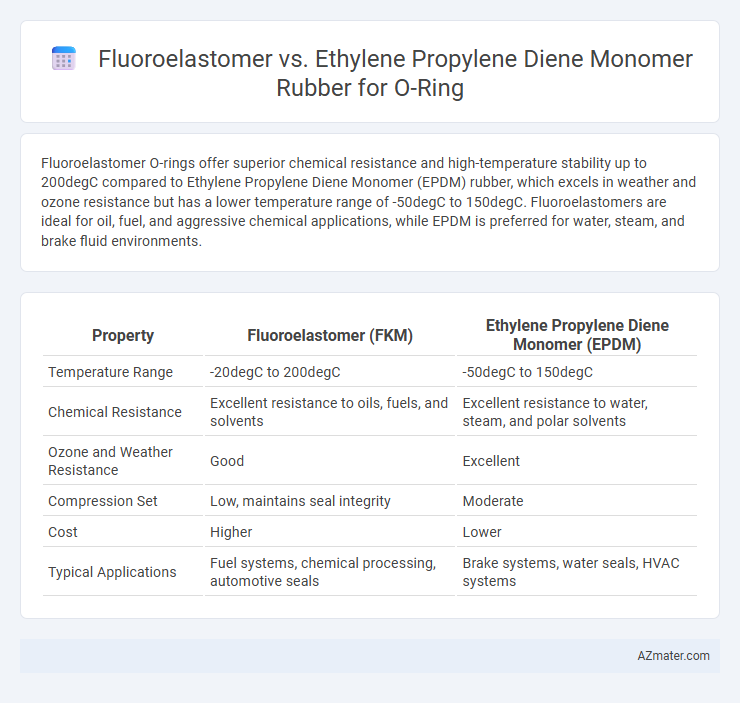
Fluoroelastomer O-rings offer superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability up to 200degC compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, which excels in weather and ozone resistance but has a lower temperature range of -50degC to 150degC. Fluoroelastomers are ideal for oil, fuel, and aggressive chemical applications, while EPDM is preferred for water, steam, and brake fluid environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluoroelastomer (FKM) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -20degC to 200degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents | Excellent resistance to water, steam, and polar solvents |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Compression Set | Low, maintains seal integrity | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Applications | Fuel systems, chemical processing, automotive seals | Brake systems, water seals, HVAC systems |
Overview of Fluoroelastomer and EPDM Rubber
Fluoroelastomer (FKM) O-rings offer exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 200degC, and excellent compression set properties, making them ideal for aggressive environments involving fuels, oils, and acids. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber O-rings provide superior resistance to weathering, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, steam, and polar solvents, with temperature tolerance typically ranging from -50degC to 150degC. The choice between Fluoroelastomer and EPDM O-rings hinges on the specific chemical compatibility and temperature demands of the application.
Key Properties Comparison: Fluoroelastomer vs EPDM
Fluoroelastomer O-rings exhibit superior chemical resistance, withstanding high temperatures up to 230degC and aggressive fuels and oils, making them ideal for automotive and aerospace sealing applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber O-rings offer excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and steam, but have limited compatibility with hydrocarbons and solvents, with an operating temperature range typically between -50degC and 150degC. The choice between fluoroelastomer and EPDM O-rings depends on the application's exposure to chemicals and temperature demands, where fluoroelastomers provide higher performance in harsh environments, while EPDM excels in water, steam, and outdoor conditions.
Chemical Resistance: Suitability in Harsh Environments
Fluoroelastomer O-rings exhibit superior chemical resistance, withstanding exposure to fuels, oils, acids, and solvents, making them ideal for harsh environments such as automotive and aerospace applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and steam but is less effective against hydrocarbons and petroleum-based fluids. Selecting Fluoroelastomer or EPDM O-rings depends on specific chemical exposure requirements, with Fluoroelastomer preferred for aggressive chemicals and EPDM suitable for water, alkalis, and polar solvents.
Temperature Performance: High and Low Extremes
Fluoroelastomer O-rings excel in temperature performance, maintaining elasticity and sealing capability in extreme environments from -26degC to 204degC, making them ideal for aerospace and automotive applications. In contrast, Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber O-rings perform well in low-temperature ranges down to -40degC but have a limited upper temperature threshold of about 150degC, suitable for water and steam sealing. The superior heat resistance and chemical stability of fluoroelastomers make them preferable for high-temperature and aggressive chemical exposures, whereas EPDM is favored for moderate temperature applications and excellent weathering resistance.
Compression Set and Long-Term Sealing
Fluoroelastomer O-rings exhibit superior compression set resistance, maintaining elasticity and sealing force after prolonged compression, which ensures enhanced long-term sealing performance in harsh chemical and high-temperature environments. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers good compression set resistance but generally falls short compared to fluoroelastomers, especially under high temperature and aggressive media exposure. For applications demanding optimal long-term sealing reliability and chemical resistance, fluoroelastomer O-rings outperform EPDM counterparts by providing lower permanent deformation and extended seal life.
Applications and Industry Usage
Fluoroelastomer O-rings excel in high-temperature and chemical-resistant applications, making them ideal for aerospace, automotive fuel systems, and chemical processing industries. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber O-rings provide superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and steam, commonly used in water systems, HVAC, and pharmaceutical equipment. Both materials suit sealing solutions but diverge significantly in chemical compatibility and thermal stability requirements across various industrial sectors.
Cost Analysis: Fluoroelastomer vs EPDM O-Rings
Fluoroelastomer O-rings typically exhibit higher upfront costs due to their complex manufacturing process and superior chemical resistance properties compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) O-rings. EPDM O-rings offer a cost-effective solution with lower material expenses and adequate performance in non-aggressive environments, making them suitable for general sealing applications. While fluoroelastomer O-rings justify their premium price through extended service life and resistance to aggressive chemicals and high temperatures, EPDM provides economic benefits in applications with less demanding conditions.
Compatibility with Fluids and Gases
Fluoroelastomer (FKM) O-rings exhibit superior chemical resistance to fuels, oils, and aggressive chemicals, maintaining stability in temperatures ranging from -26degC to 204degC, making them ideal for sealing applications involving hydrocarbons and aromatic solvents. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber shows excellent compatibility with polar fluids, such as water, steam, and certain acids, and performs well in temperatures between -40degC and 125degC but degrades rapidly in petroleum-based fluids. Selecting the appropriate O-ring depends on the specific fluid or gas environment, with FKM preferred for hydrocarbon-rich conditions and EPDM suited for water-based or acidic media.
Environmental and Regulatory Considerations
Fluoroelastomer O-rings exhibit superior resistance to harsh chemicals and extreme temperatures, meeting stringent environmental regulations such as REACH and FDA standards, essential for applications in aerospace and pharmaceutical industries. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides excellent ozone, weathering, and UV resistance with lower environmental impact but may not comply with all chemical resistance requirements or FDA approvals. Choosing between these materials involves balancing regulatory compliance with performance needs, considering factors like RoHS and WEEE directives, and the specific environmental stresses of the application.
Choosing the Right O-Ring Material for Your Application
Fluoroelastomer O-rings excel in high-temperature resistance, chemical stability, and durability, making them ideal for aerospace, automotive fuel systems, and chemical processing industries. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber O-rings offer superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and steam, suited for water, brake fluids, and outdoor applications. Selecting the right O-ring material depends on environmental conditions, chemical exposure, and temperature requirements to ensure optimal sealing performance and longevity.
Infographic: Fluoroelastomer vs Ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com