing the risk of cracks during temperature fluctuations. The enhanced elasticity of graphene composites facilitates faster, more efficient installation and decreases labor time, especially on irregular surfaces or areas with multiple penetrations. In contrast, EPDM membranes require additional care during installation to avoid stretching beyond their elastic limits, which can lead to membrane failure over time.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Graphene-enhanced rubber roofing membranes offer superior durability and UV resistance, significantly reducing material waste and extending roof lifespan compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber. The incorporation of graphene improves the membrane's mechanical properties, enabling thinner, lighter materials that require less raw resource extraction, lowering the environmental footprint. EPDM, while recyclable, typically demands more frequent replacement cycles, increasing landfill contributions and energy consumption over time.
Cost Analysis and Long-Term Value
Graphene-enhanced rubber roofing membranes offer higher initial costs compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) due to advanced material properties and production complexities. However, the superior tensile strength, UV resistance, and thermal conductivity of graphene composites translate into extended service life and reduced maintenance expenses. Long-term value favors graphene-enhanced membranes by minimizing lifecycle costs and enhancing roofing durability in diverse environmental conditions.
Future Trends in Roofing Membrane Materials
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior tensile strength, thermal conductivity, and weather resistance compared to traditional Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, positioning it as a key material in the next generation of roofing membranes. Future trends emphasize sustainability and durability, with graphene composites enabling longer-lasting, more environmentally friendly roofing solutions that resist UV radiation and extreme temperatures. Increased integration of nanomaterials like graphene is expected to revolutionize roofing membranes by reducing maintenance costs and enhancing overall building energy efficiency.
Infographic: Graphene-enhanced rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Roofing membrane
 azmater.com
azmater.com